Embed presentation
Download to read offline




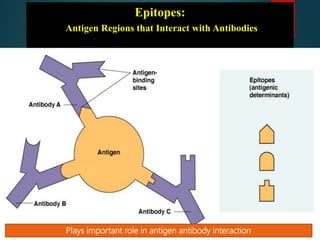
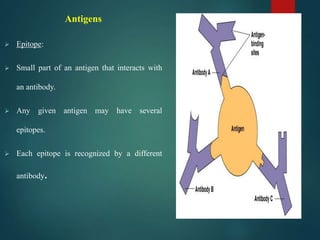

The document discusses antigens, which are mostly proteins or polysaccharides from foreign organisms that elicit an immune response. Antigens can come from microbes like bacteria or viruses, or be non-microbial in origin like pollen or transplanted tissues. They must have a molecular weight over 10,000 or be coupled to a carrier molecule to be recognized. Antigens have properties like their chemical composition, molecular weight, and ability to be processed. There are two main types of antigens: exogenous antigens from outside the body and endogenous antigens from within the body. Epitopes are small parts of antigens that specifically interact with antibodies.





