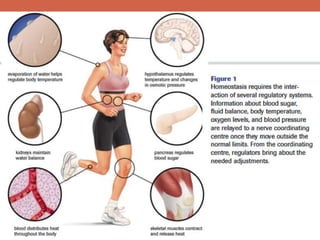
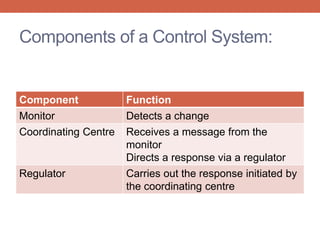
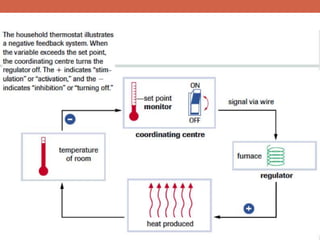
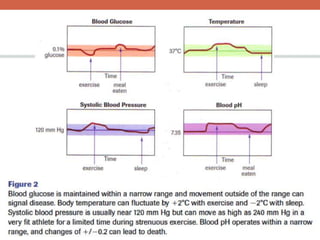
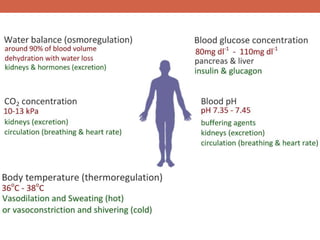
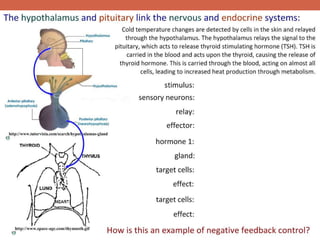
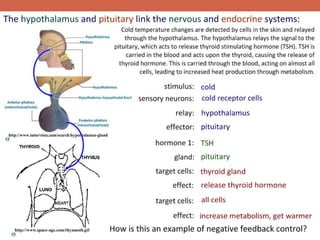
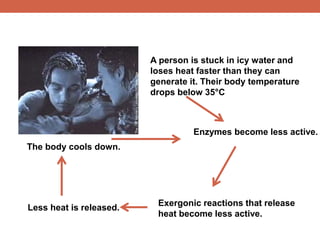
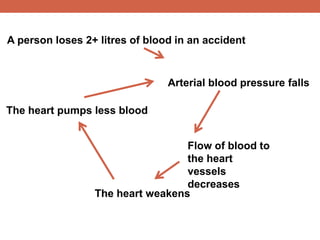
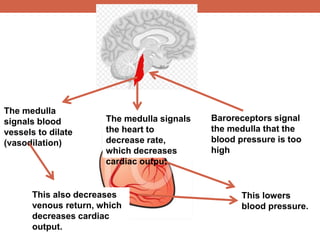
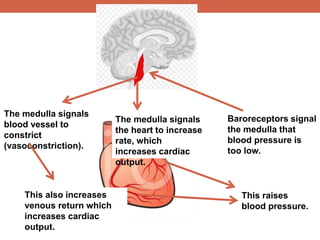
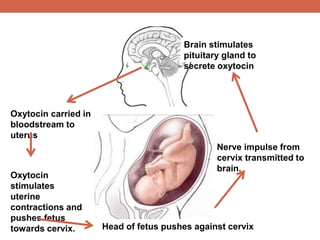
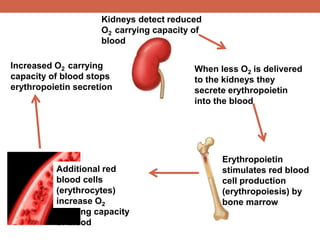
The document discusses homeostasis and control systems in the human body. It explains that various internal variables like blood sugar, body temperature, and pH levels must stay within certain ranges to maintain homeostasis. When changes occur internally or externally, feedback systems work to regulate monitors, coordinating centers, and regulators to return levels to the normal range. Negative feedback is the most common type of response that works to reverse changes, while positive feedback reinforces changes. Multiple organ systems interact together to continuously monitor and adjust conditions to uphold homeostasis.