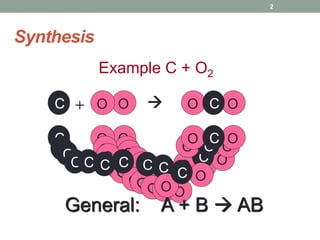
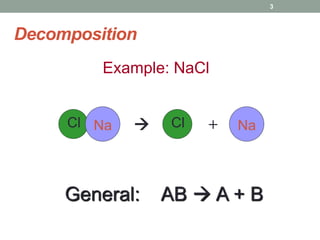
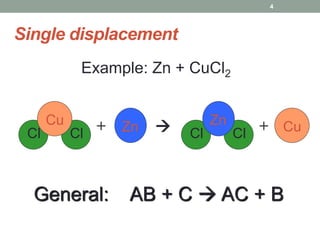
1. The document describes different types of chemical reactions including synthesis, decomposition, single displacement, double displacement, combustion, acid-base, and neutralization reactions.
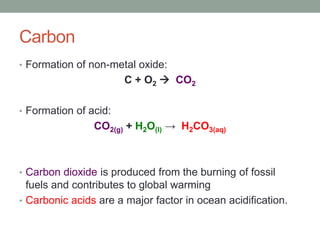
2. Metals react with oxygen to form metal oxides which are bases. Non-metals react with oxygen to form non-metal oxides which are acids.
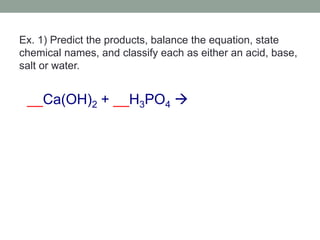
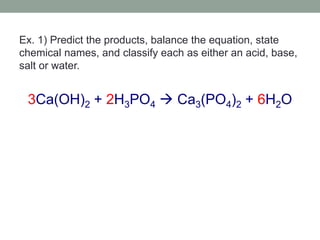
3. Acid-base reactions involve acids and bases reacting to form salts and water in a neutralization reaction.