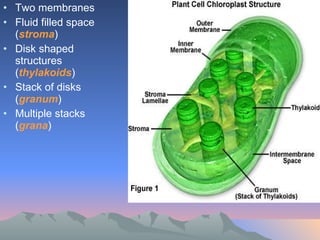
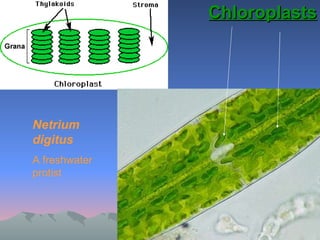
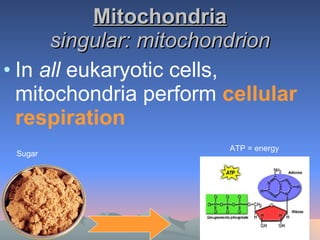
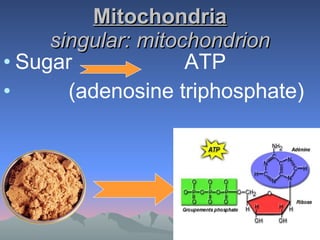
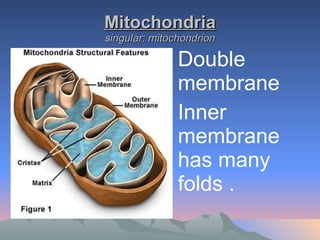
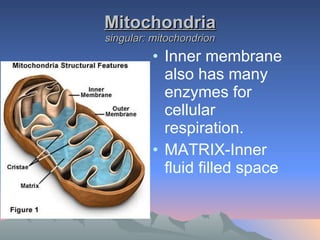
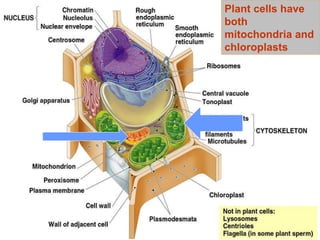
Chloroplasts and mitochondria are organelles that act as cellular power stations. Chloroplasts harness light energy from the sun through photosynthesis to produce sugars and oxygen in plant and algal cells. Mitochondria convert the sugars produced by chloroplasts into ATP through cellular respiration, providing energy for all eukaryotic cells. Both organelles have double membranes and internal structures that allow them to perform these essential energy conversion functions.