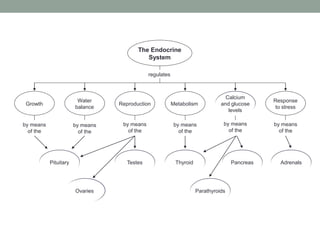
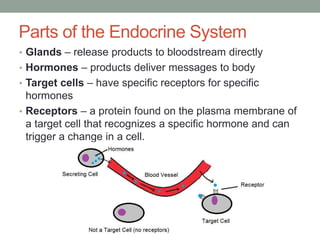
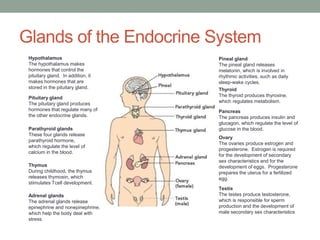
The endocrine system regulates growth, metabolism, water balance, reproduction and stress response through glands that release hormones into the bloodstream. The major glands include the pituitary, thyroid, parathyroids, adrenals, pancreas, ovaries and testes. Hormones deliver messages to target cells through receptors and work in coordination with other body systems like interacting with the nervous system.