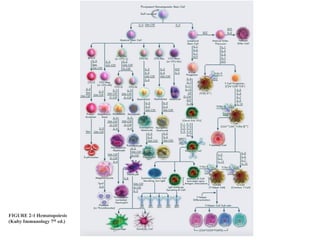
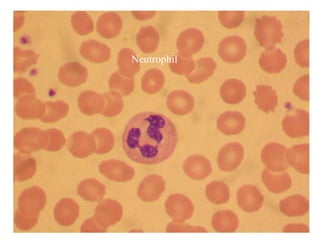
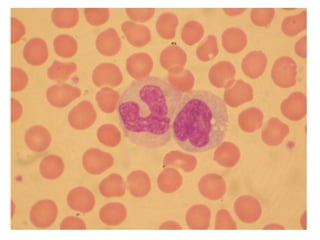
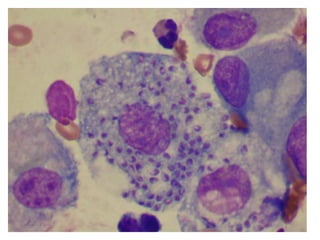
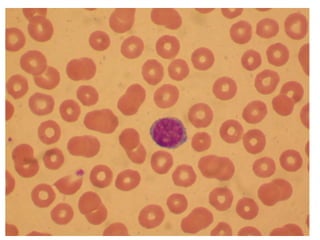
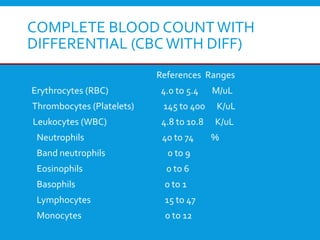
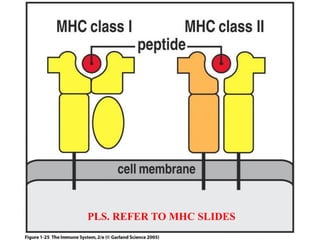
The document provides an introduction to immunology and outlines key concepts of the immune system. It discusses the cells of the immune system including phagocytes, lymphocytes and antigen presenting cells. The innate immune response is mediated by phagocytes and natural killer cells that recognize pathogens non-specifically. The adaptive immune response involves antigen presentation and the generation of pathogen-specific antibodies and T-cells with memory. Major lymphoid tissues that support immune cell development and response include the bone marrow, thymus, spleen and lymph nodes.