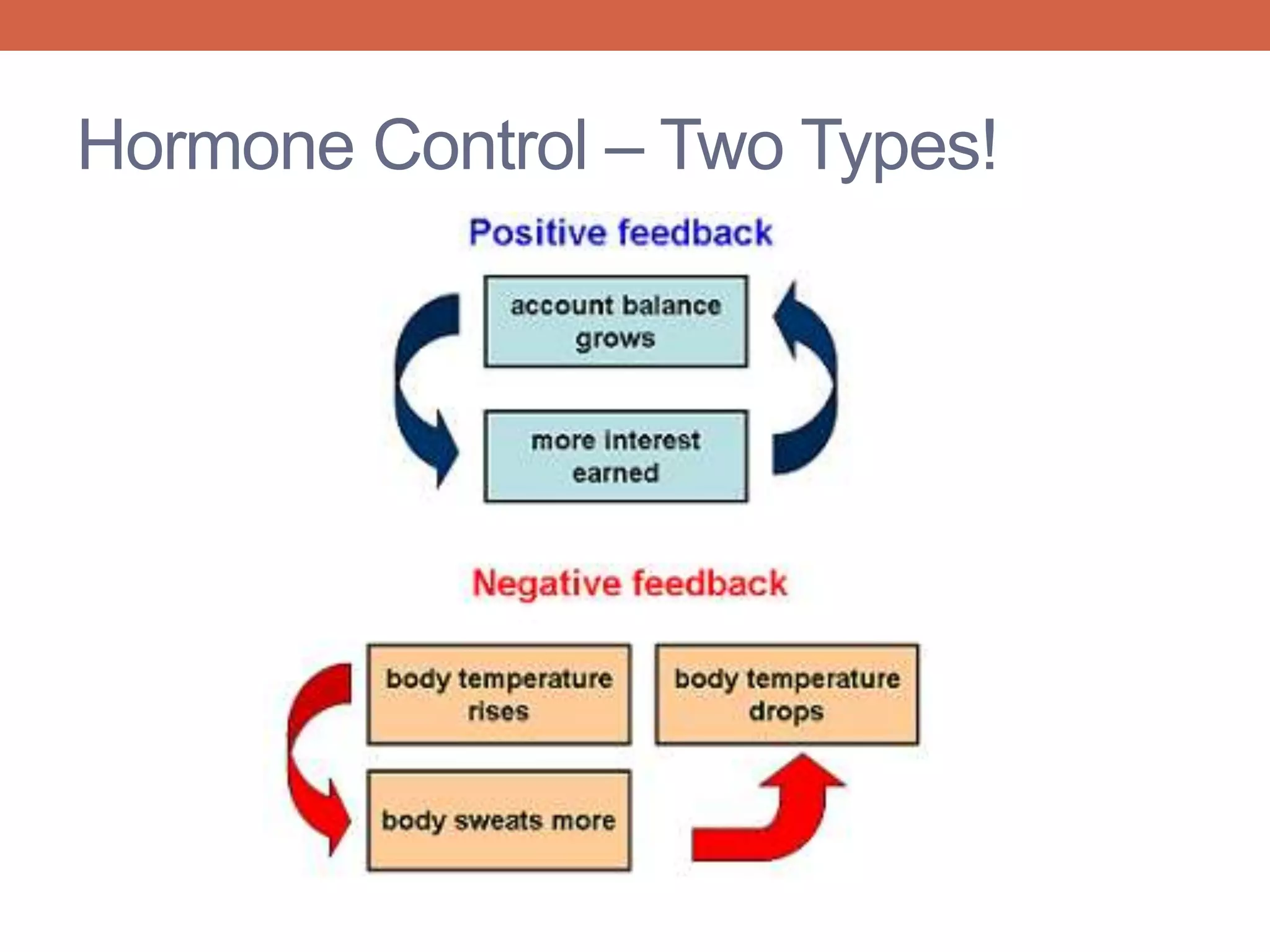
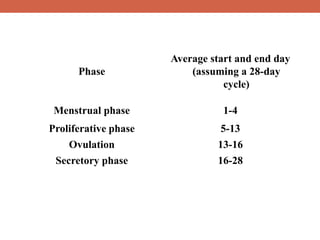
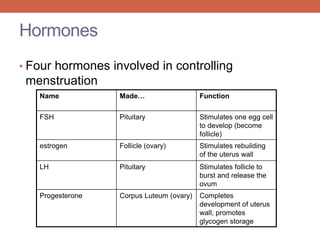
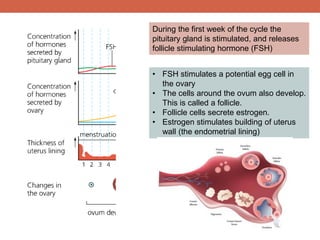
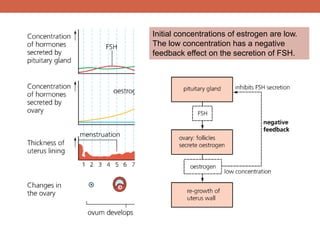
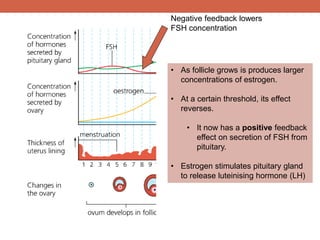
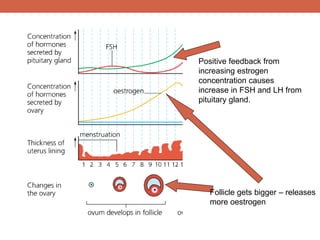
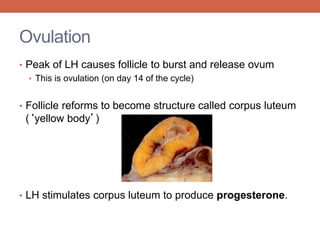
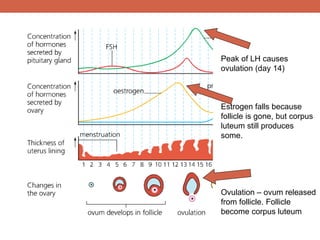
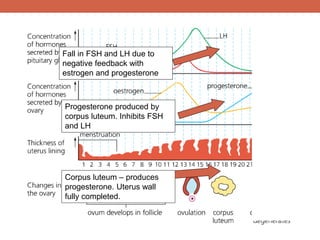
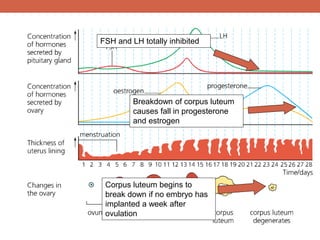
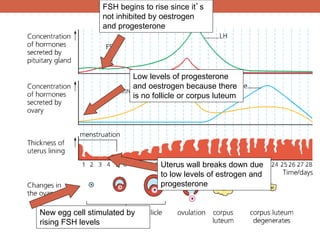
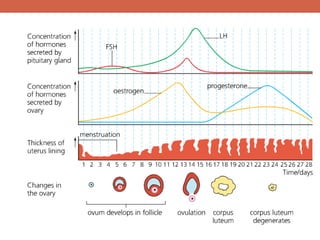
The menstrual cycle is controlled by hormones from the pituitary gland and ovaries. It aims to release an egg once a month to allow for potential fertilization and pregnancy. The cycle involves three phases - the menstrual, proliferative, and secretory phases. Estrogen stimulates growth of the uterine lining during the proliferative phase, while progesterone maintains the lining during the secretory phase in preparation for potential implantation. If implantation does not occur, progesterone and estrogen levels fall, causing the uterine lining to shed and result in menstruation, restarting the cycle.