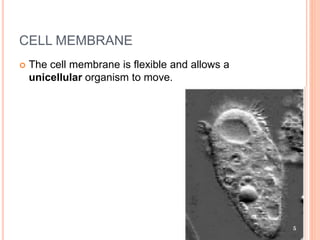
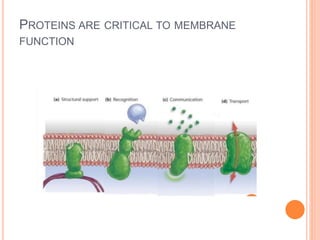
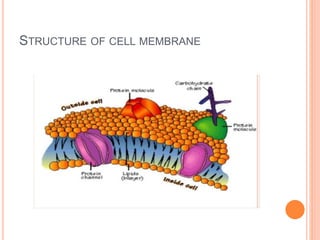
The cell membrane is a phospholipid bilayer 7.5-10 nm thick that separates the interior of a cell from its external environment. It is composed of lipids, proteins, and carbohydrates. Lipids make up the majority and form a fluid bilayer with hydrophobic tails facing inward and hydrophilic heads outward. Embedded proteins carry out important functions like transport and cell signaling. The fluid mosaic model describes the cell membrane as a fluid bilayer with integral and peripheral proteins diffusing within. The cell membrane regulates what enters and exits the cell and also serves structural and signaling roles.