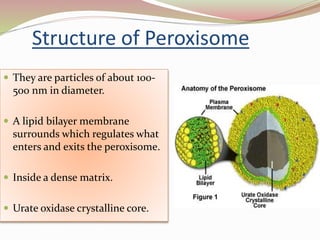
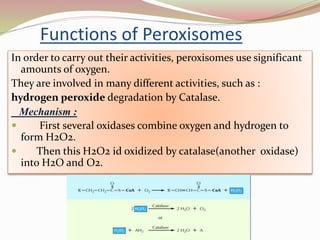
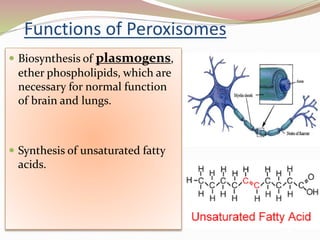
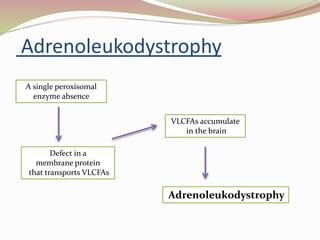
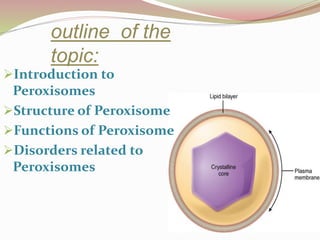
This presentation summarizes key information about peroxisomes. Peroxisomes are membrane-bound organelles found in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells that contain oxidase enzymes and help breakdown hydrogen peroxide. They have a dense matrix and participate in important functions like fatty acid breakdown, alcohol detoxification, and bile acid/cholesterol synthesis. Disorders can arise if single peroxisomal enzymes are abnormal, affecting the nervous system, liver, and other organs. Two examples given are adrenoleukodystrophy, which involves VLCFA metabolism, and Zellweger's syndrome, caused by a lack of functional peroxisomes due to mutations affecting transport of enzymes.



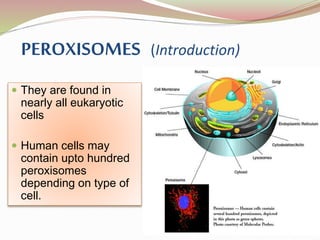
![ They are called “Peroxisomes” because they are
the site of synthesis and degradation of Hydrogen
Peroxide [H2O2], a highly reactive and toxic
oxidizing agent.
PEROXISOMES (Introduction)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/peroxisomes-150606162547-lva1-app6891/85/Peroxisomes-6-320.jpg)