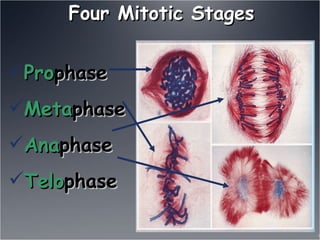
The document describes the four mitotic stages:
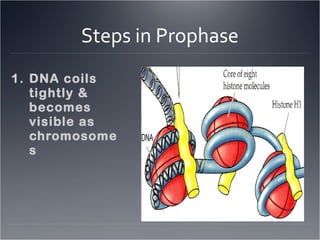
1. Prophase, where DNA coils into chromosomes and the nucleus and nucleolus disappear.
2. Metaphase, where chromosomes align in the middle of the cell.
3. Anaphase, where sister chromatids are separated and pulled to opposite ends.
4. Telophase, where the nucleus and chromosomes reform and the cell divides into two daughter cells through cytokinesis.