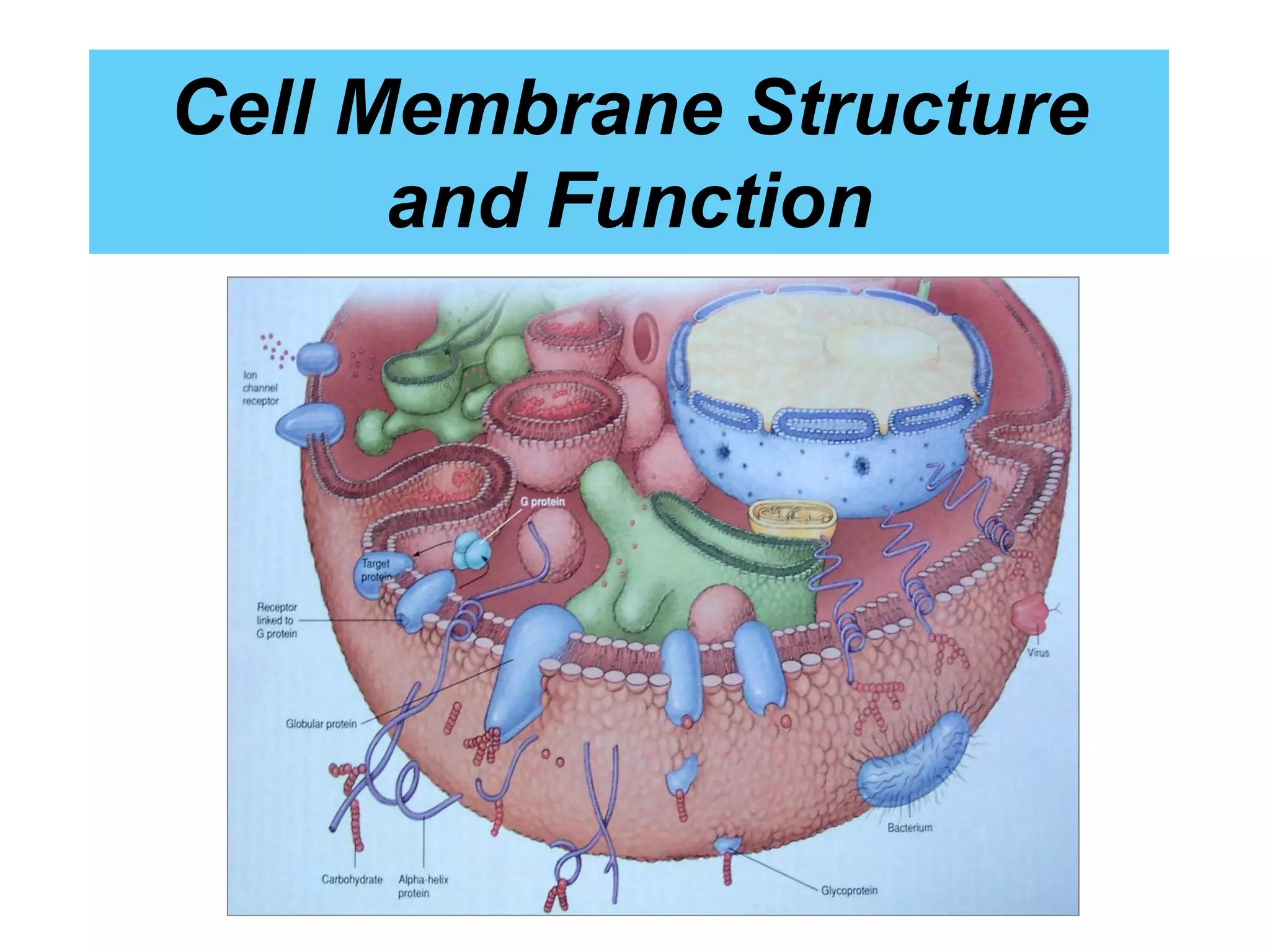
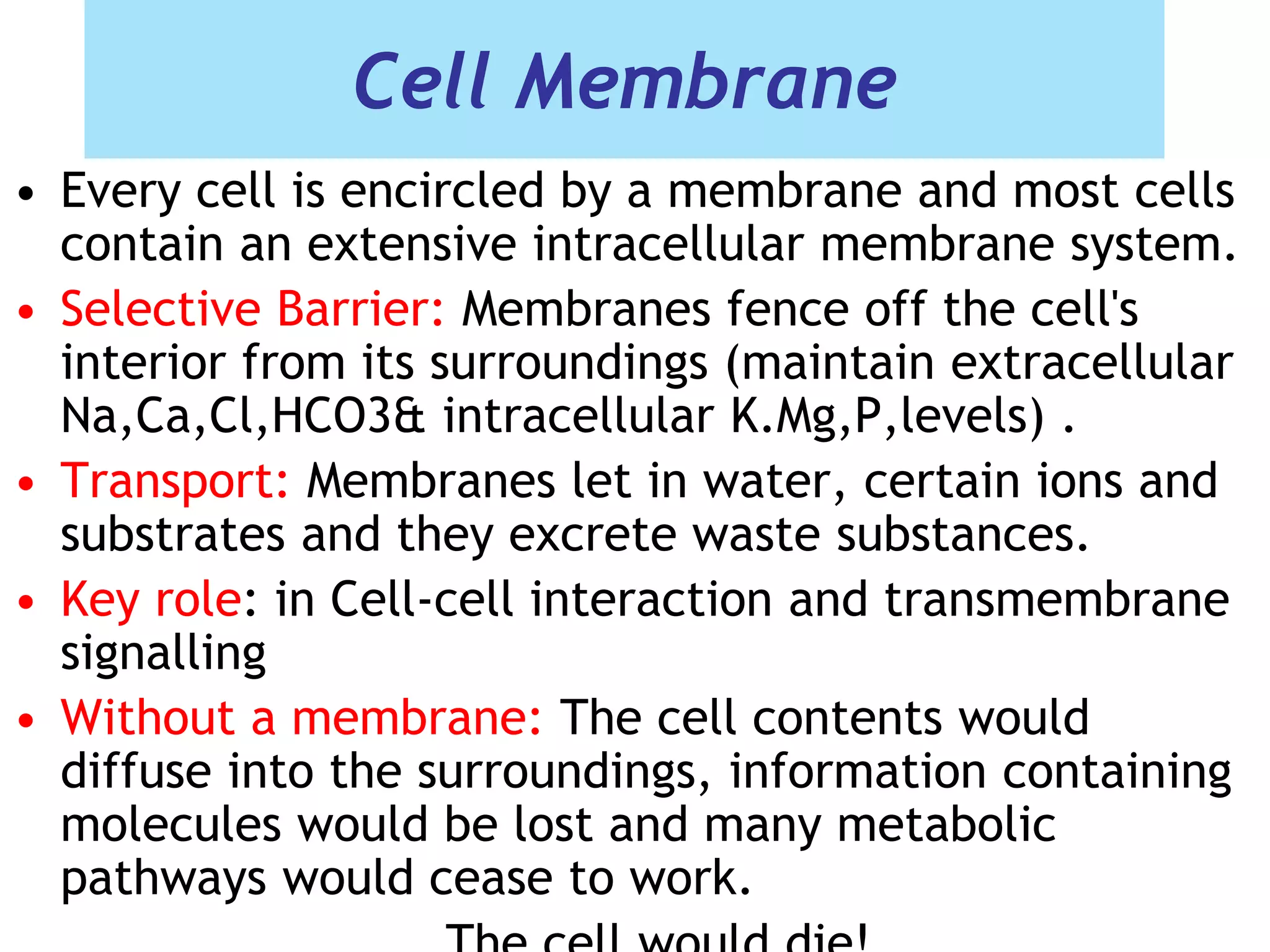
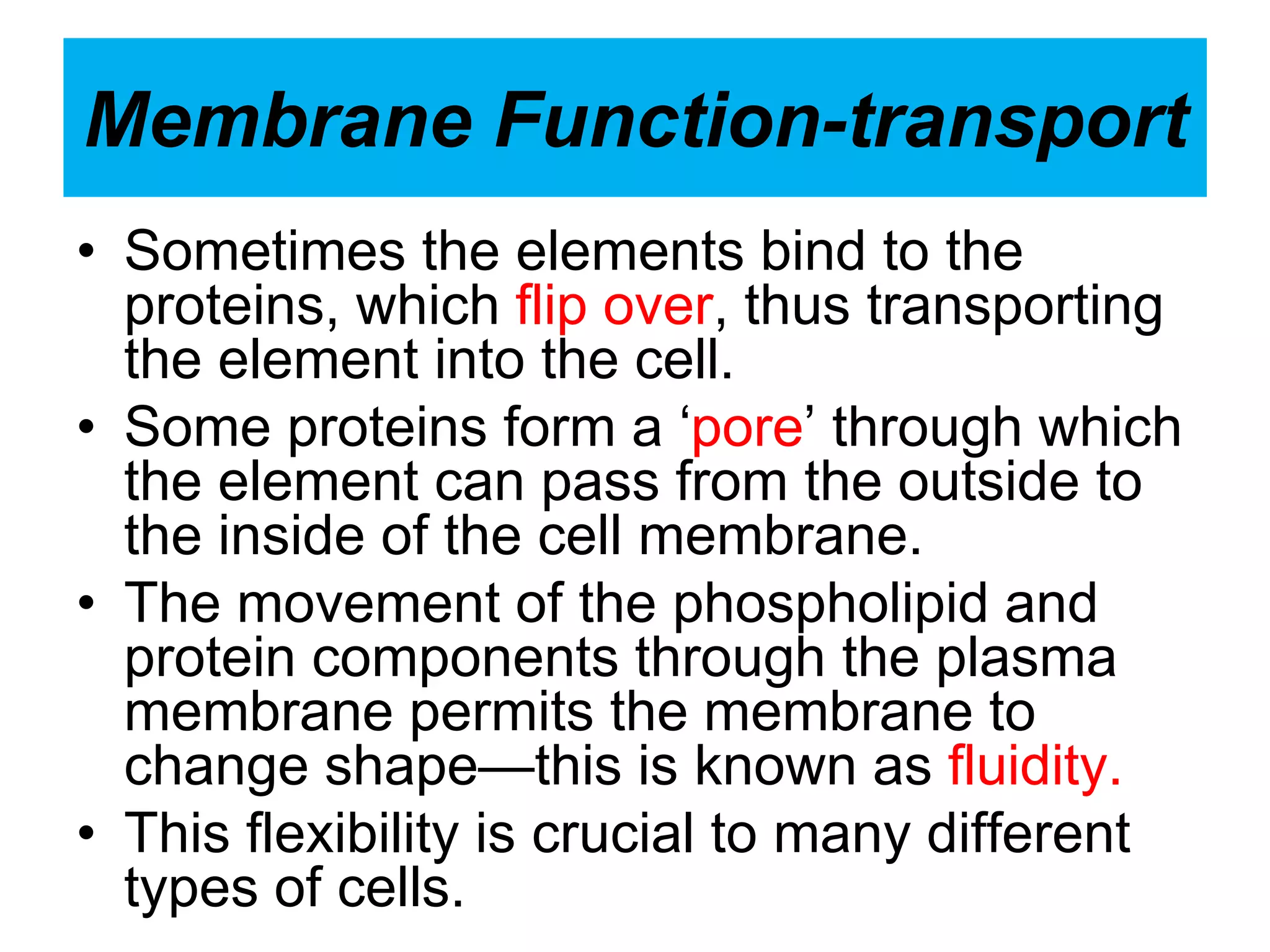
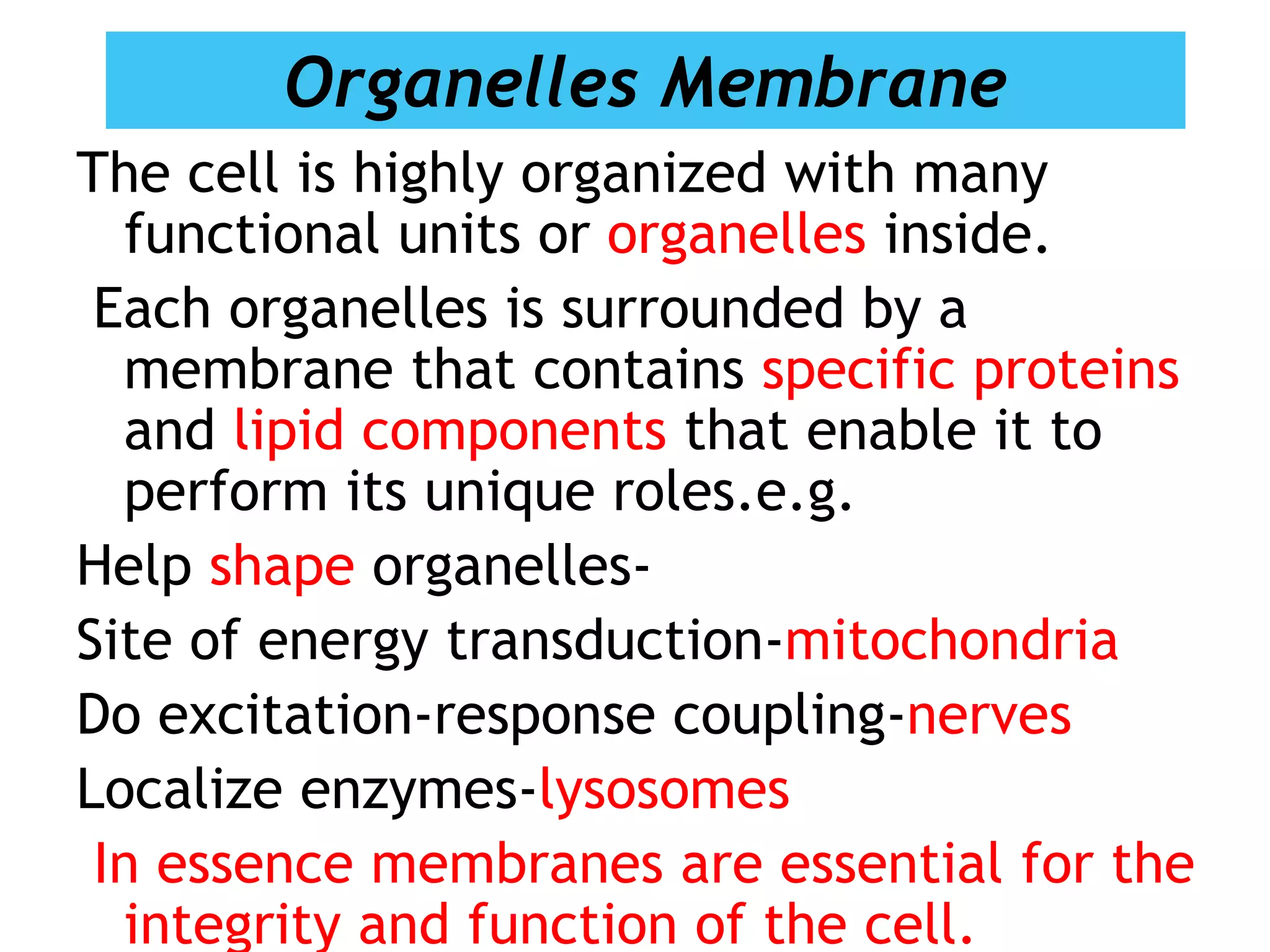
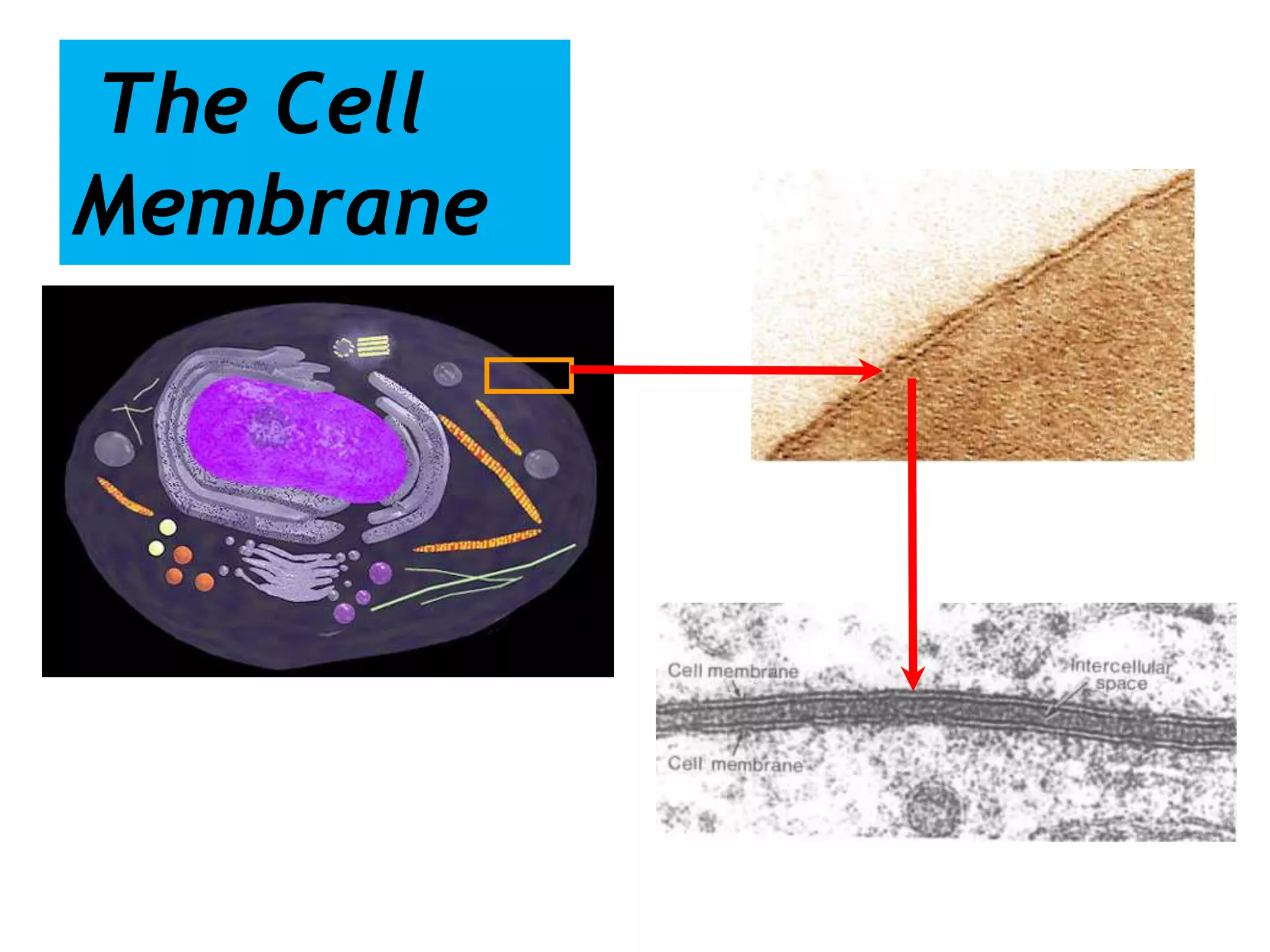
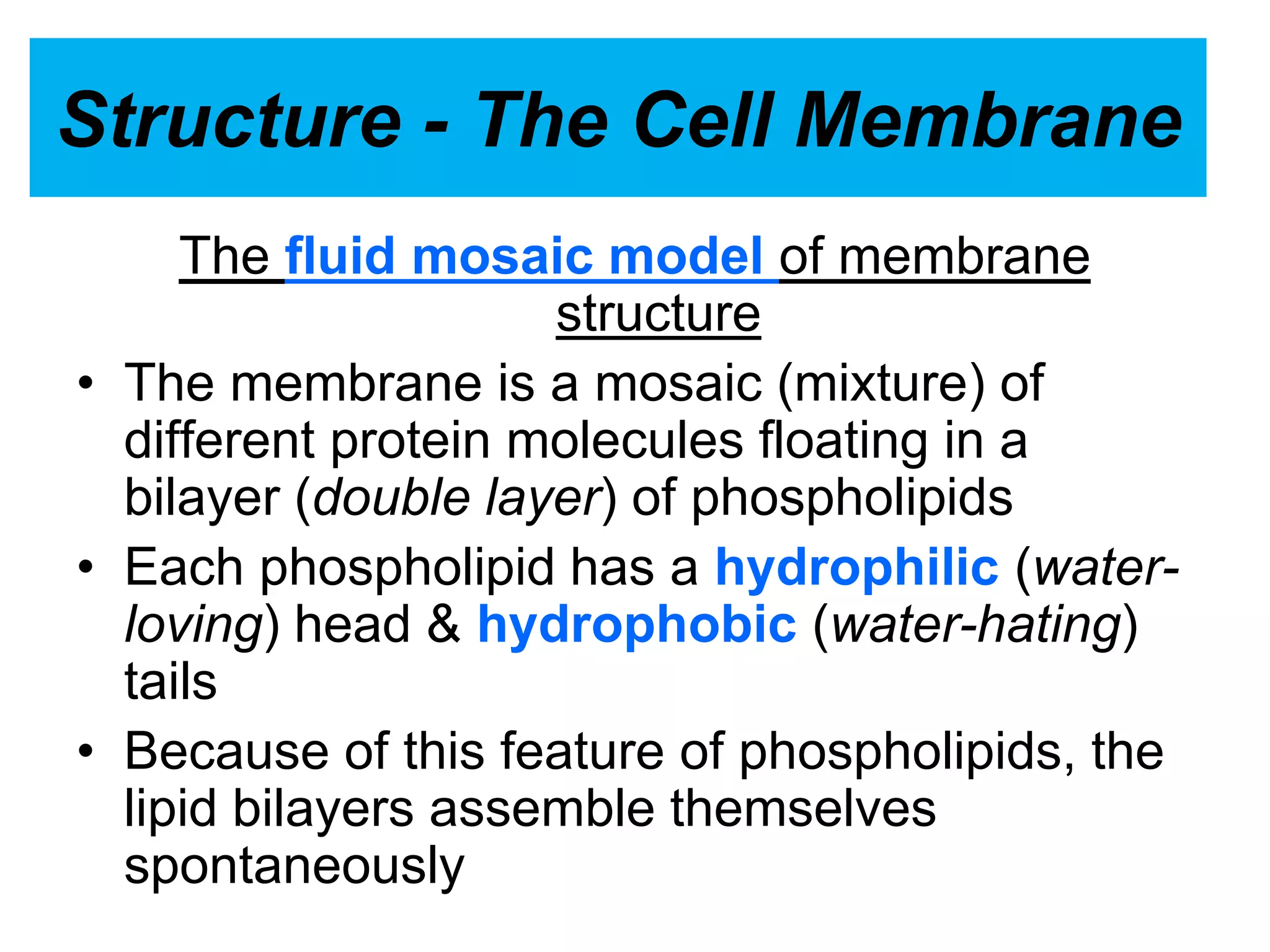
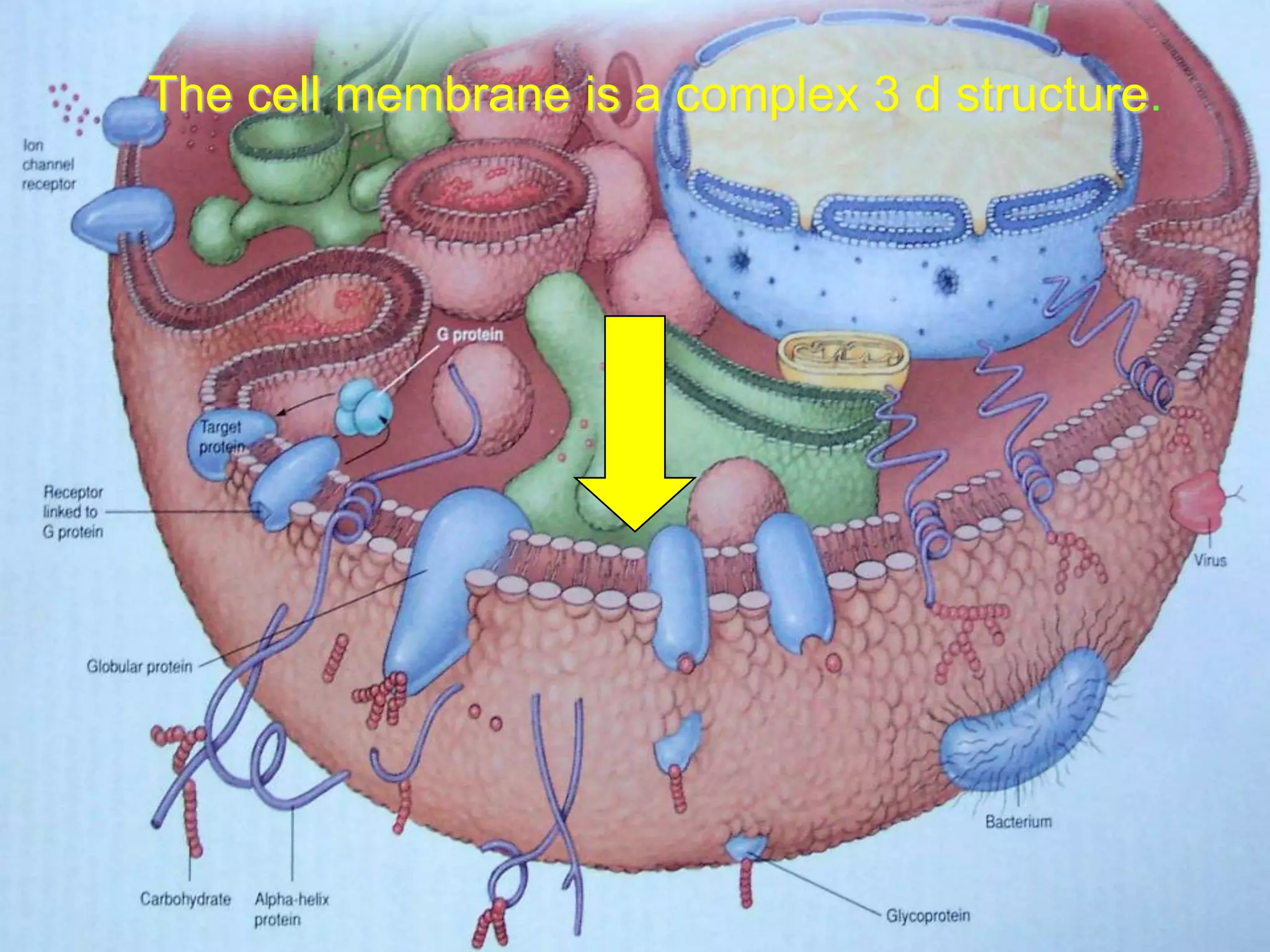
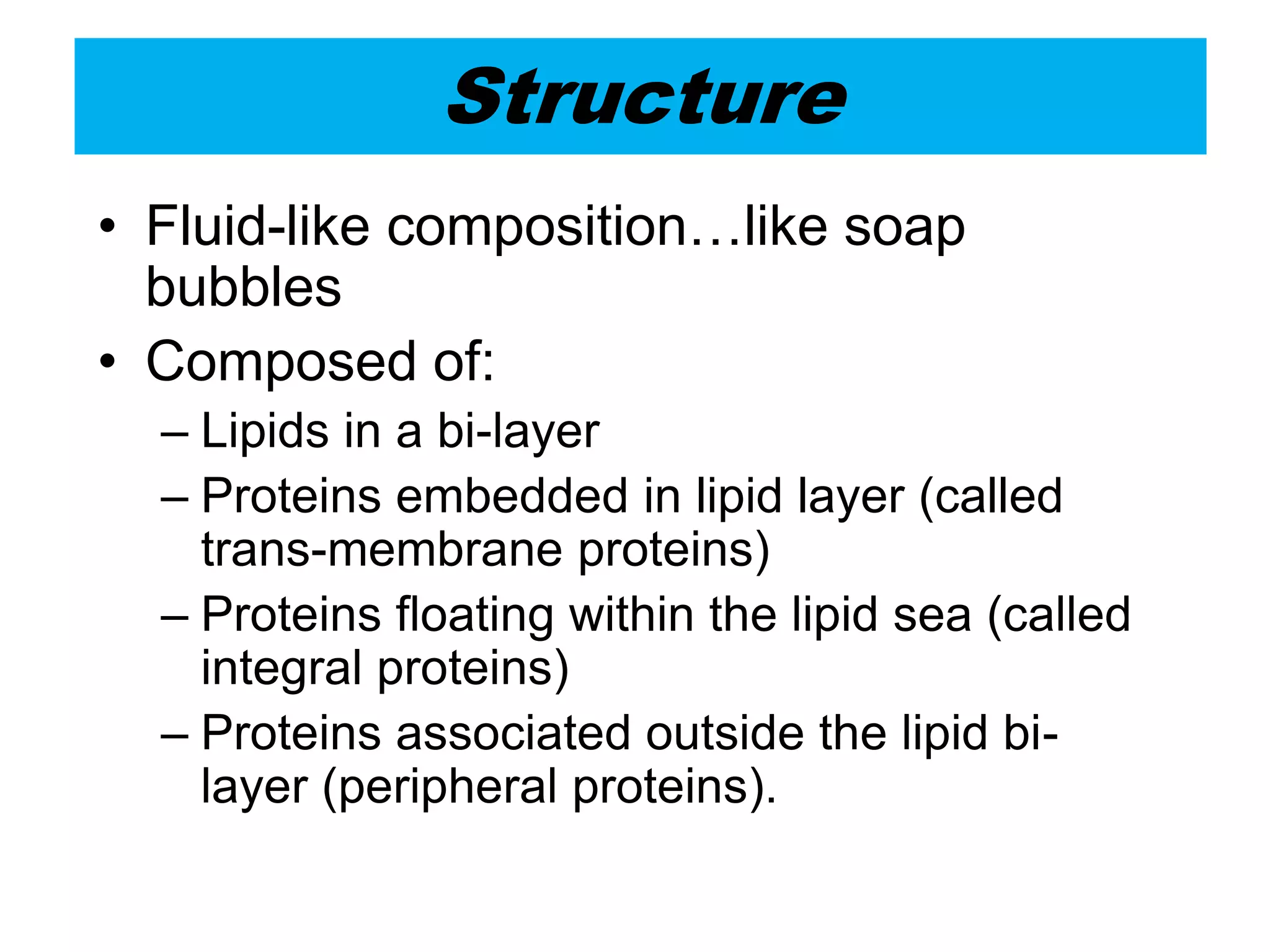
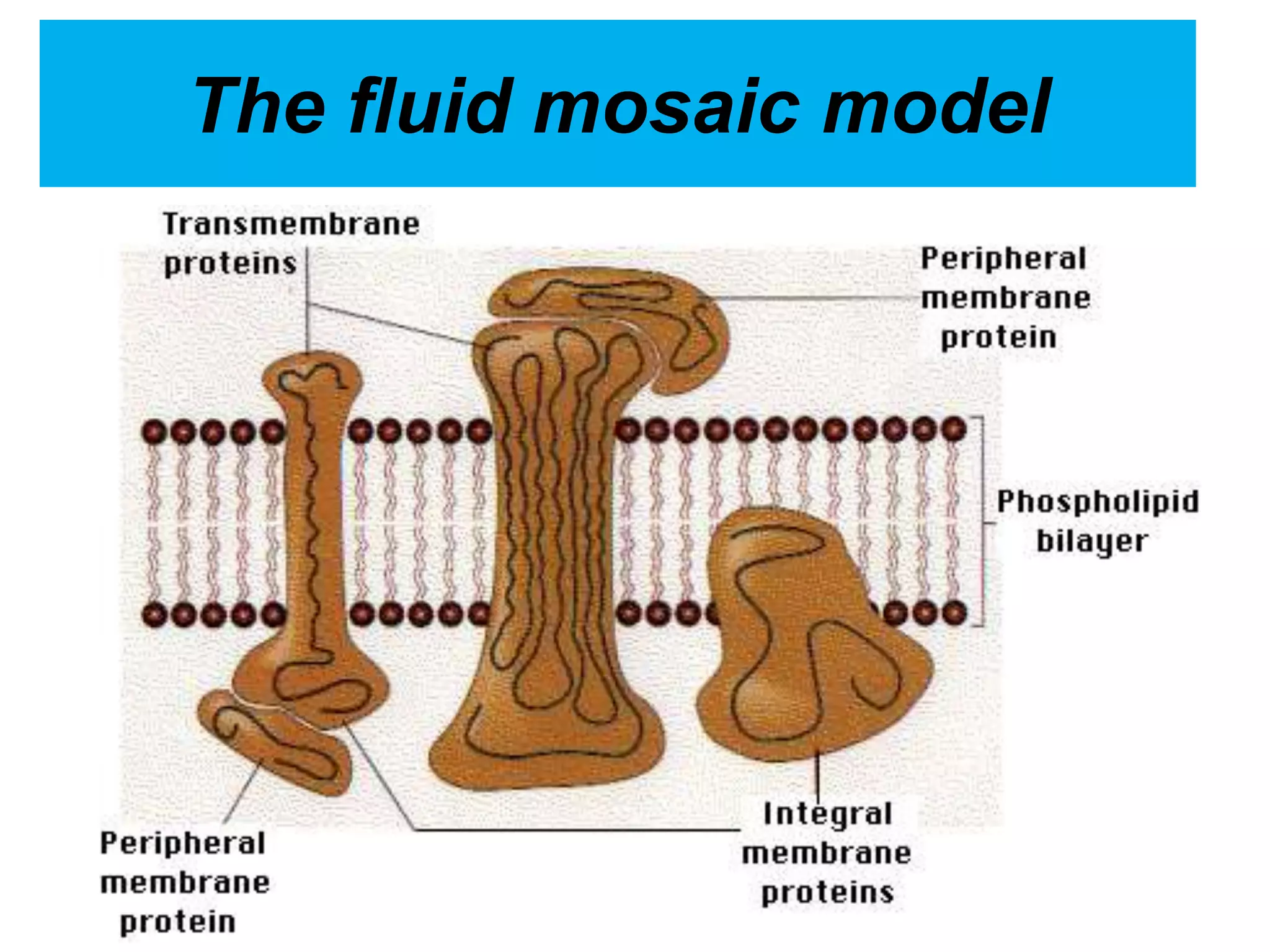
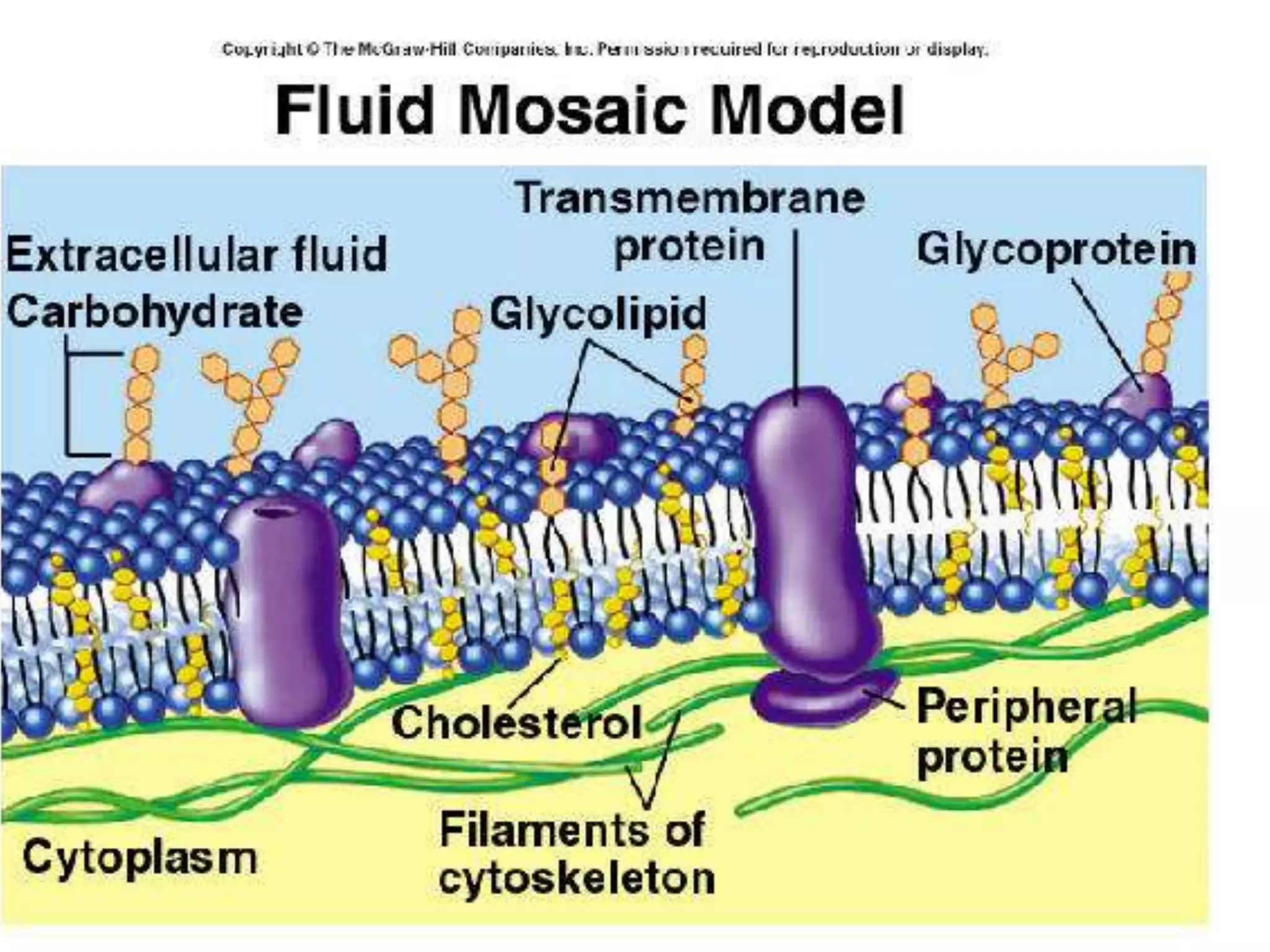
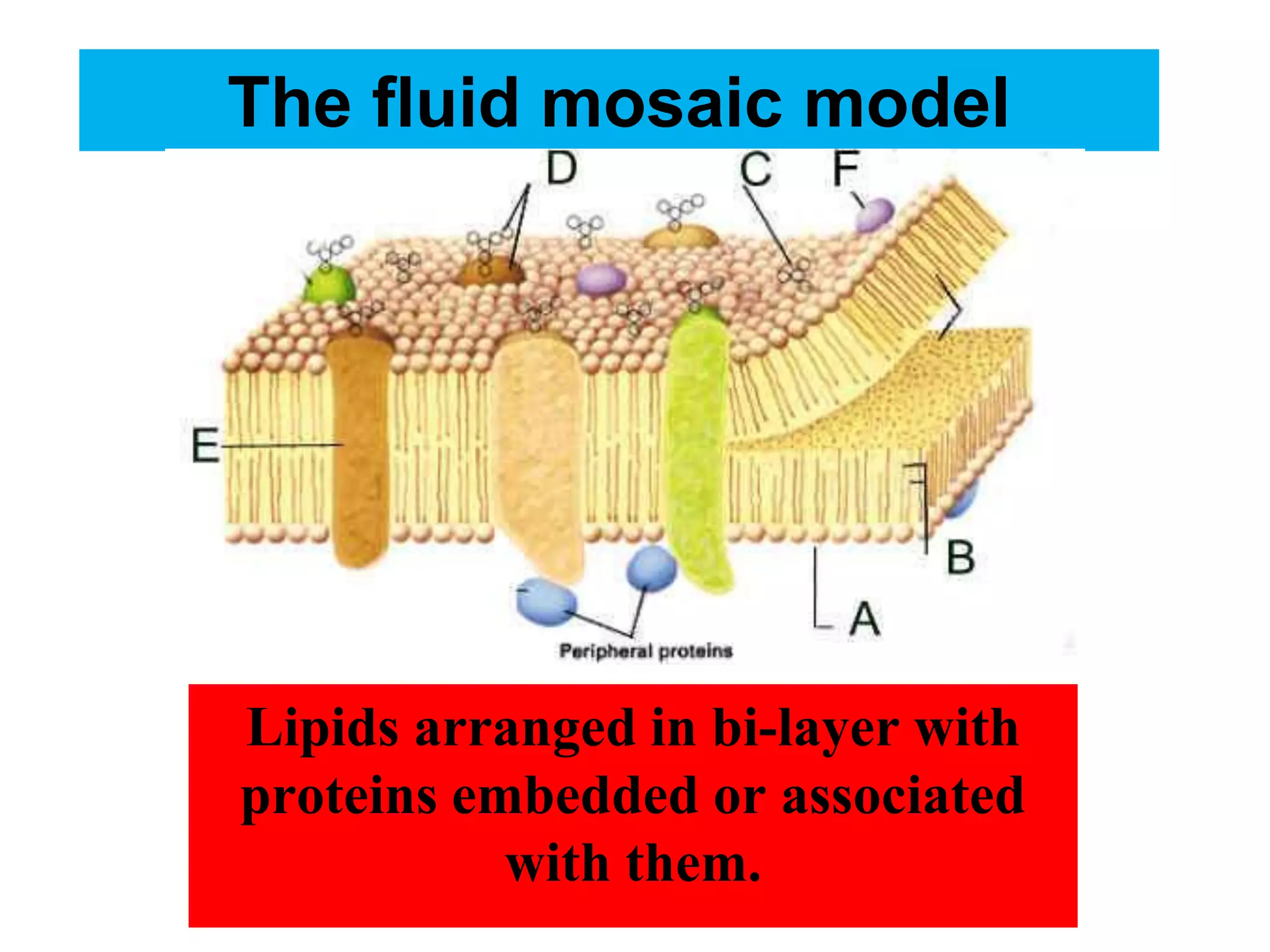
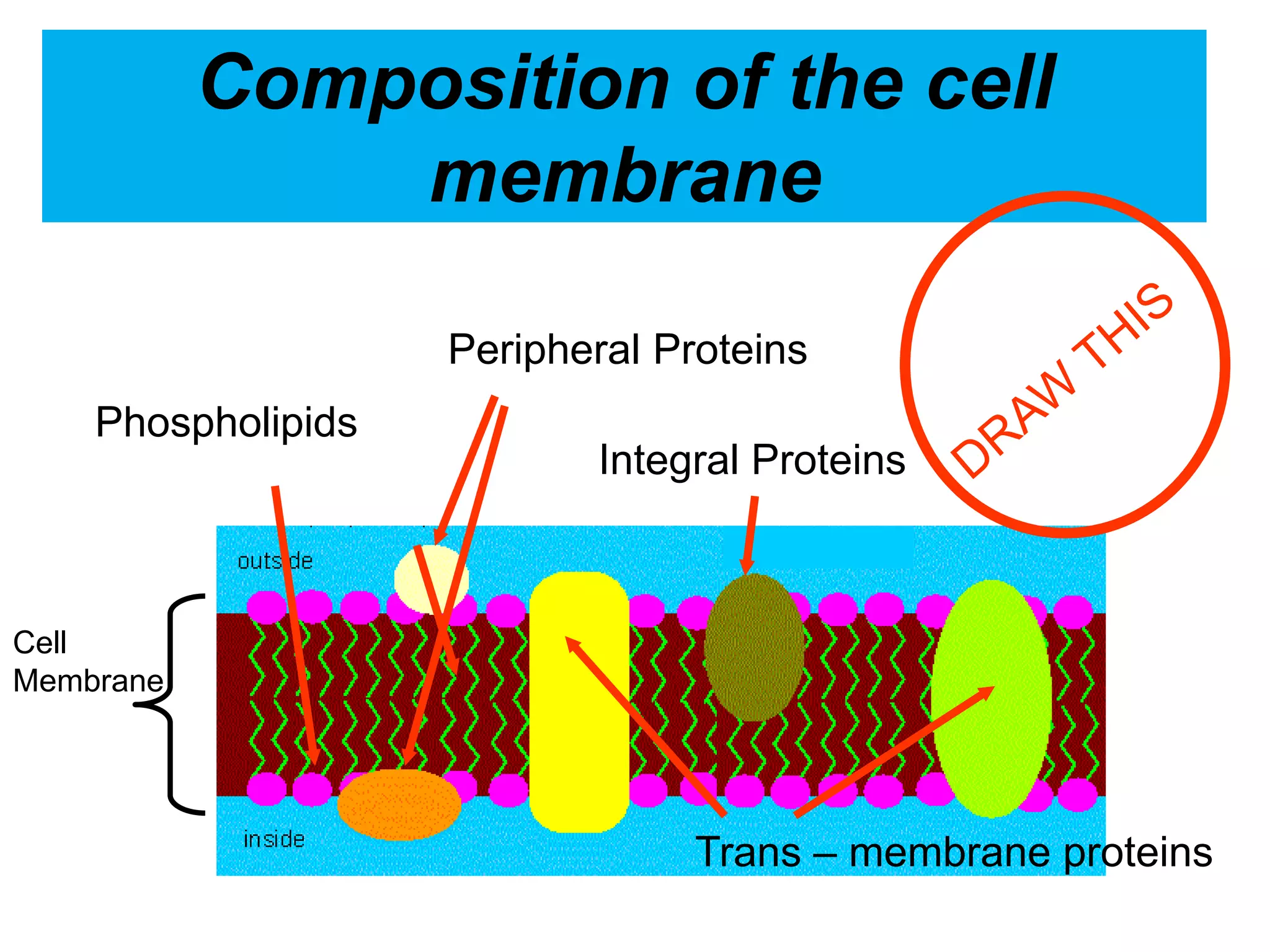
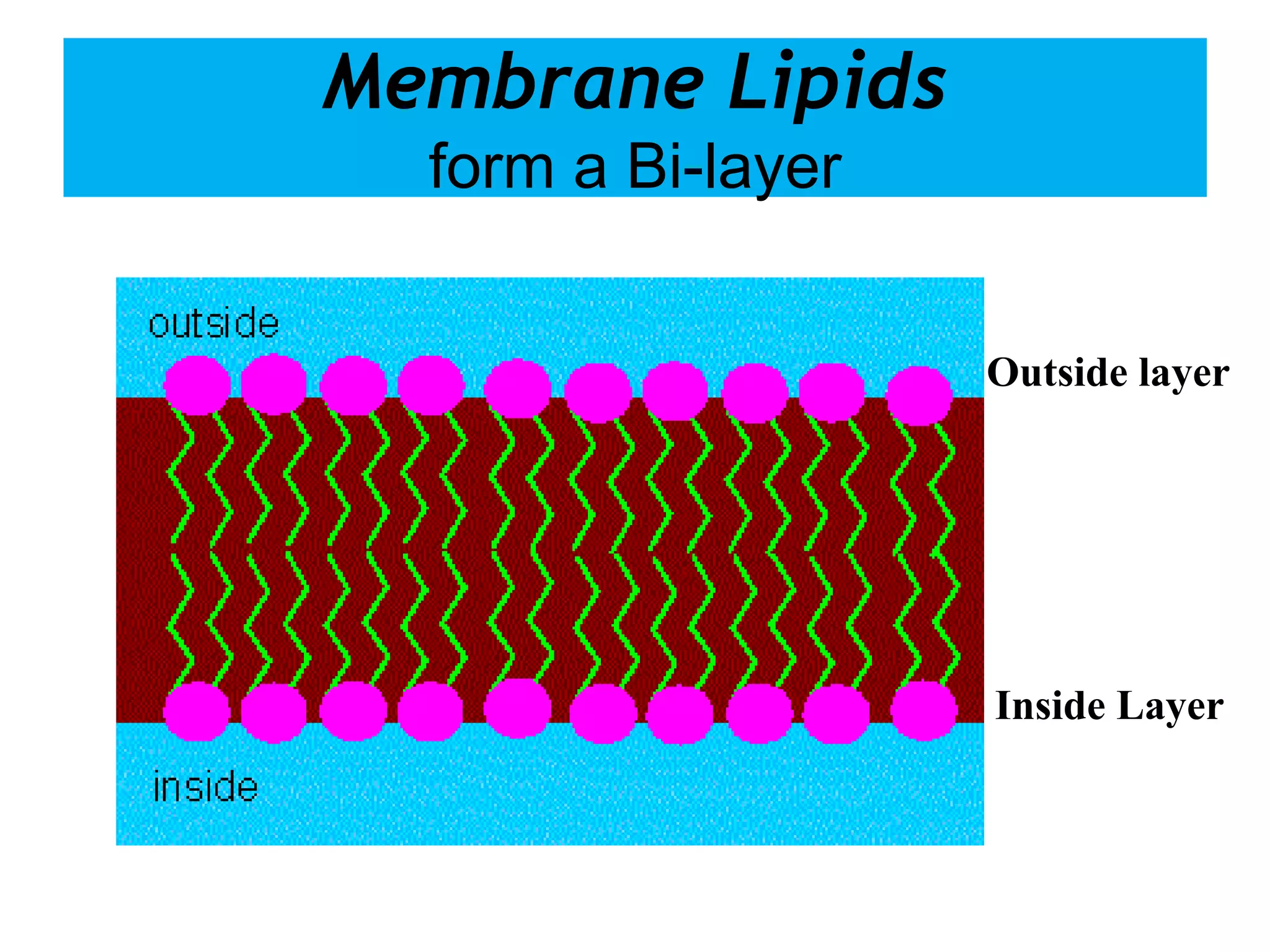
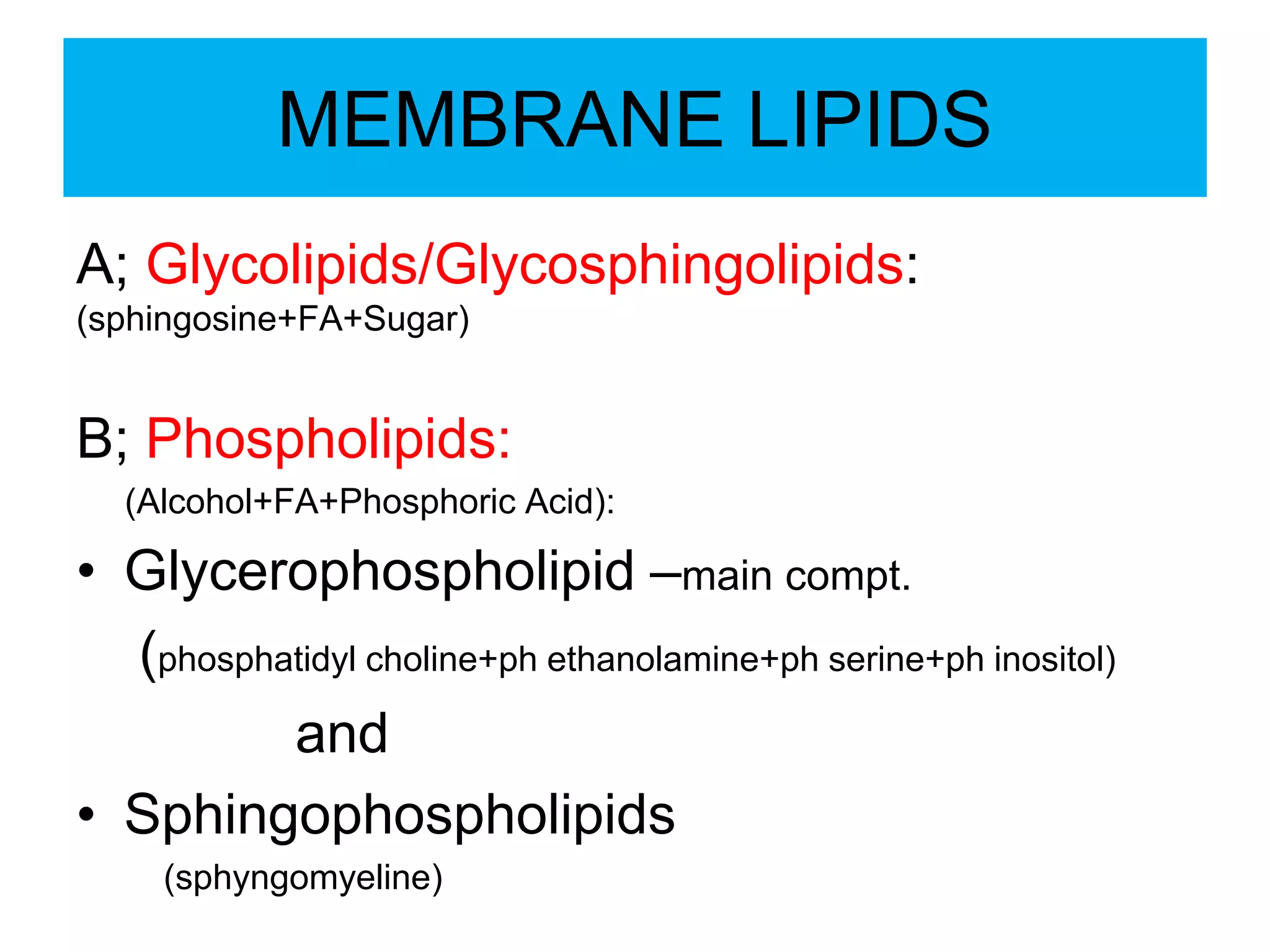
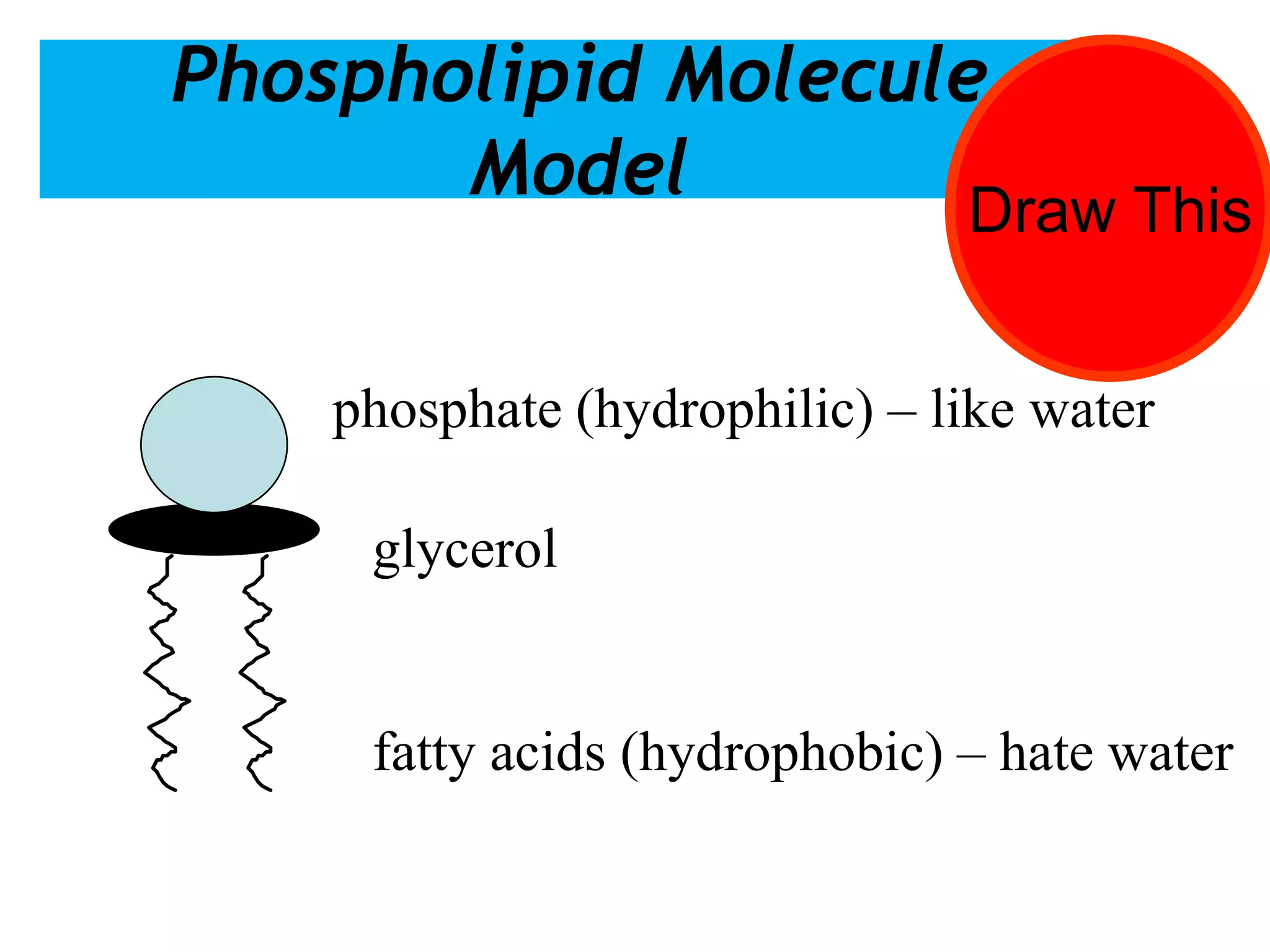
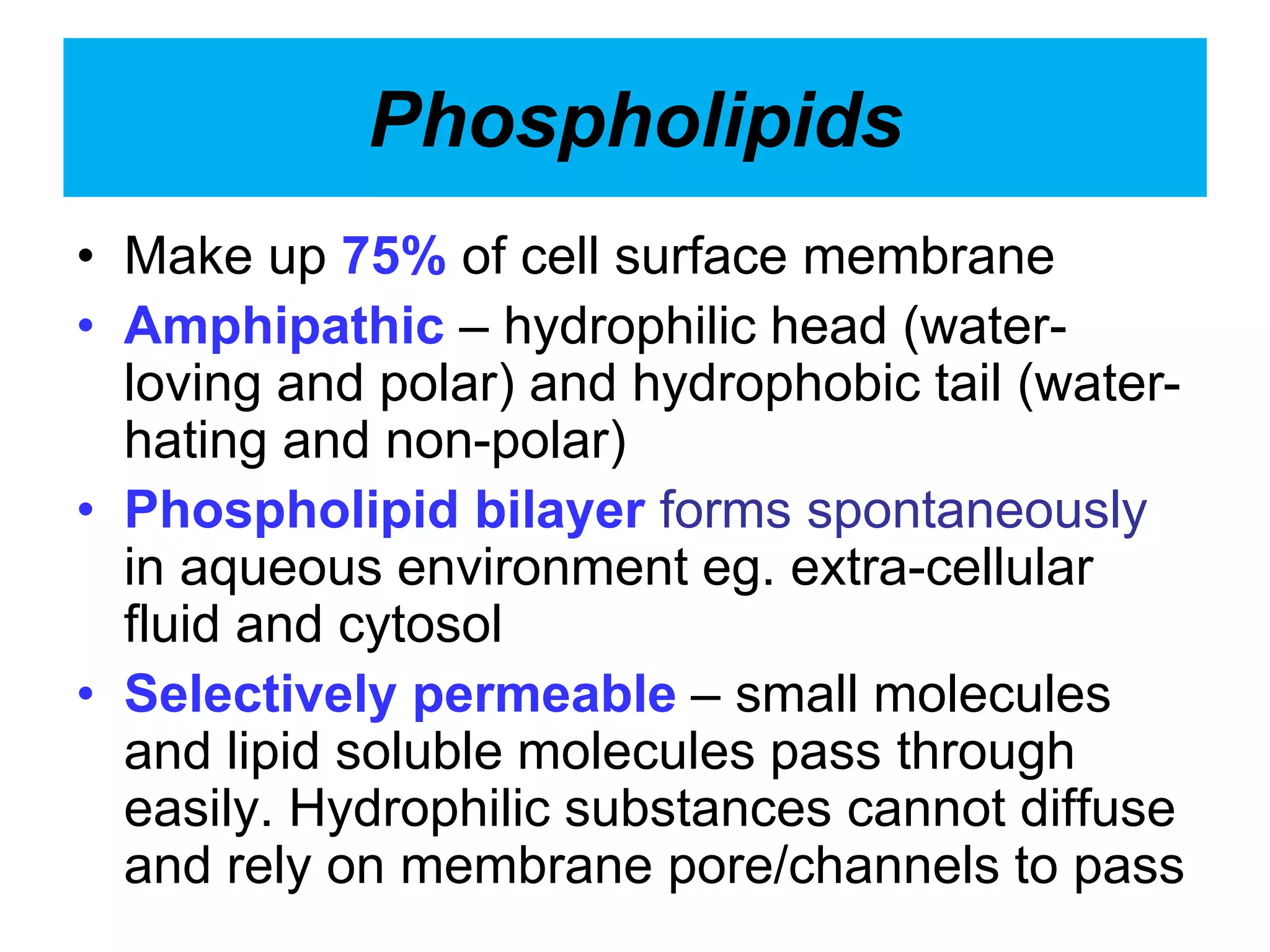
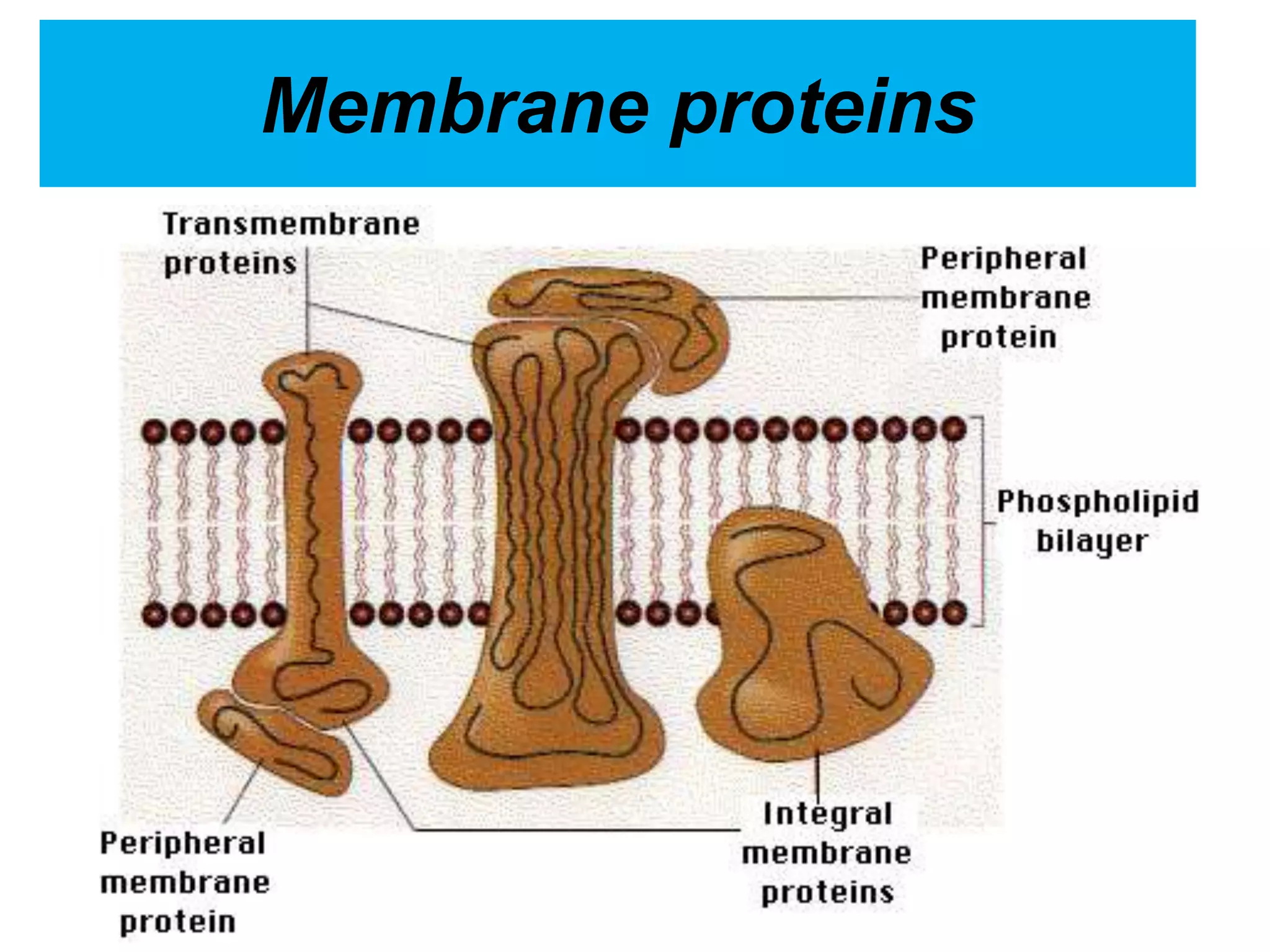
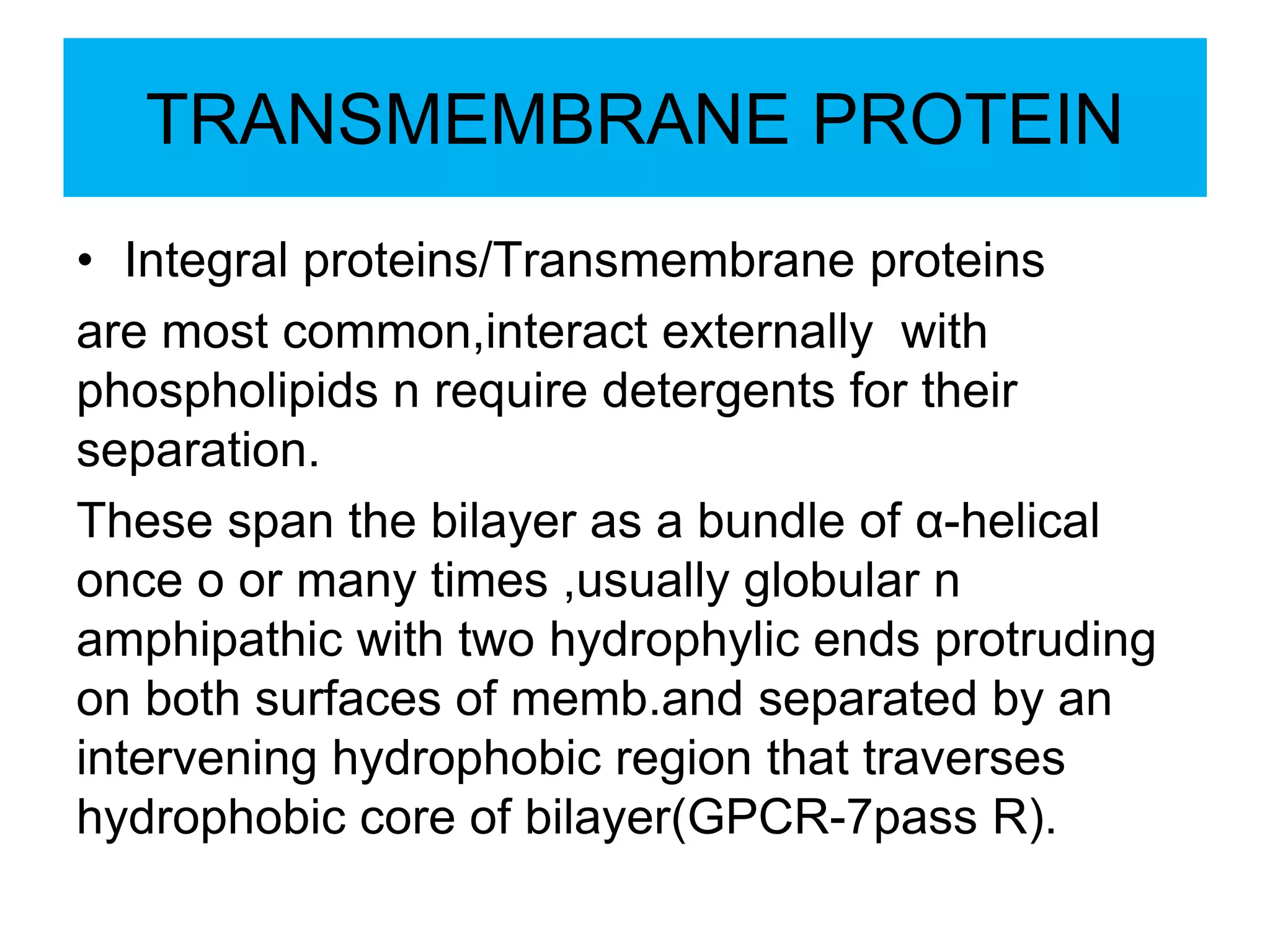
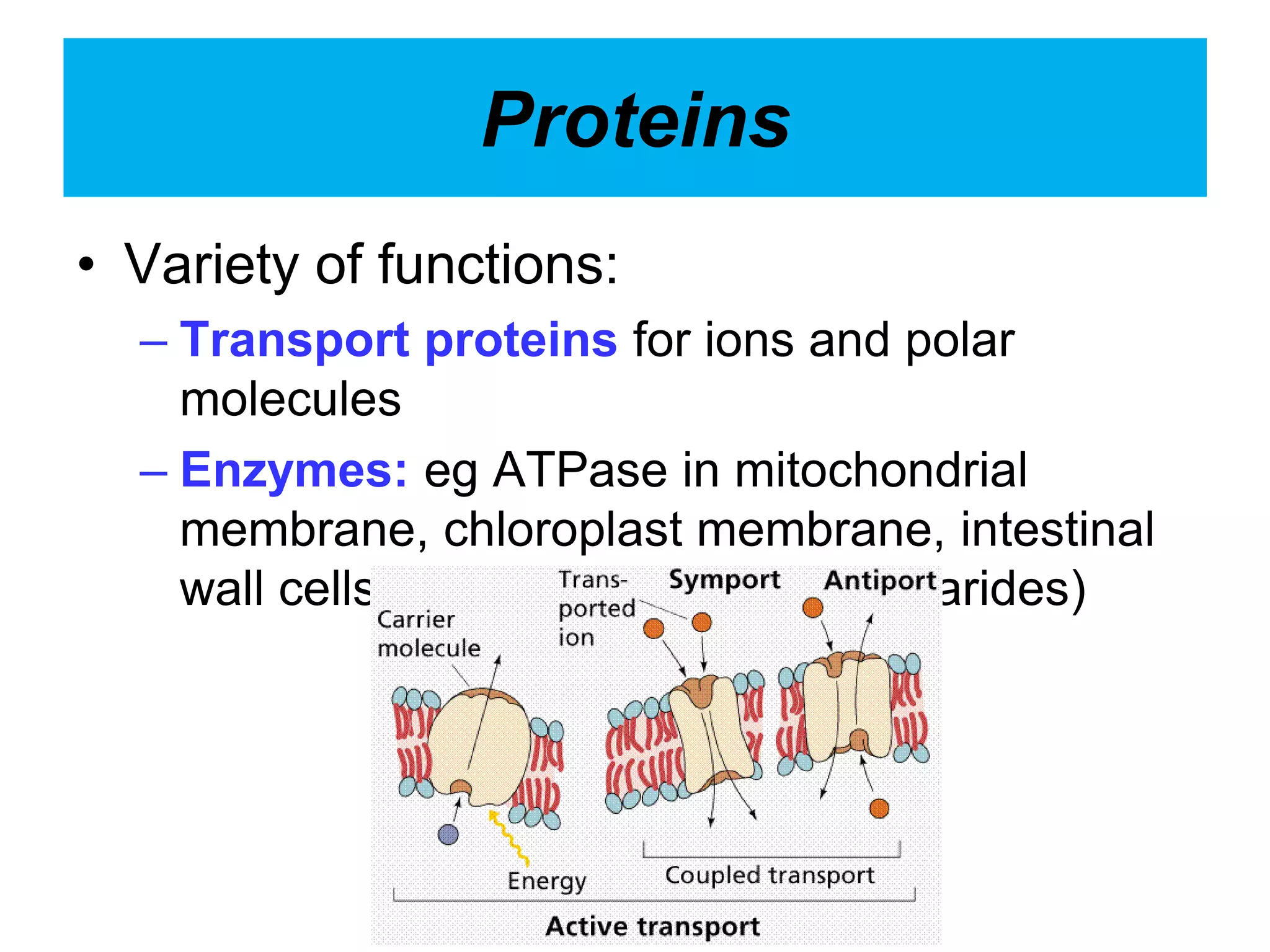
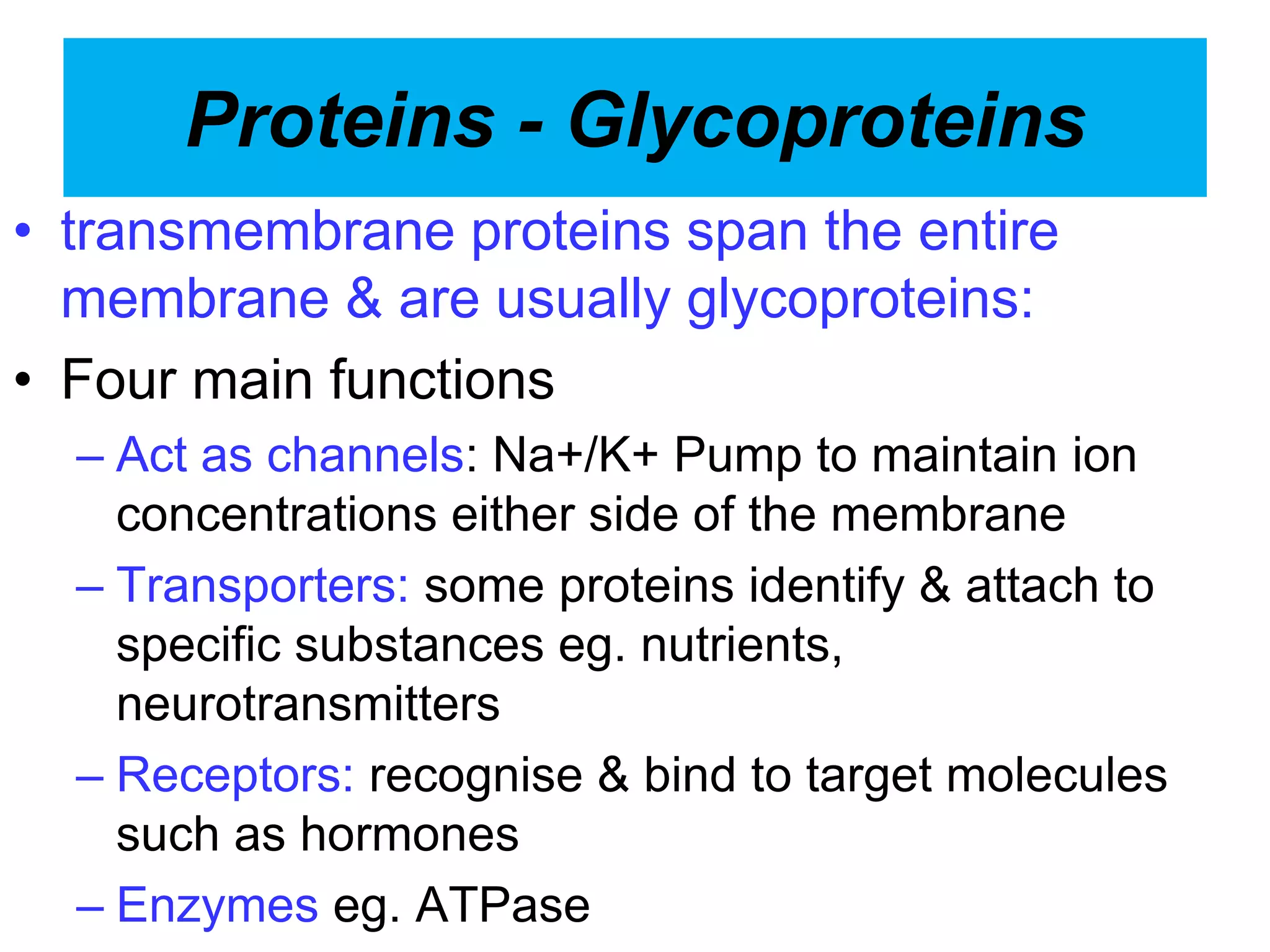
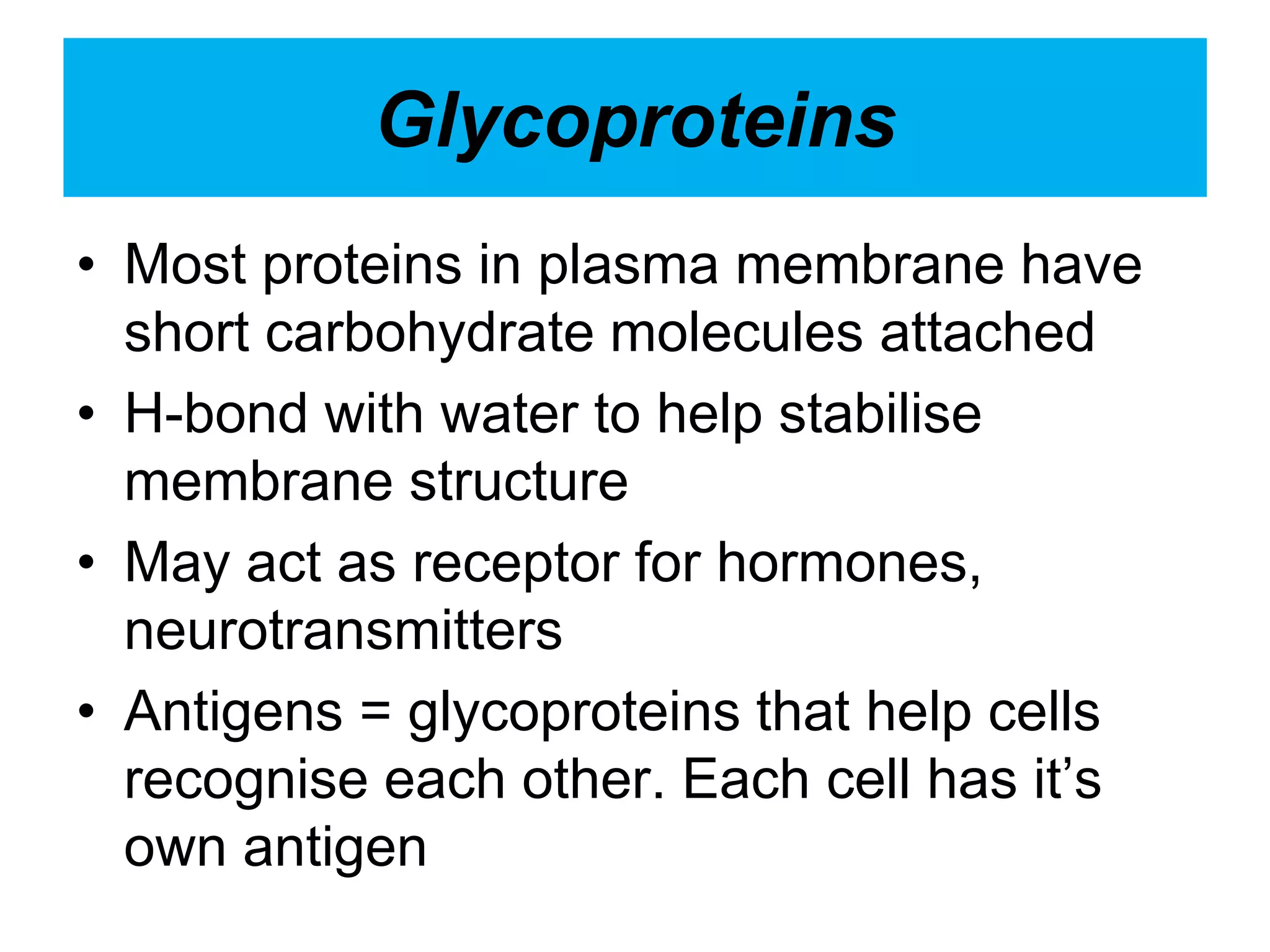
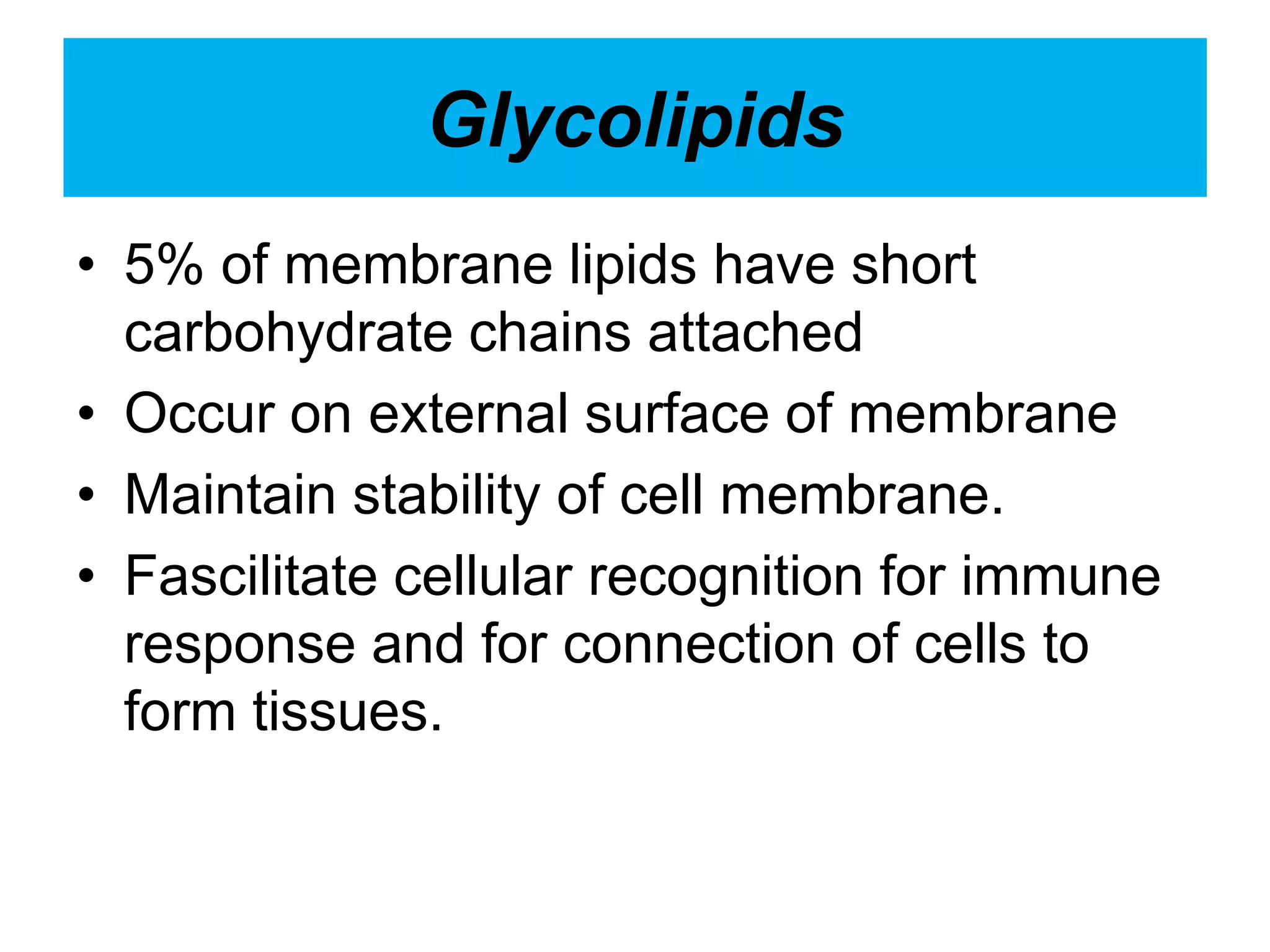
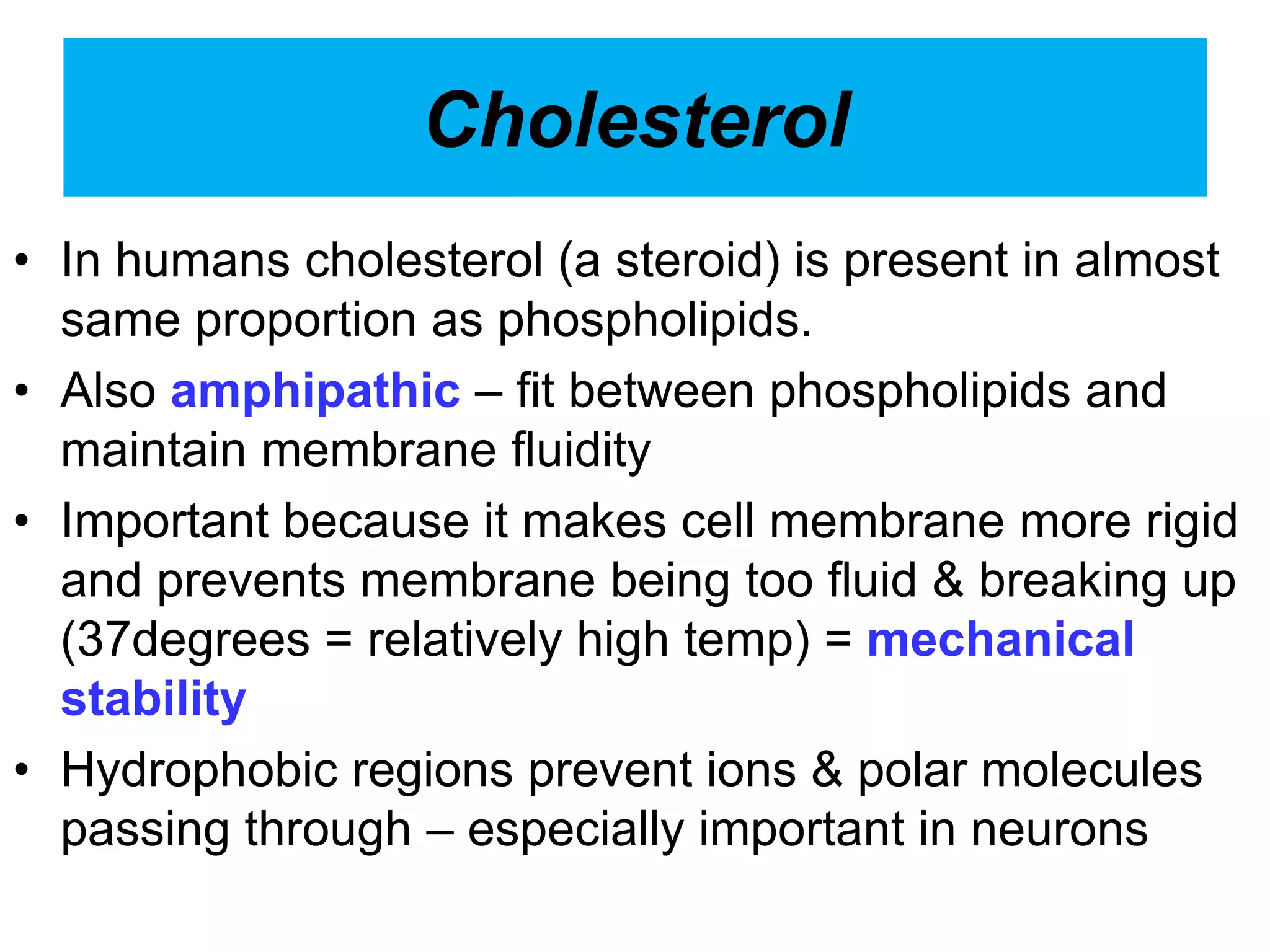
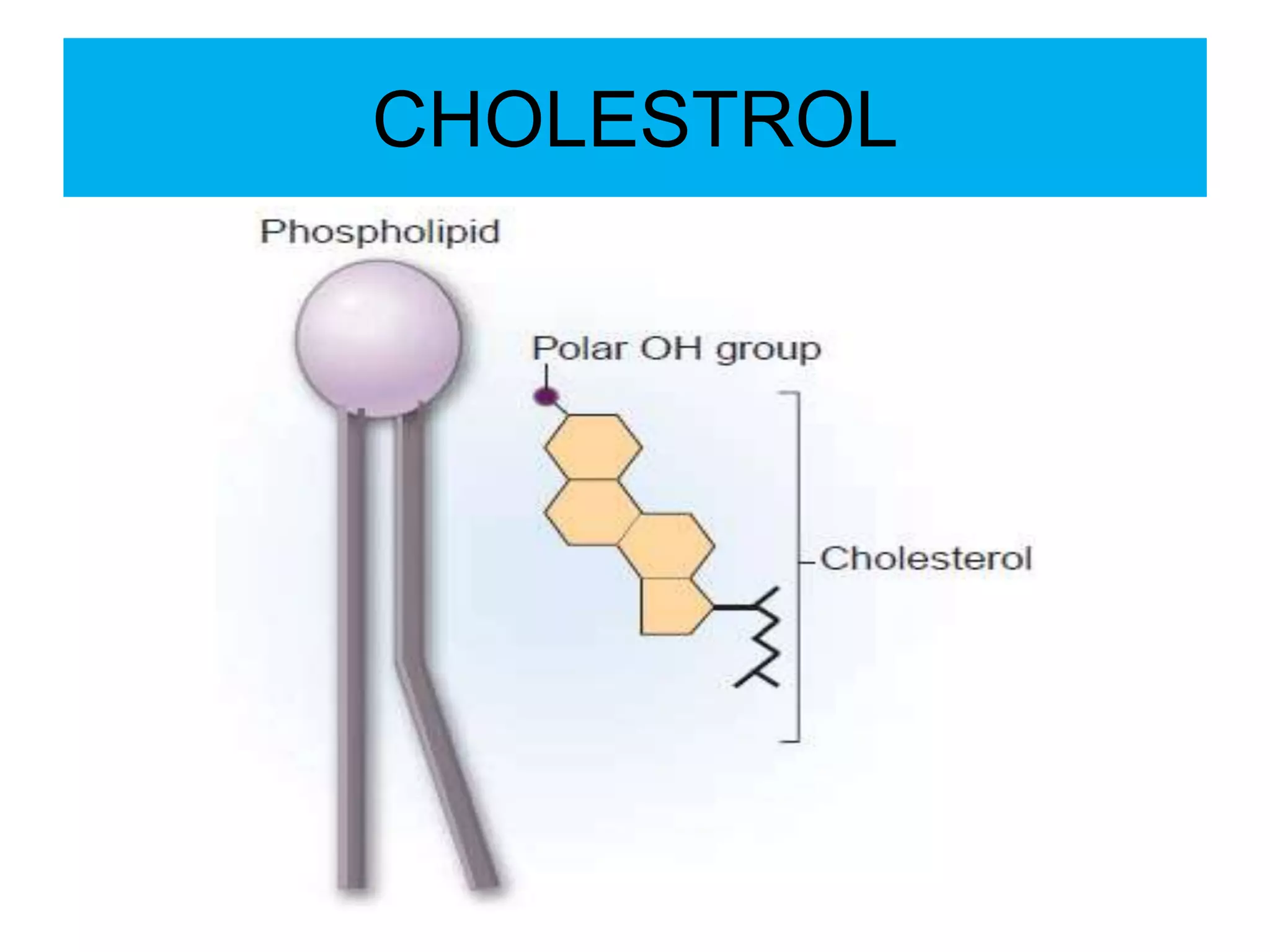
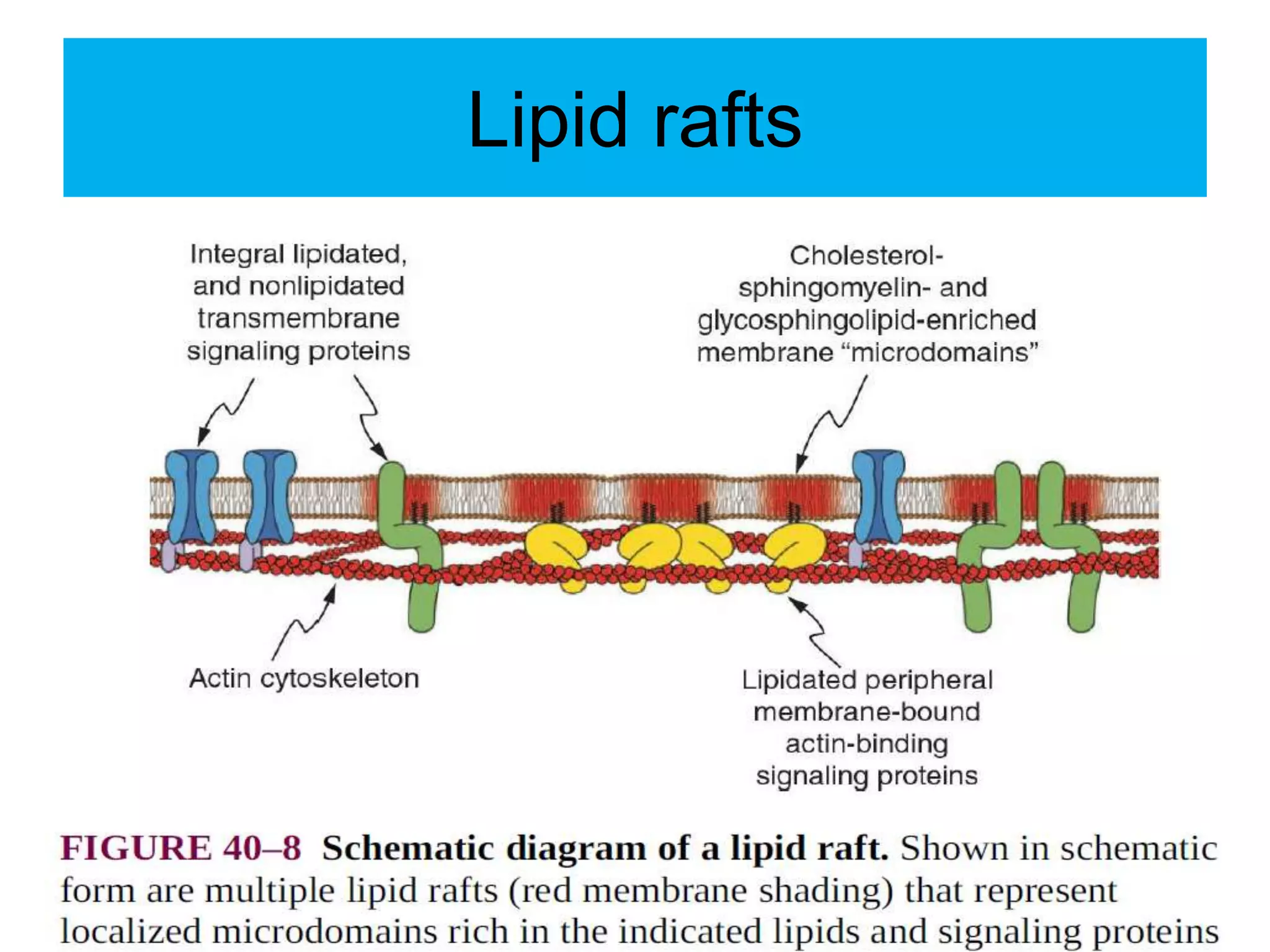
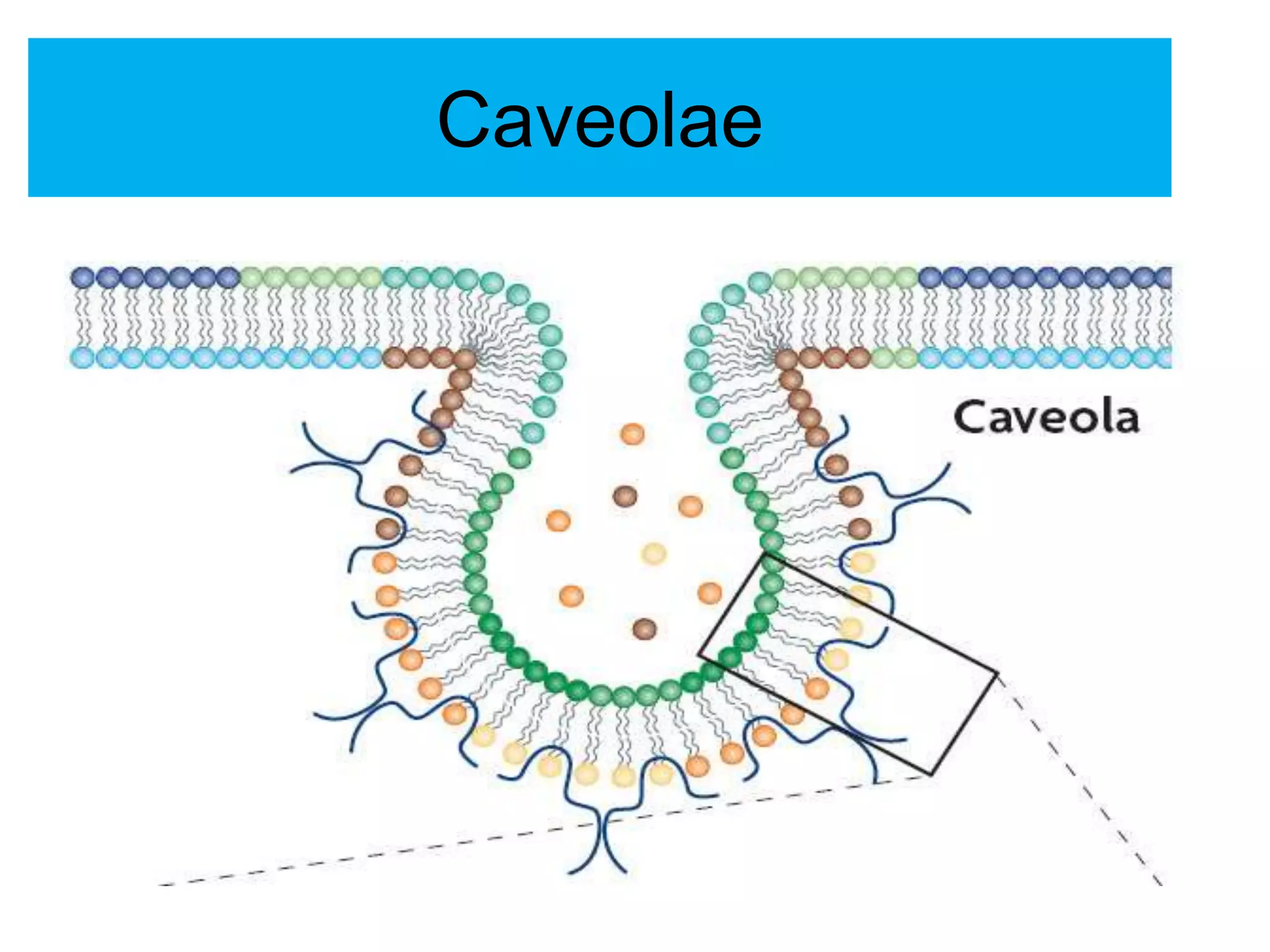
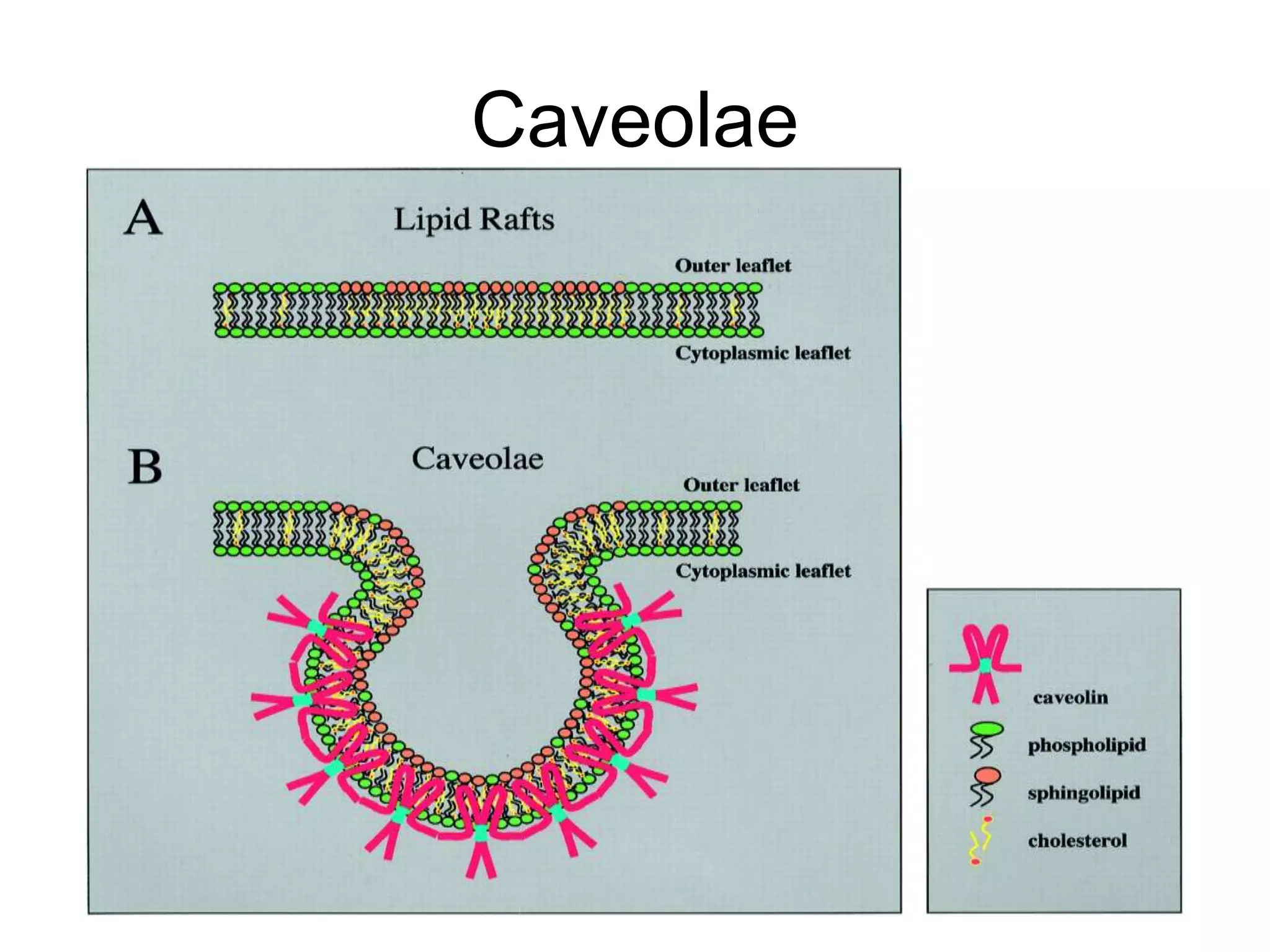
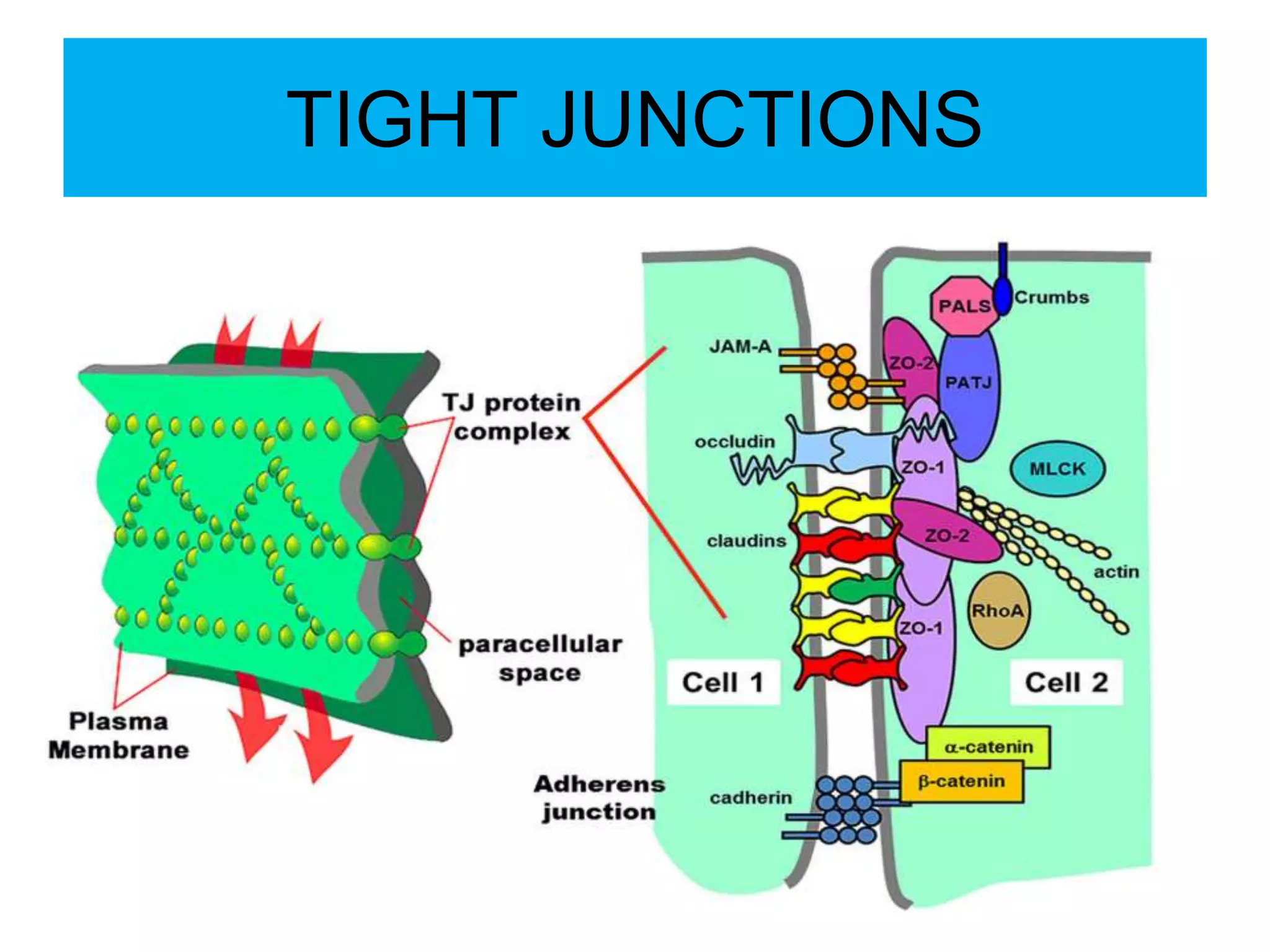
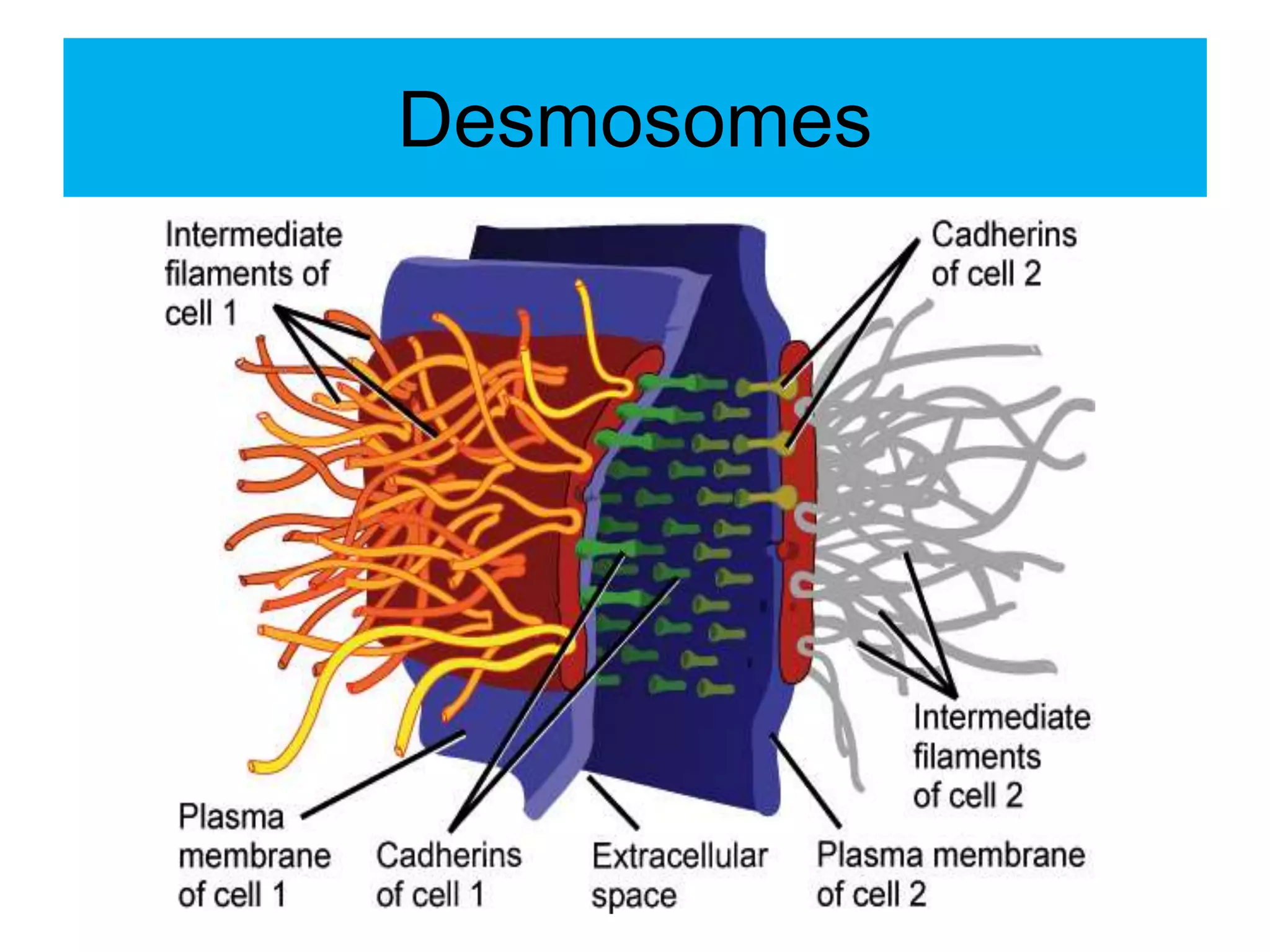
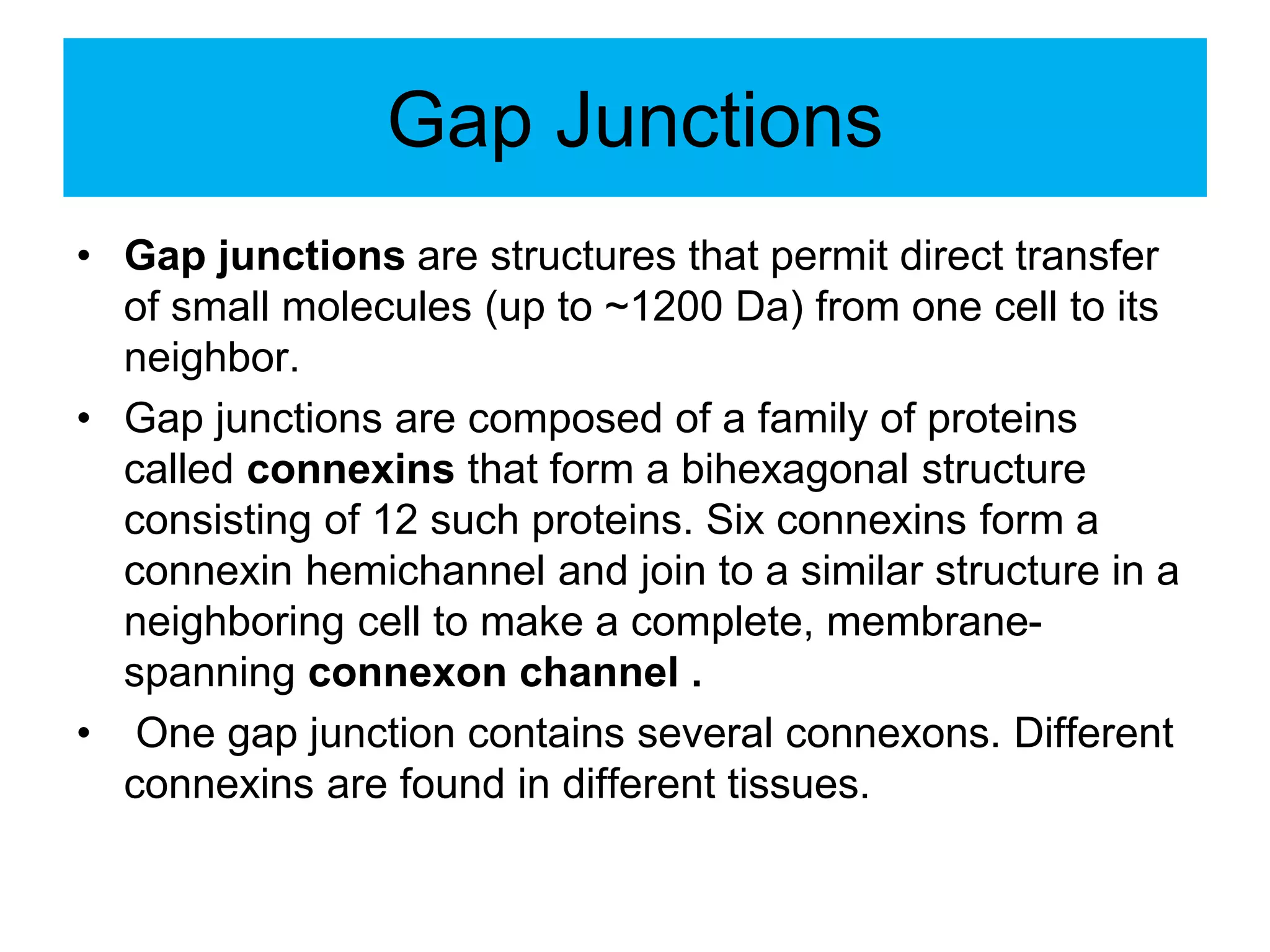
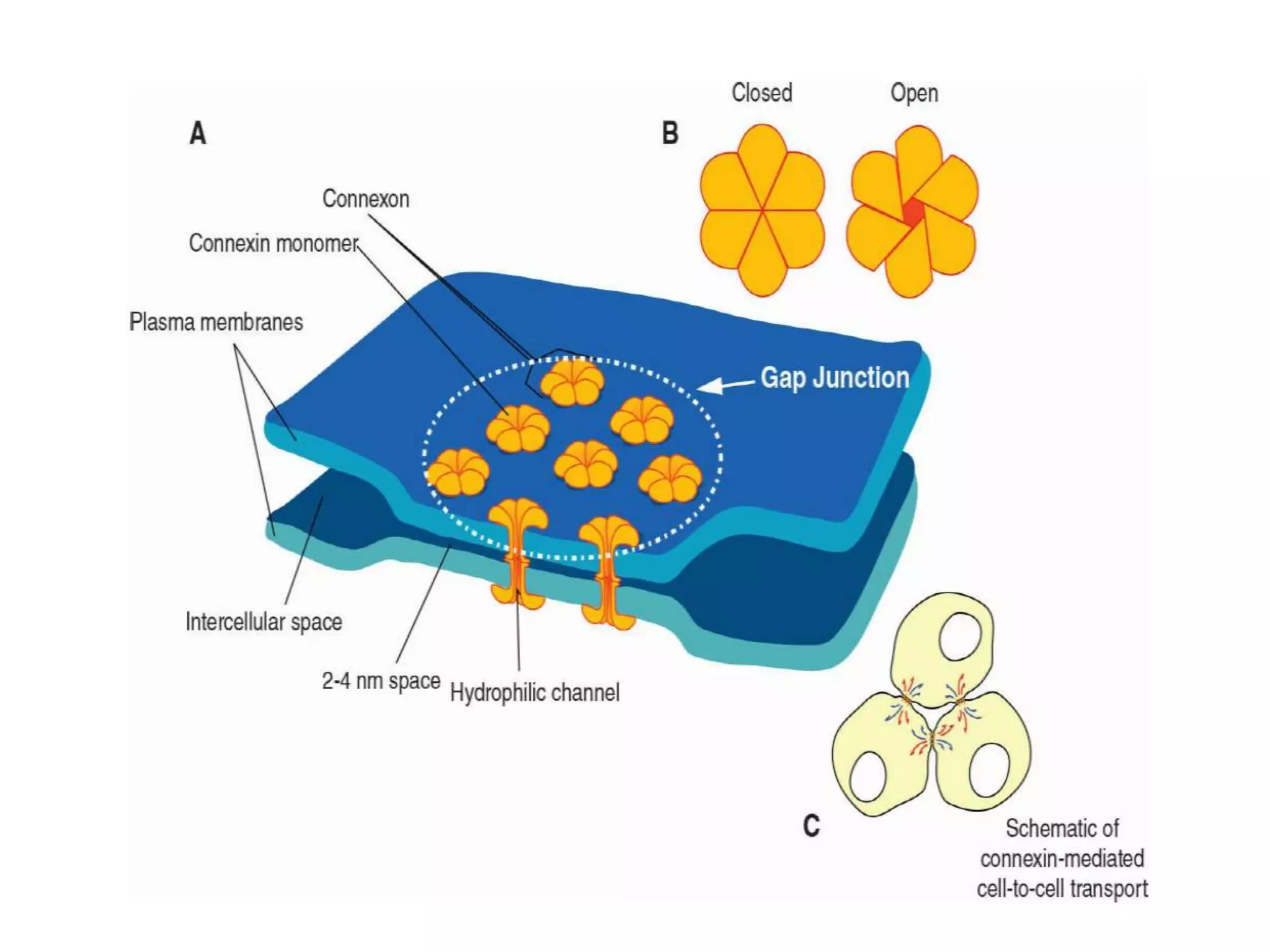
The cell membrane is a complex 3D structure that encircles the cell. It is composed of a phospholipid bilayer with proteins embedded within it. The phospholipid bilayer forms spontaneously, with the hydrophobic tails facing each other and the hydrophilic heads facing outwards towards the extracellular fluid and cytoplasm. This structure allows the membrane to be selectively permeable. Membrane proteins perform important functions like transport, signaling, and identity. Together, the lipid bilayer and embedded proteins create a dynamic structure that is essential for cell integrity and function.