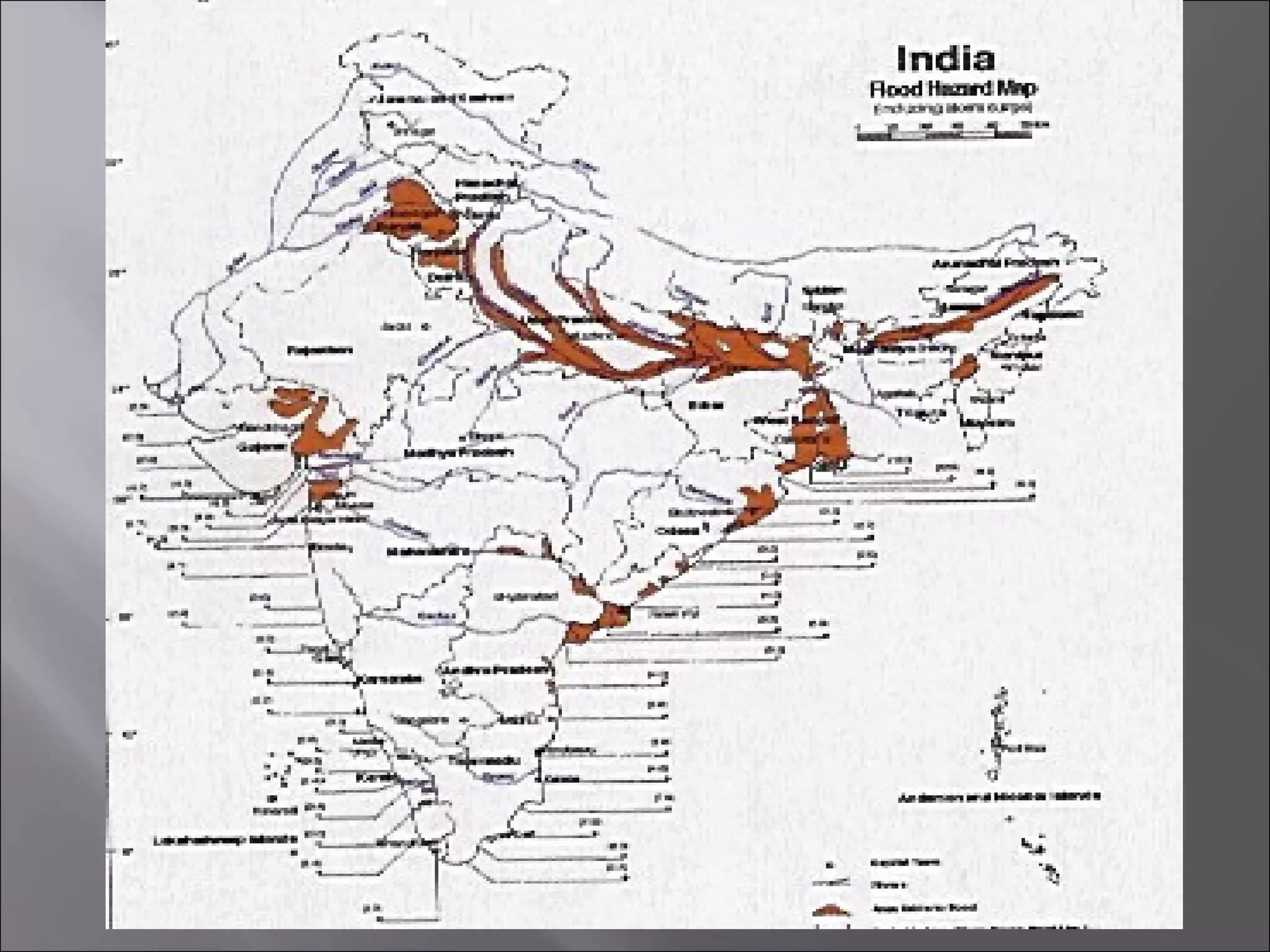
The document discusses the impacts of floods, exacerbated by climate change and urban development, highlighting various types of flooding such as flash floods and riverine floods. It emphasizes the importance of disaster management, response mechanisms, and the role of governmental and non-governmental organizations in assisting affected populations. It also outlines preventative measures, environmental effects, and historical flood events impacting regions like Mozambique and Bangladesh.