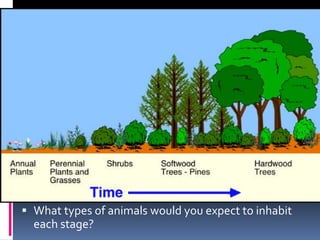
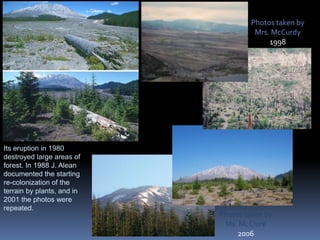
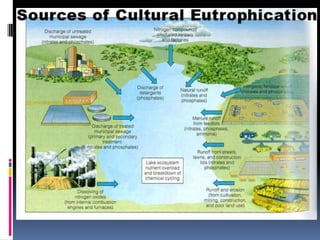
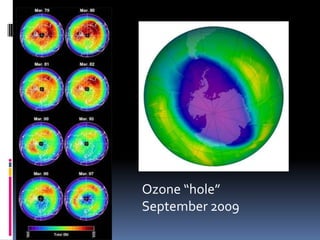
When an ecosystem is disturbed through natural or human causes, it undergoes ecological succession over time as species populations change. Succession can be primary on new lands or secondary in previously inhabited areas. In secondary succession, smaller pioneer species arrive first, followed by larger species that feed on them as habitat changes. Eventually a climax community develops if the ecosystem remains undisturbed. Human activities like pollution and overharvesting of resources can disrupt succession and damage ecosystems. A sustainable approach preserves biodiversity, habitats, and uses resources renewably so they are available for future generations.