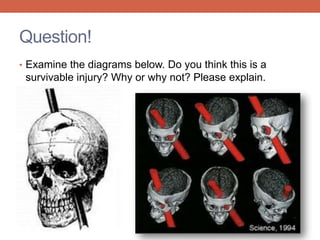
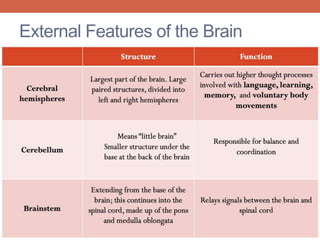
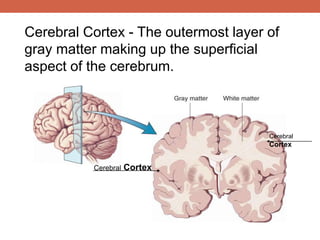
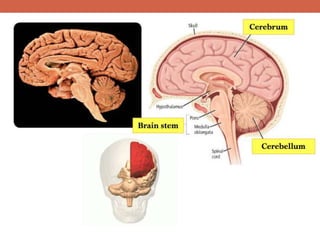
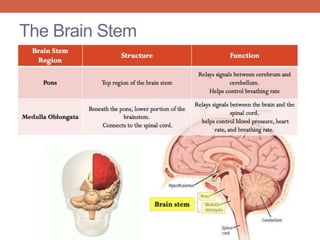
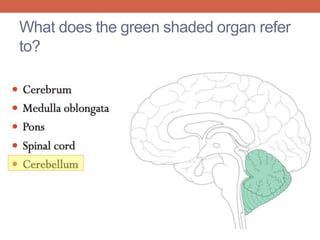
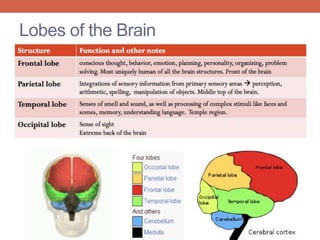
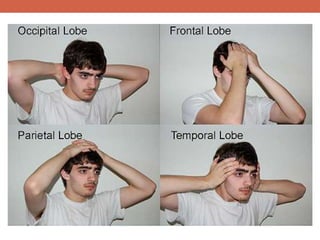
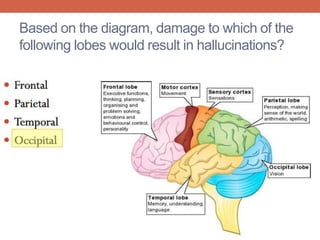
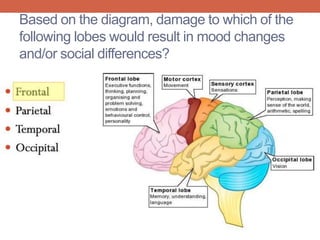
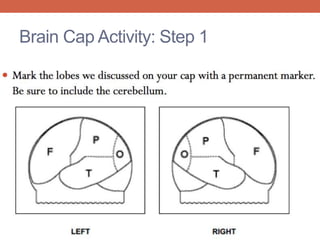
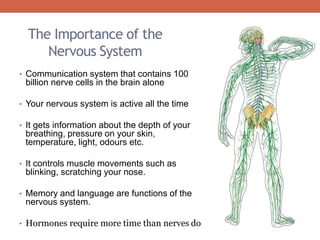
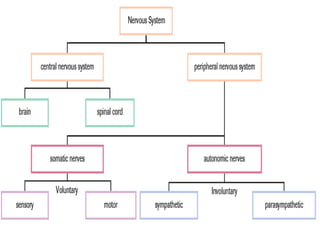
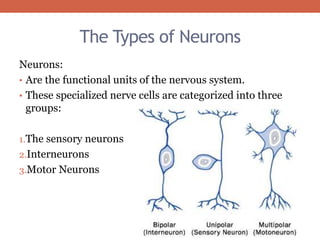
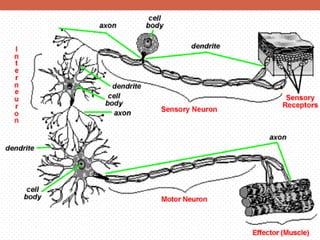
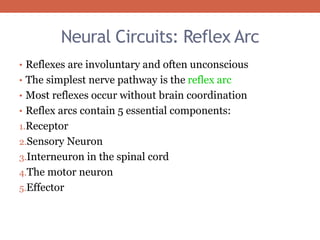
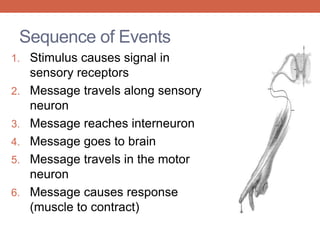
The nervous system is responsible for maintaining homeostasis in the body. It does this through communication between the brain and body via the central and peripheral nervous systems. The brain is made up of different sections that each perform specific tasks to regulate internal conditions. Within the nervous system, there are sensory neurons that receive information, interneurons that integrate and interpret signals, and motor neurons that activate responses in the body's effectors like muscles and glands. Together these neurons form reflex arcs that allow for rapid involuntary responses essential for homeostasis.