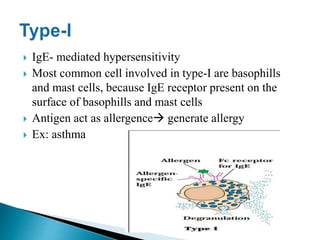
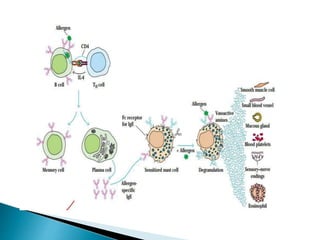
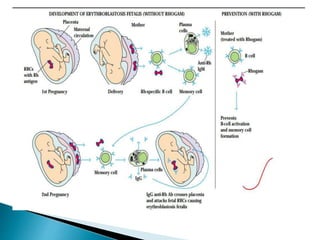
Hypersensitivity refers to an increased immune response, classified into four types: IgE-mediated (Type I), antibody-mediated (Type II), immune complex-mediated (Type III), and delayed-type hypersensitivity (Type IV). Immediate hypersensitivity occurs within 12 hours, while delayed-type hypersensitivity takes 24-48 hours, often involving T cells and cytokines. The document details the mechanisms and examples of each type, highlighting the roles of various immune cells and antibodies.