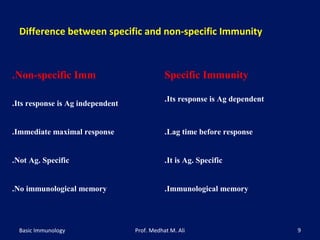
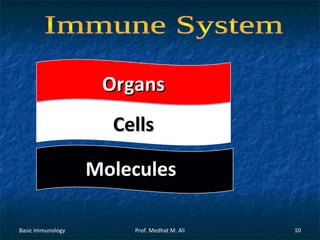
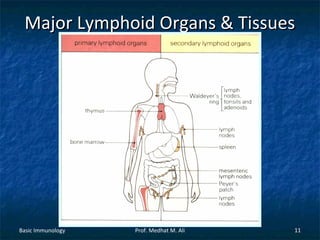
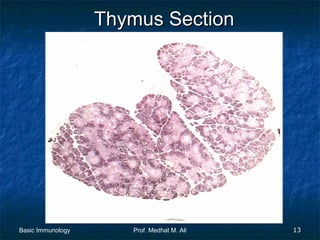
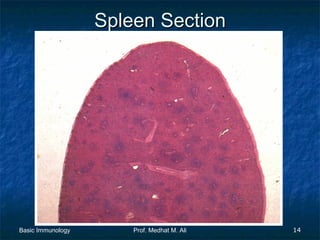
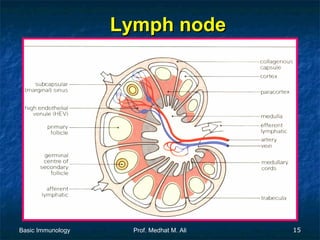
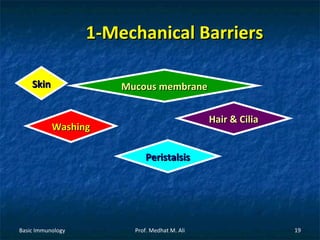
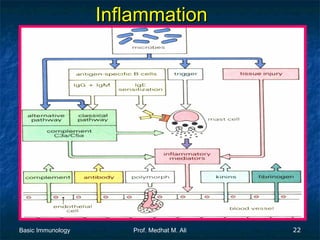
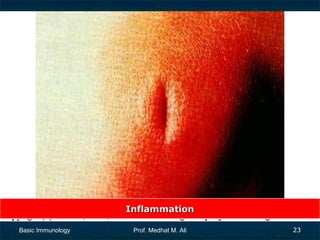
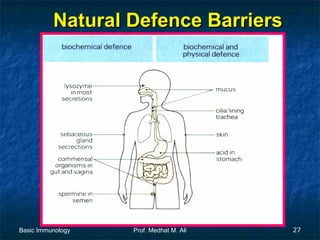
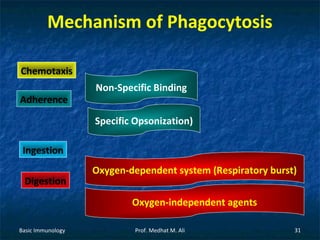
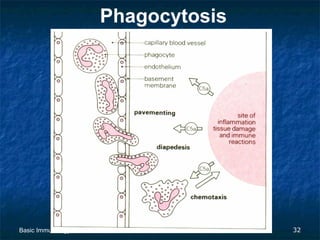
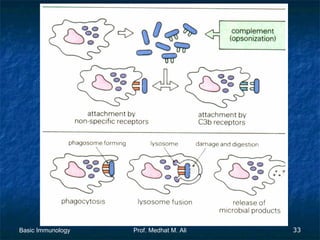
This document provides an overview of basic immunology. It defines immunology as the study of how the body defends itself from foreign agents. The immune system consists of organs like the thymus and lymph nodes, cells like macrophages and lymphocytes, and molecules like immunoglobulins. The document outlines the differences between innate (non-specific) immunity and acquired (specific) immunity. It also describes the mechanisms of phagocytosis, a key component of innate immunity, and the roles of cells like neutrophils, macrophages, eosinophils and basophils in the phagocytic process.