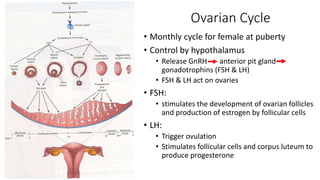
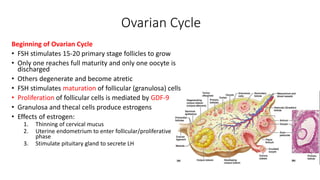
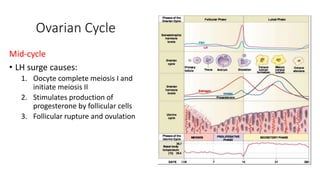
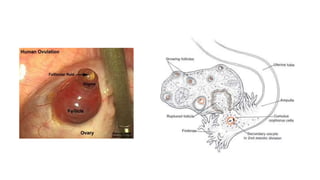
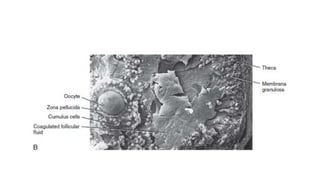
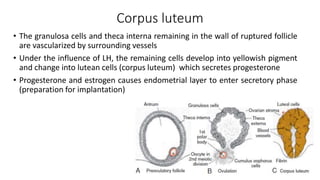
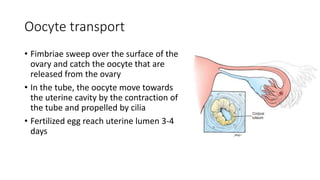
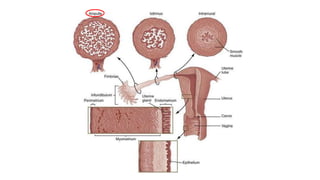
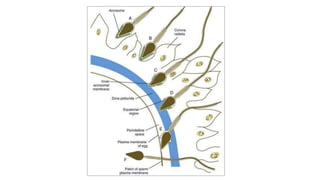
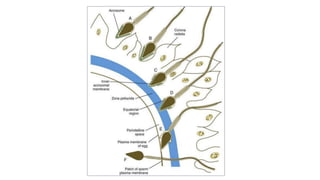
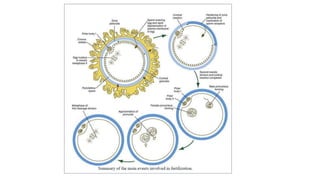
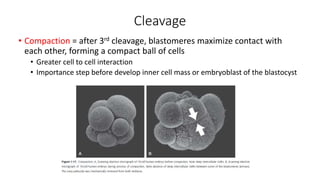
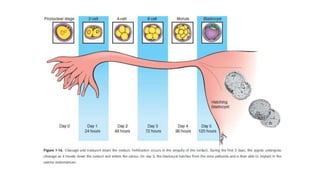
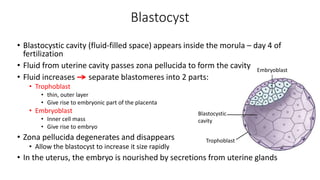
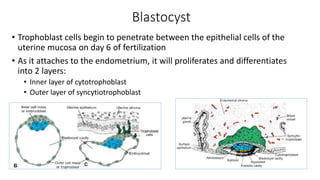
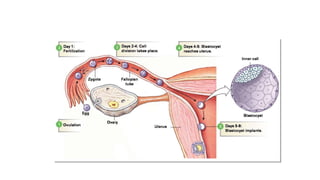
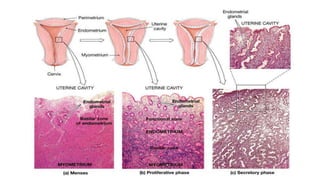
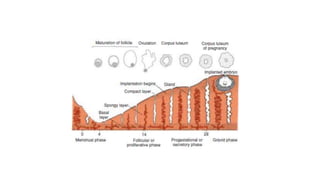
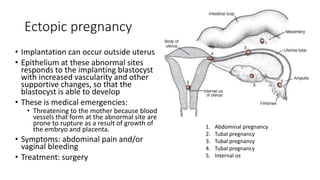
The document discusses the processes of ovulation, fertilization, and implantation. It explains that ovulation is triggered by hormones like LH and FSH, leading to the release of an egg. If fertilization by sperm occurs, the fertilized egg undergoes cell division and develops into a blastocyst over a week. The blastocyst then implants in the uterus by attaching to the endometrial lining with the help of hormonal changes brought on by the corpus luteum.