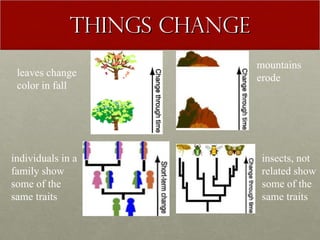
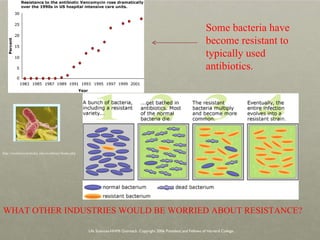
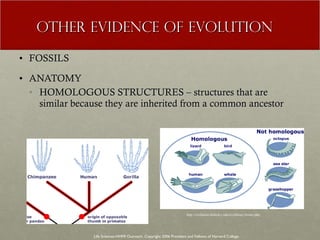
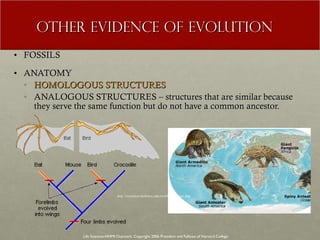
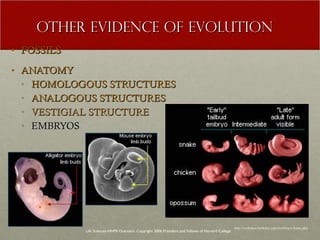
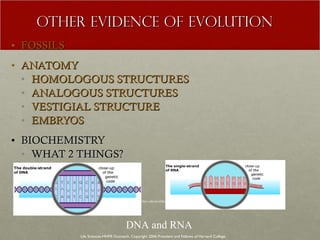
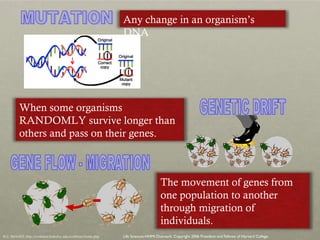
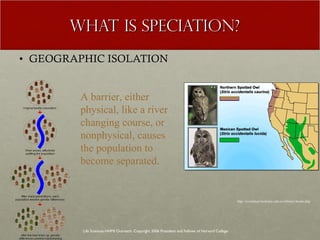
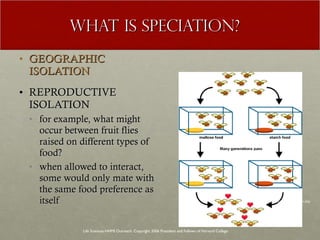
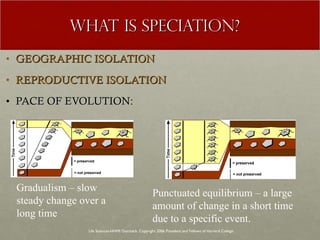
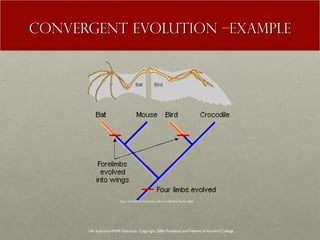
The document discusses Charles Darwin's theory of evolution by natural selection. It explains that Darwin observed variations within species that seemed to be advantageous for survival. Over generations, natural selection favored individuals with these beneficial variations, leading to evolution of new species. The document also provides several lines of evidence that support the theory, including fossils, anatomical similarities between organisms, and genetic and biochemical data. Mechanisms like mutation, genetic drift, and gene flow can drive evolution by altering the gene pool over time.