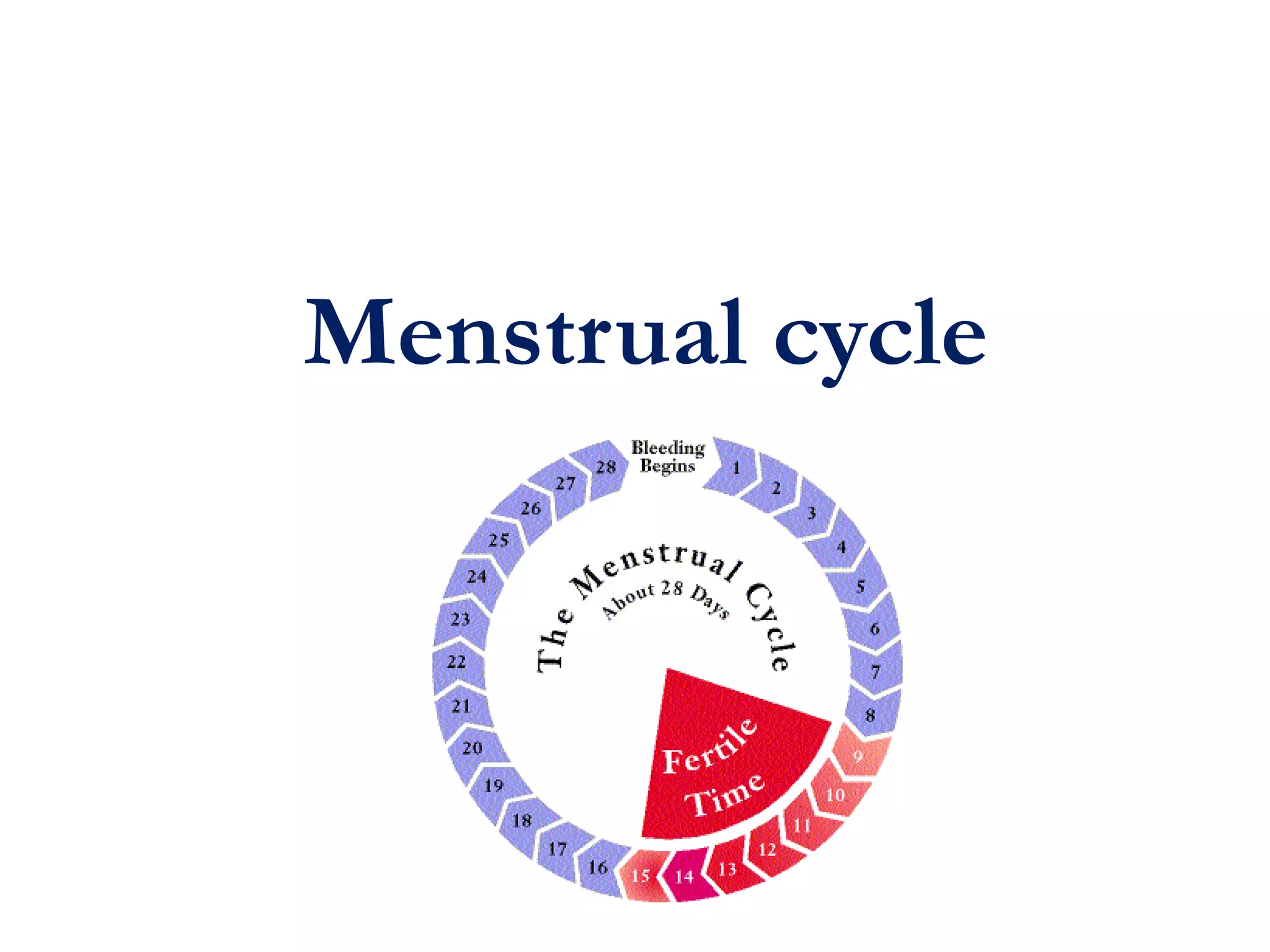
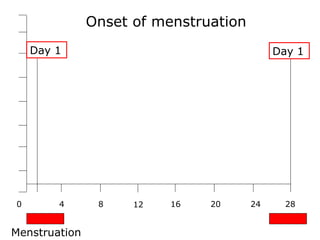
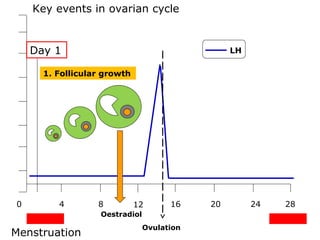
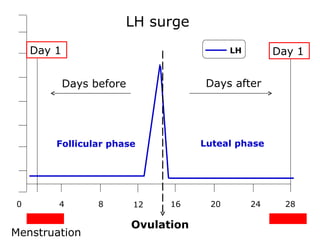
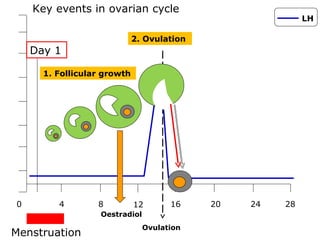
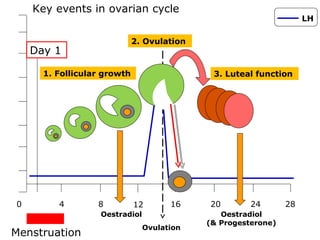
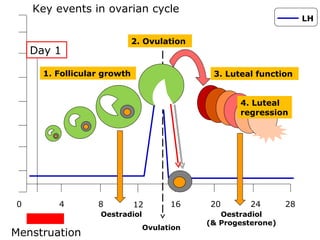
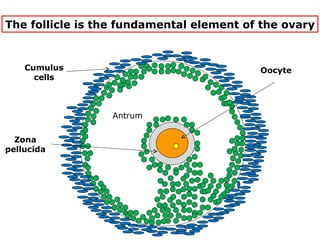
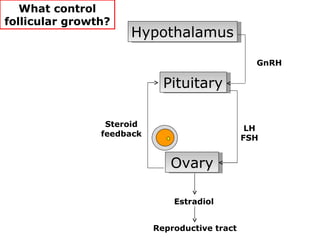
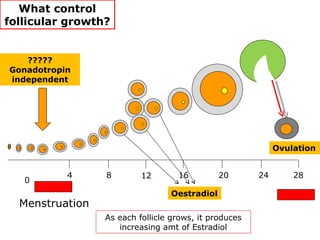
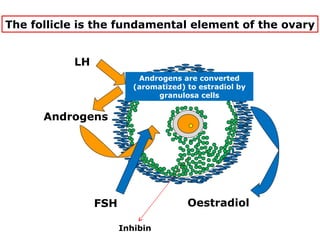
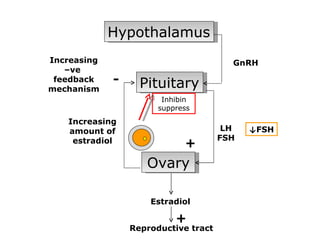
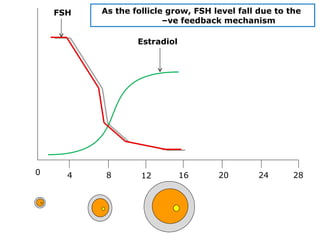
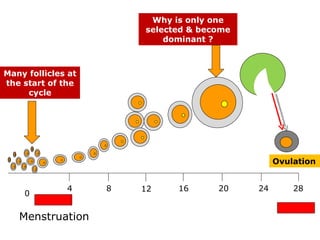
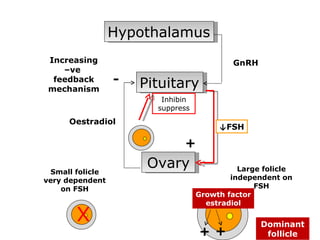
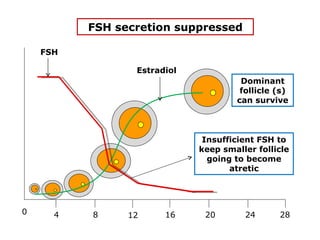
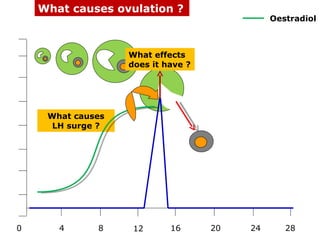
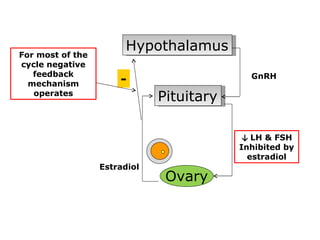
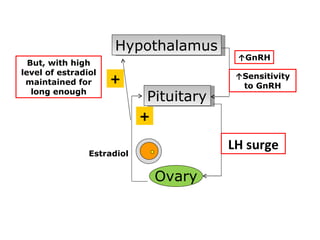
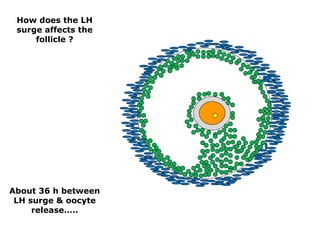
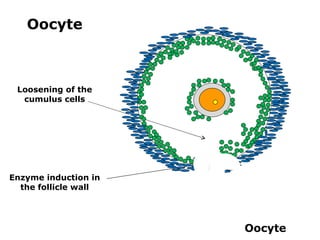
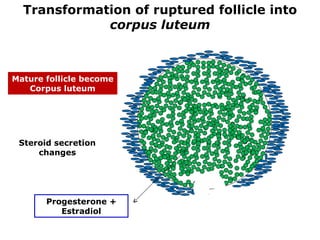
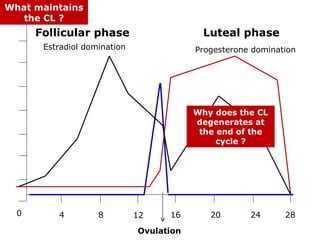
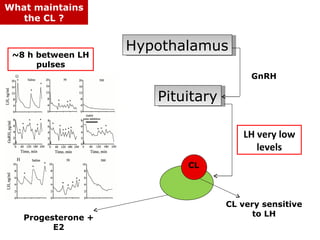
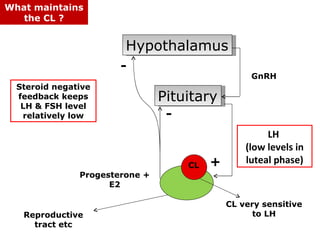
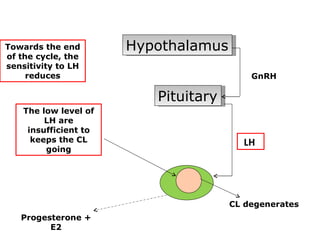
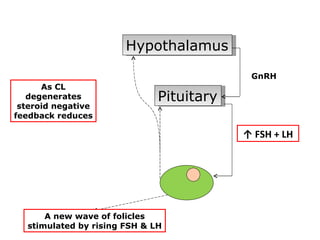
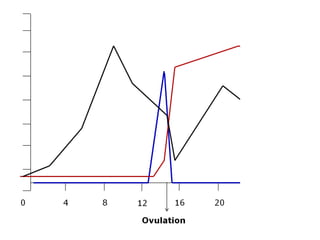
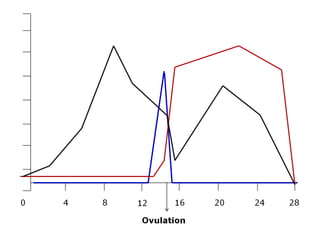
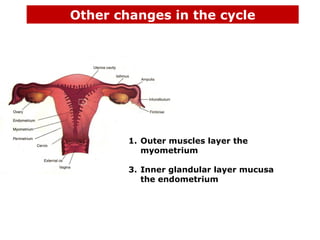
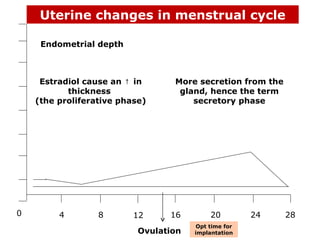
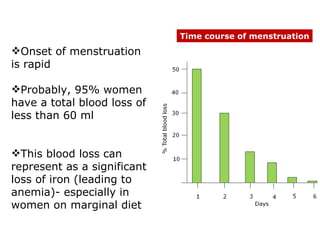
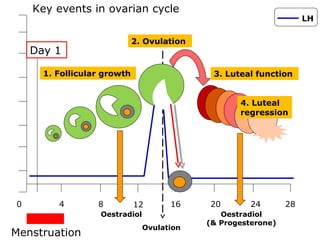
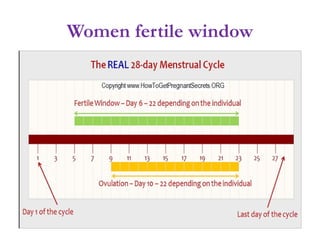
The menstrual cycle involves changes in the ovaries and uterus across approximately 28 days. In the ovaries, a follicle grows and matures, culminating in ovulation around day 14 when the mature egg is released. After ovulation, the ruptured follicle transforms into the corpus luteum which secretes progesterone and estrogen to prepare the uterus in case of fertilization. If fertilization does not occur, progesterone and estrogen levels drop and the endometrial lining is shed through menstruation, starting a new cycle.