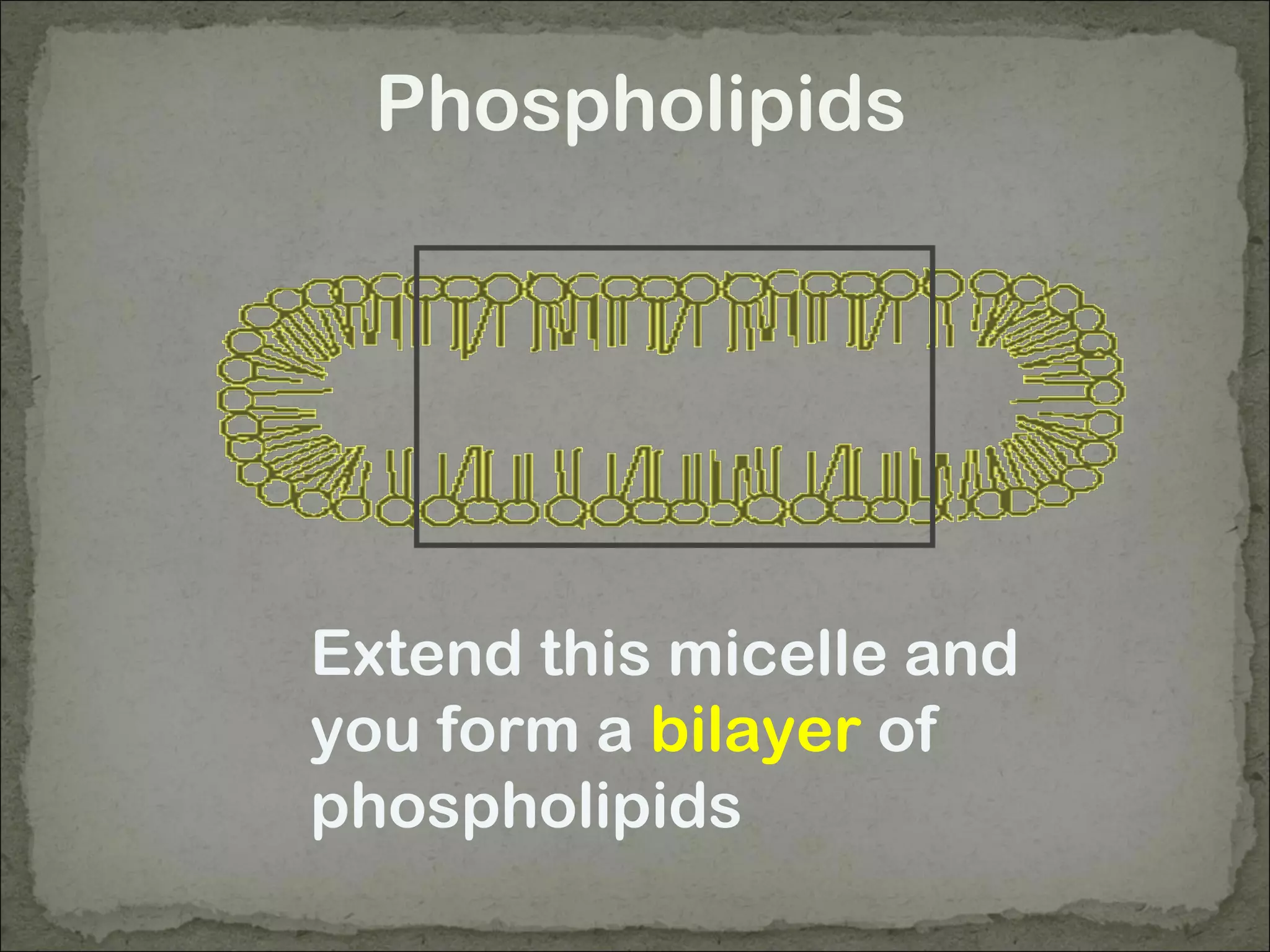
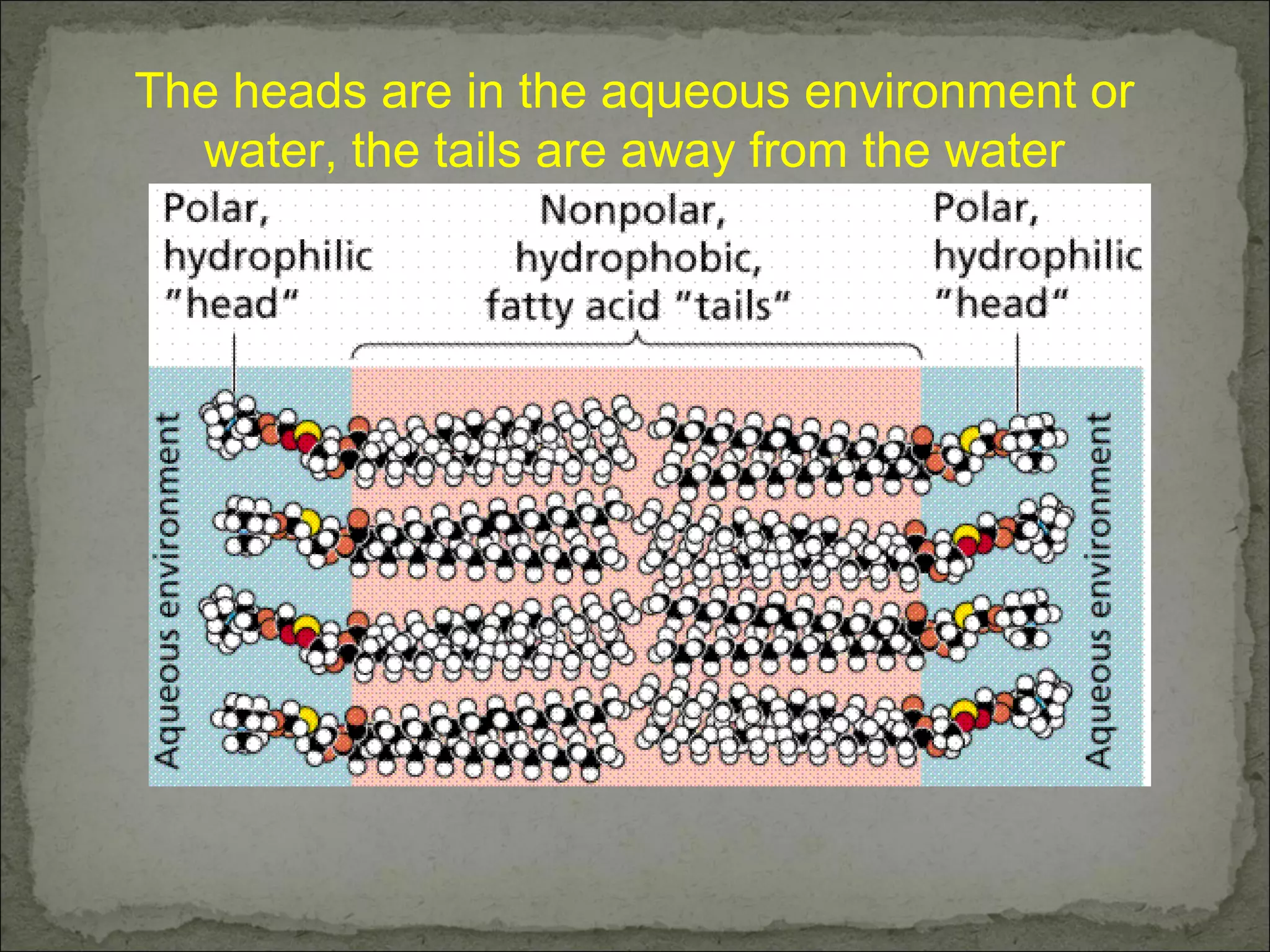
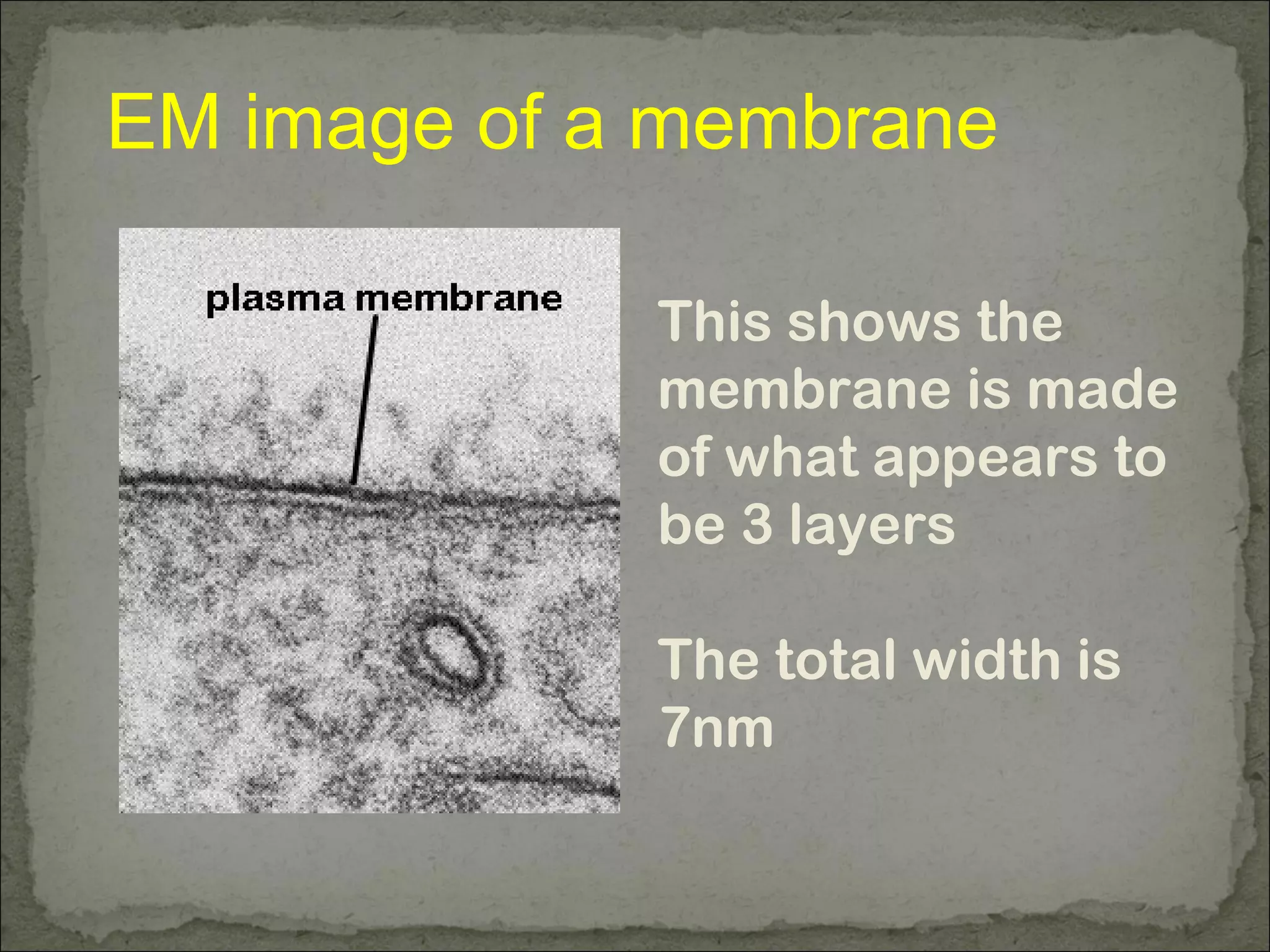
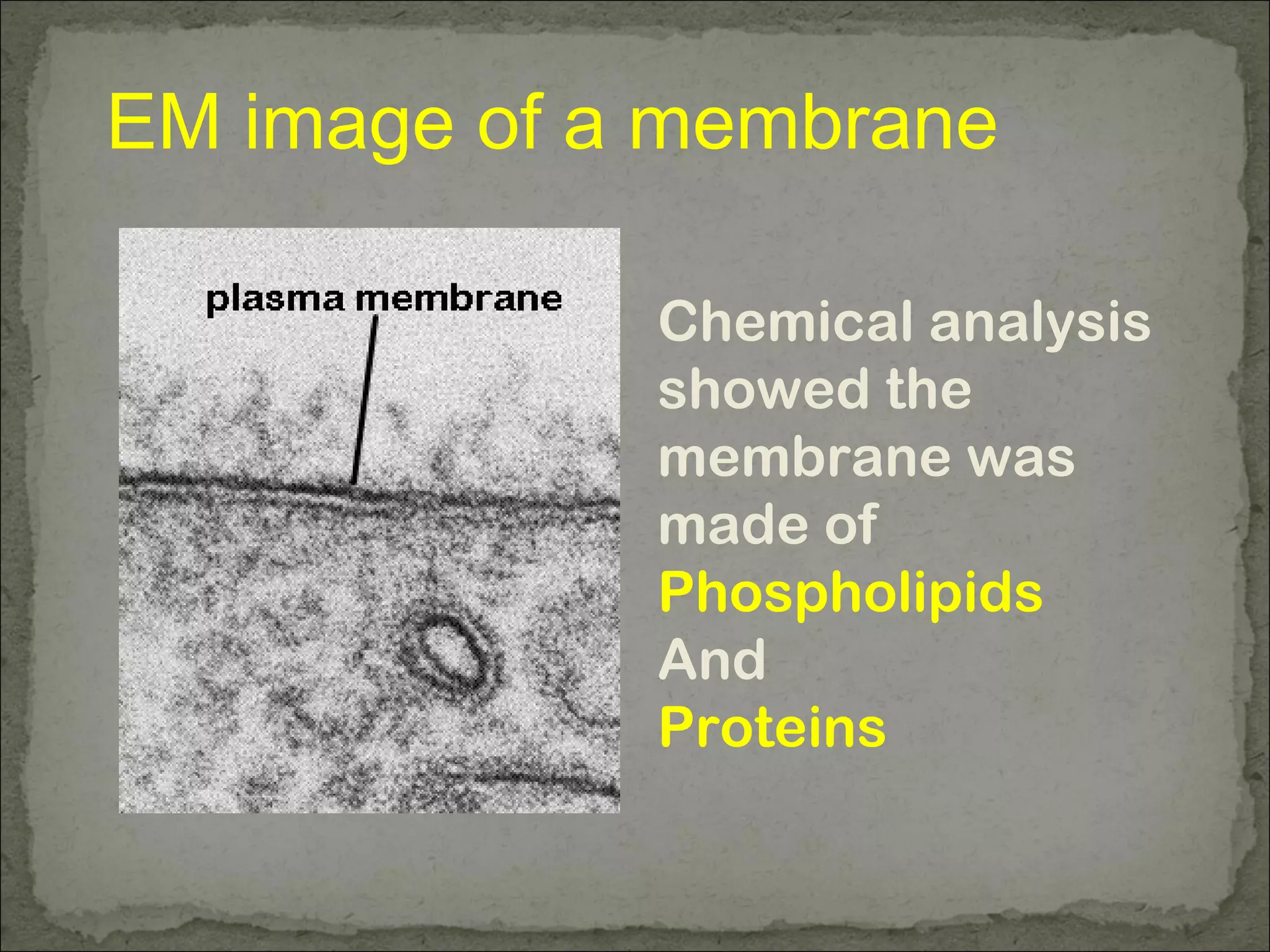
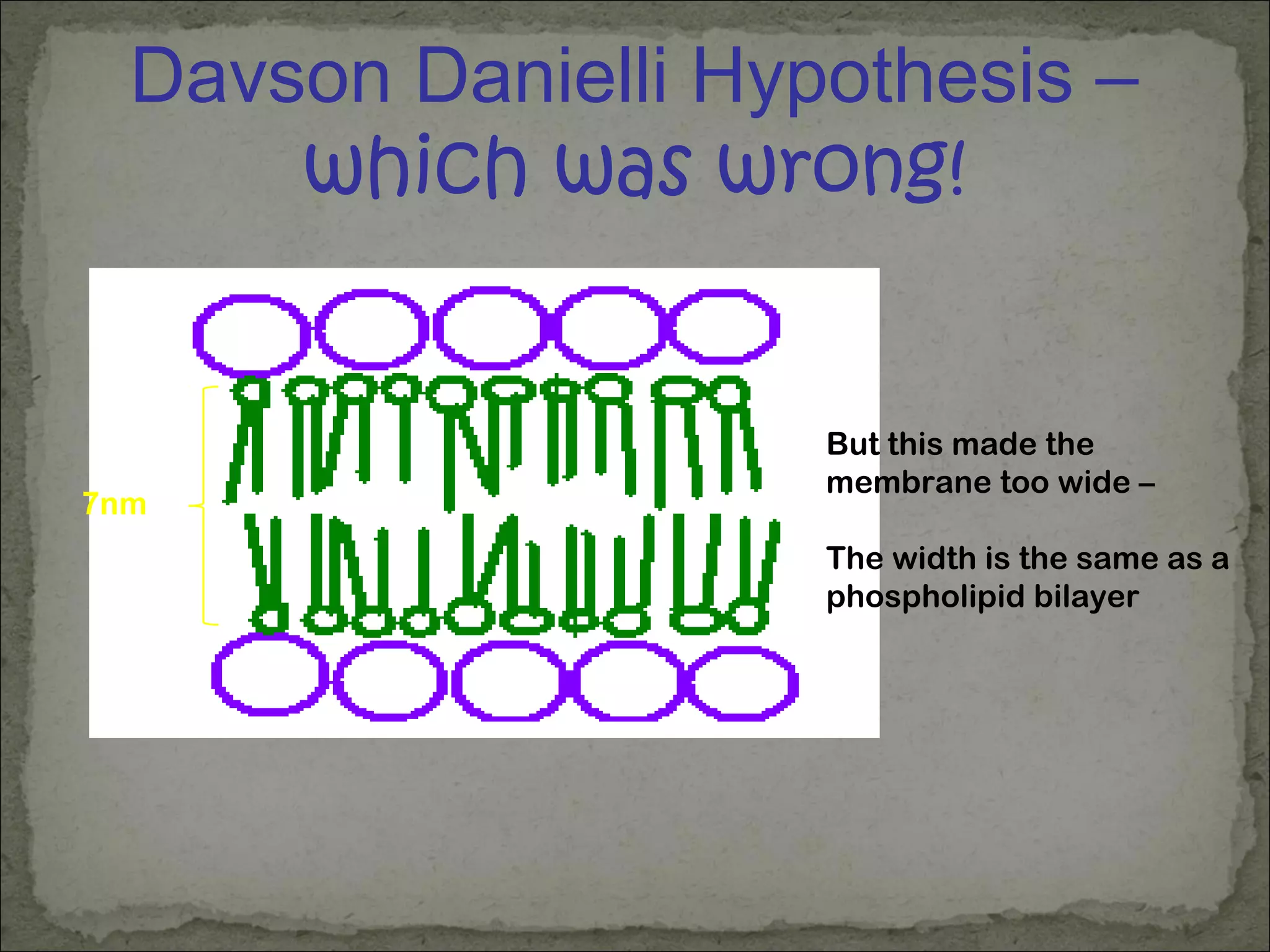
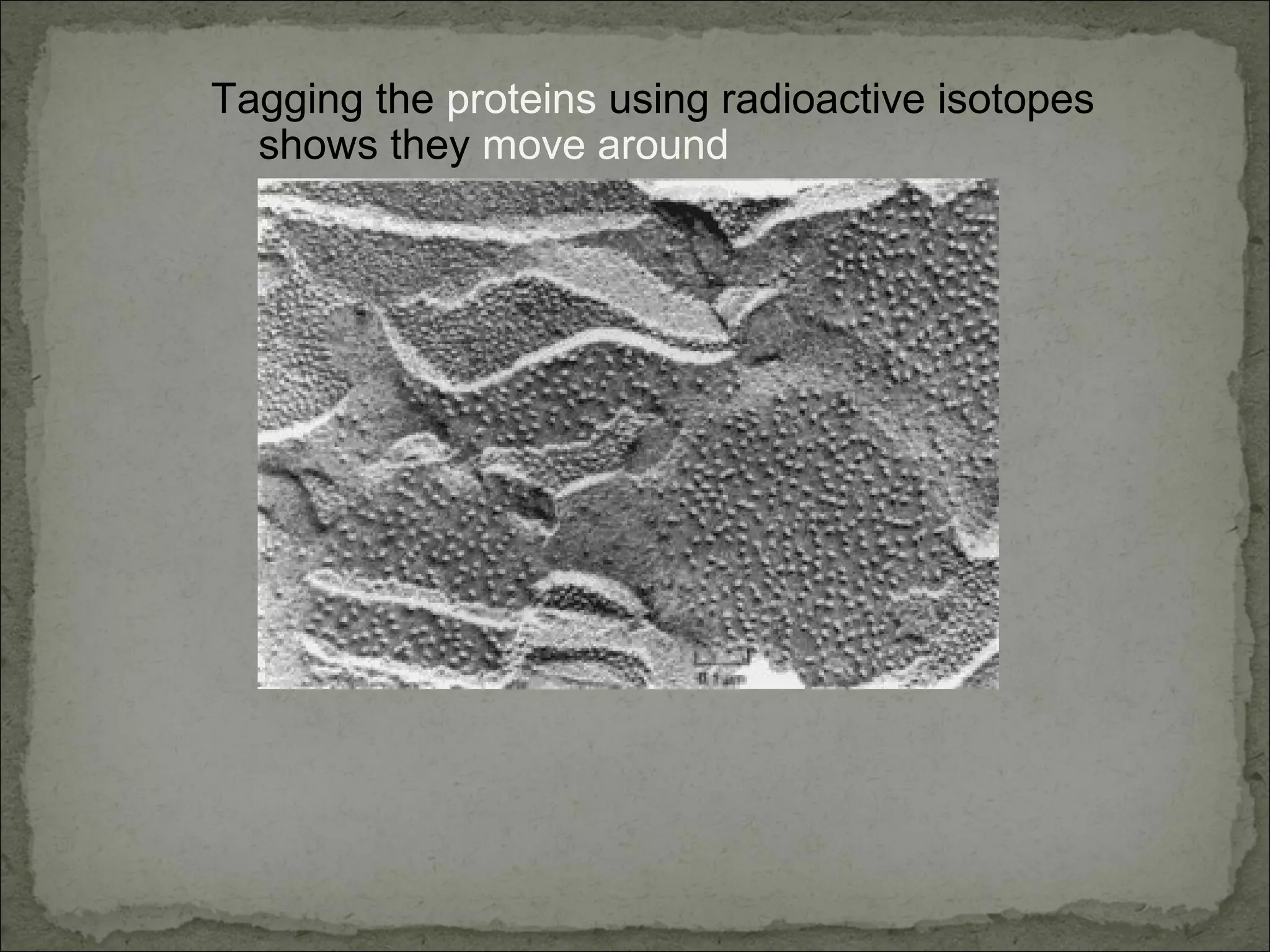
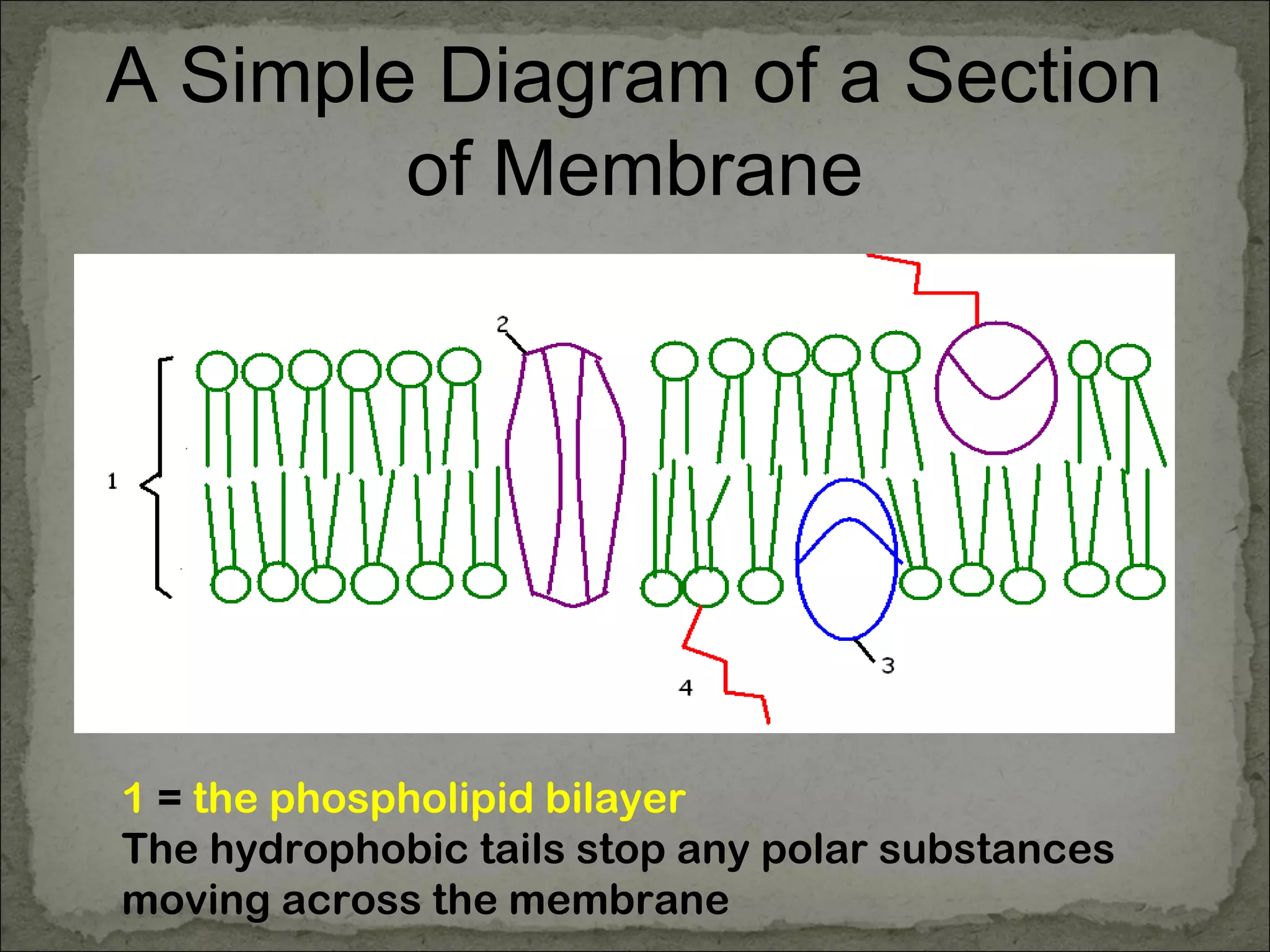
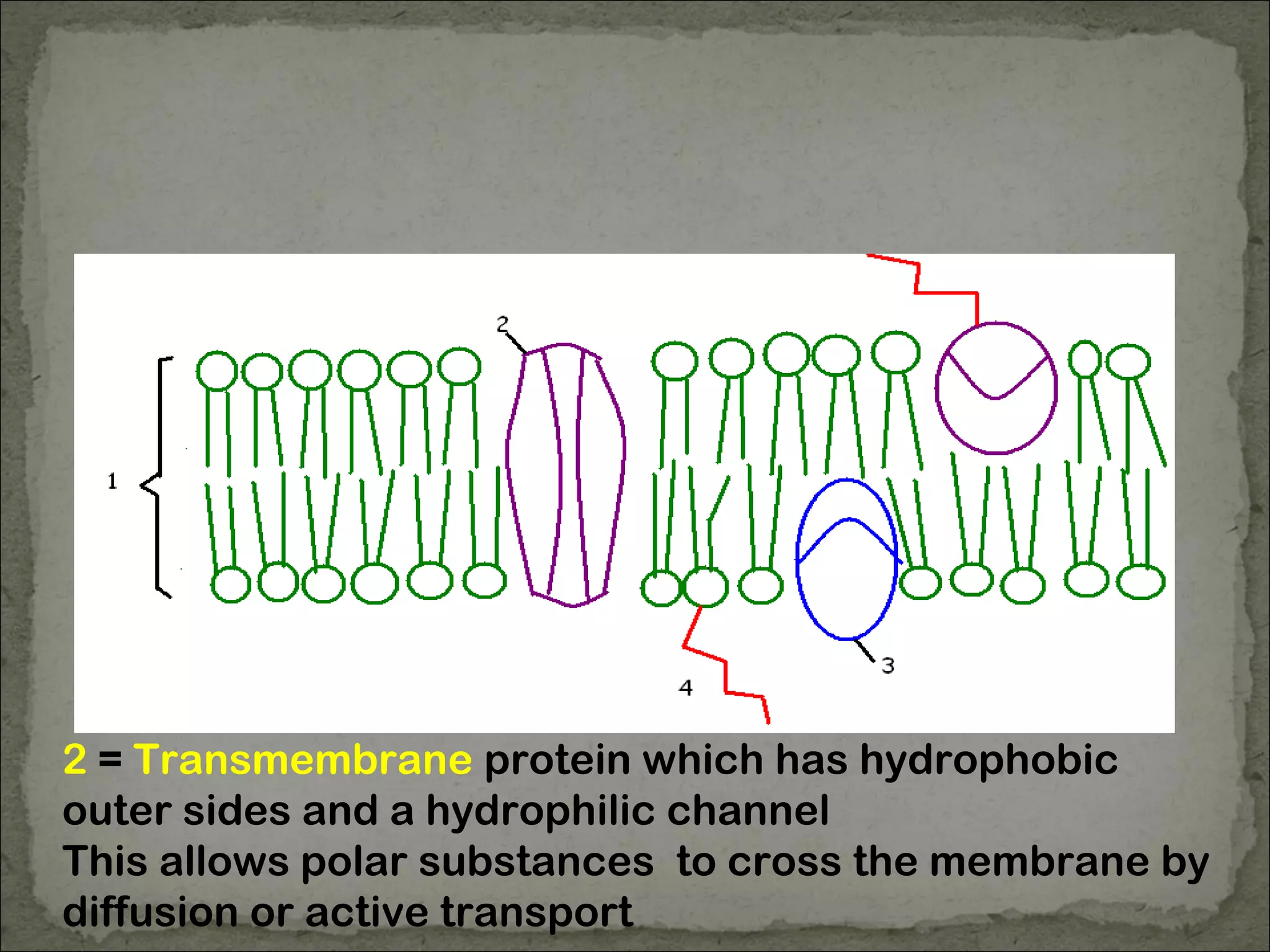
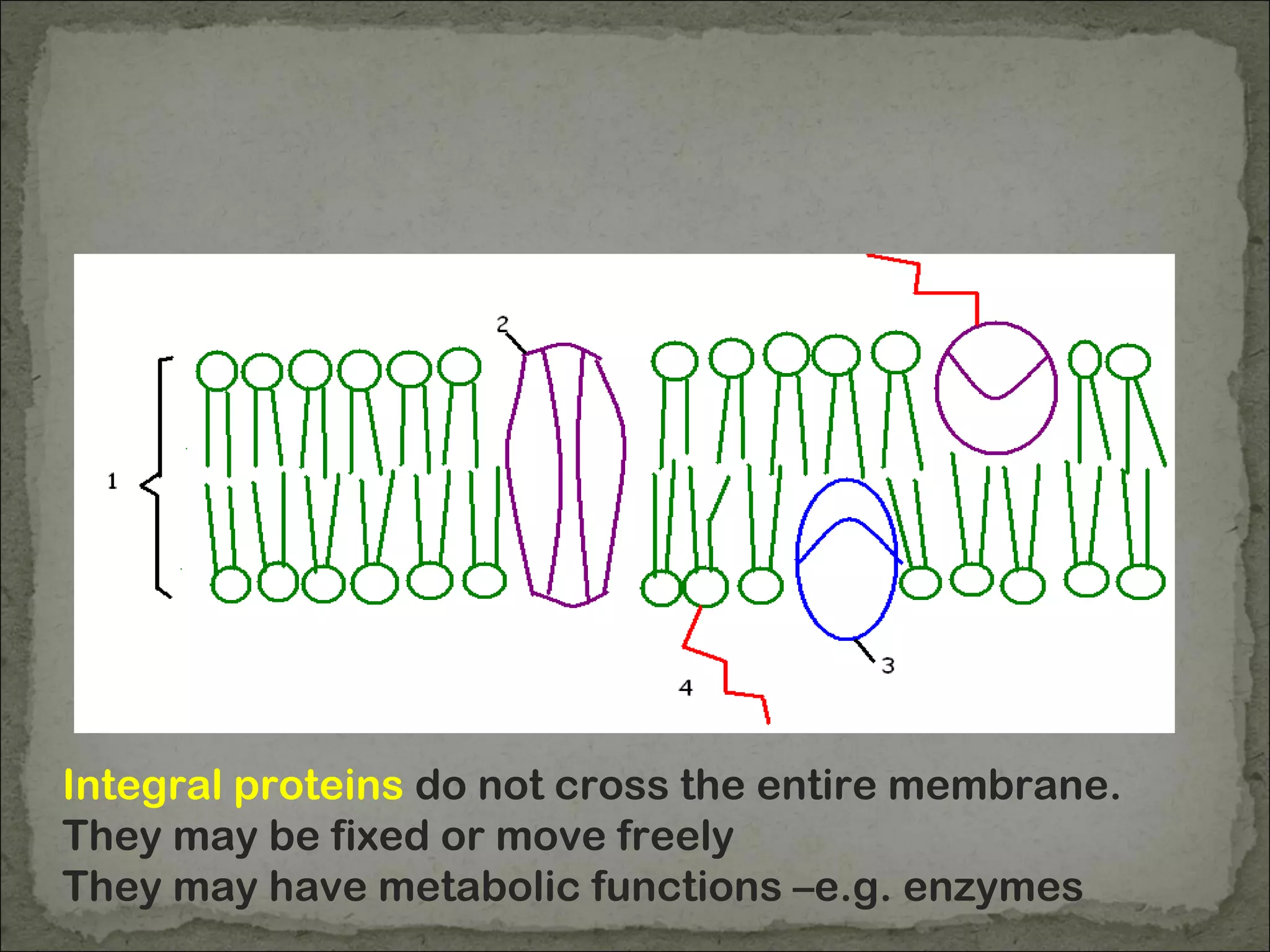
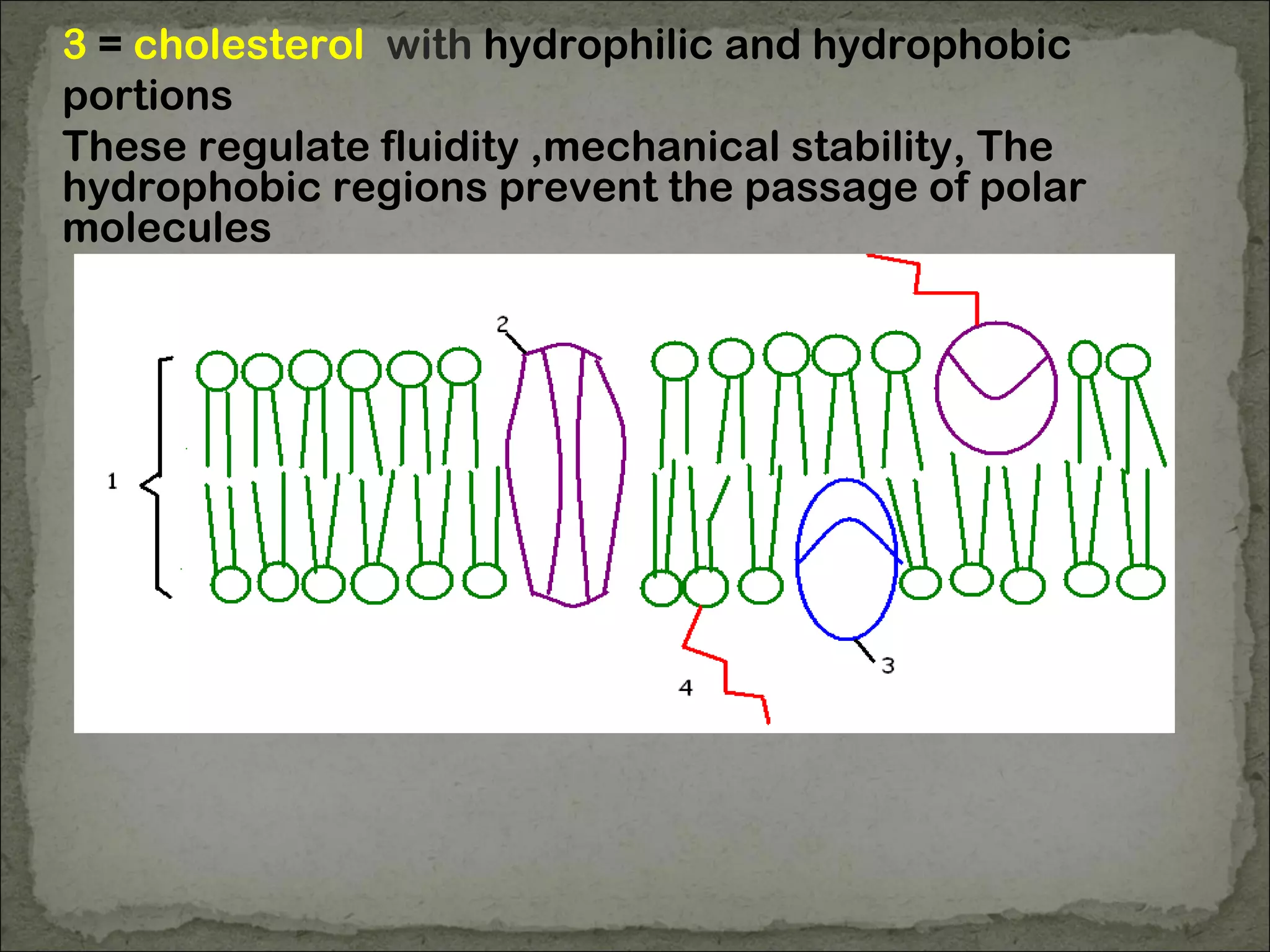
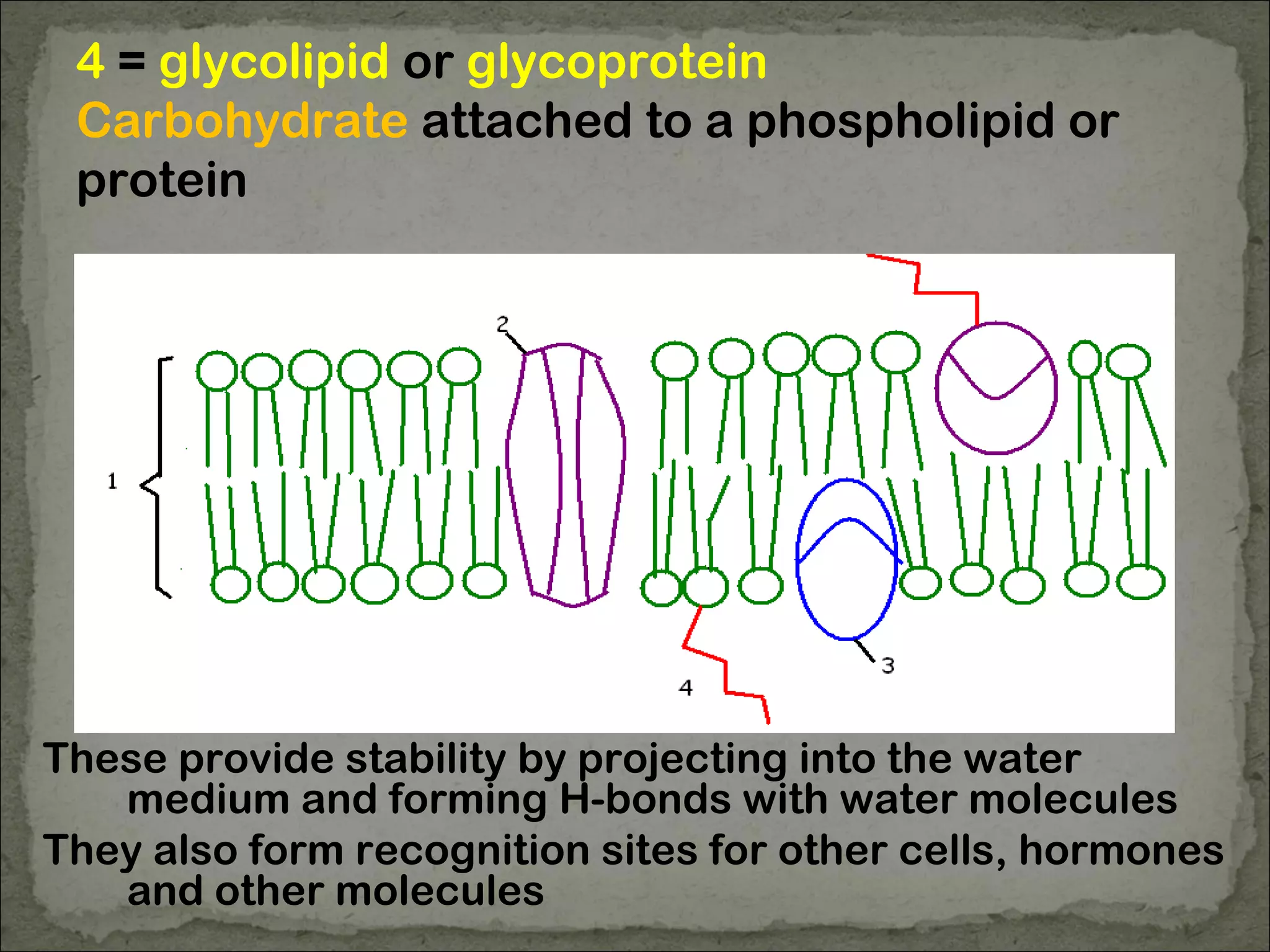
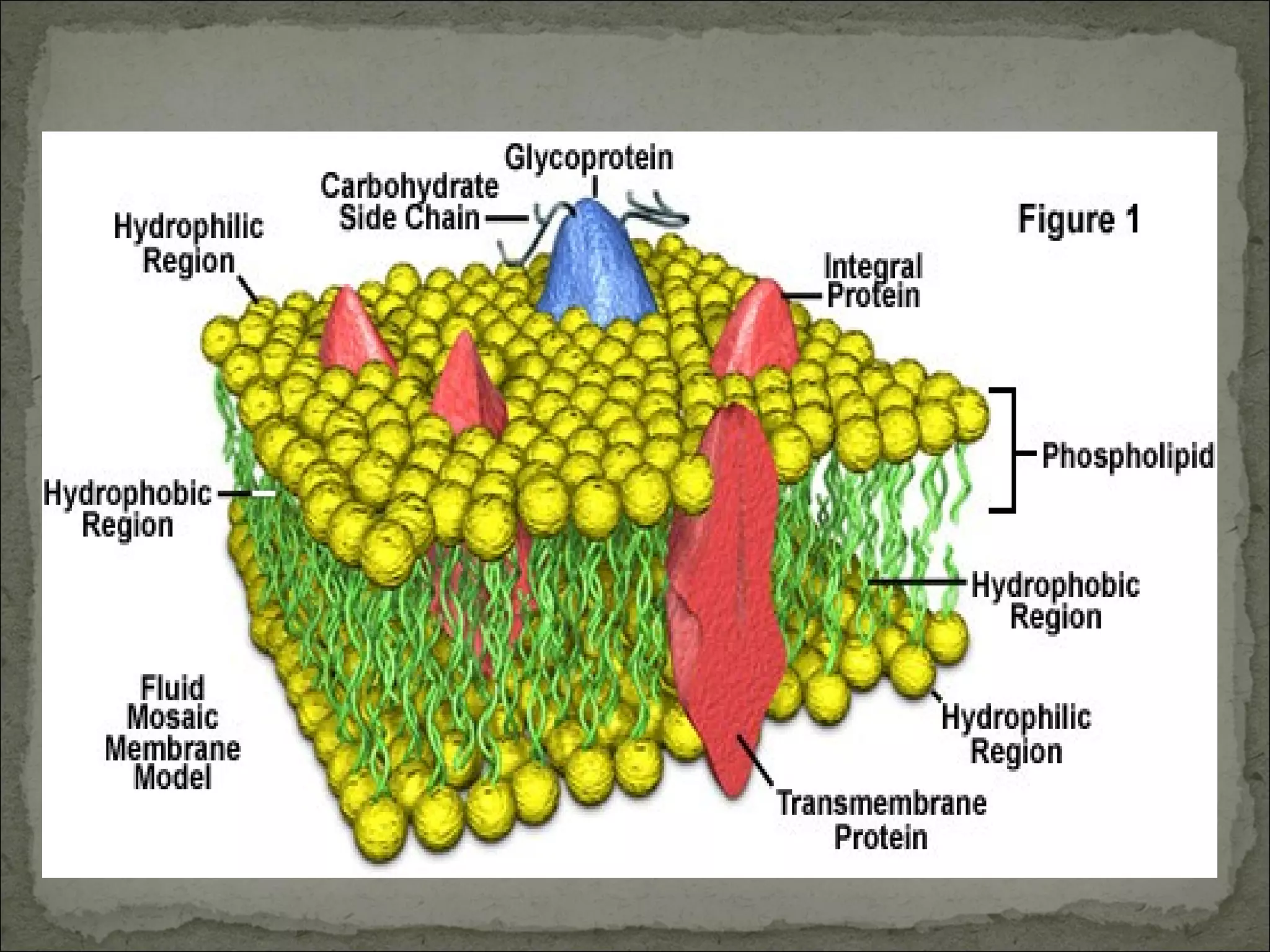
The cell membrane is made up of a phospholipid bilayer only 7nm wide. Phospholipids have a hydrophilic phosphate head and hydrophobic fatty acid tails which allow them to spontaneously form a bilayer in water with heads facing out and tails inside. The membrane also contains proteins, which early models incorrectly thought layered on top of the phospholipids but are now known to float within the fluid bilayer. The fluid mosaic model describes the current understanding of the membrane with proteins and phospholipids forming a flexible yet selective barrier.