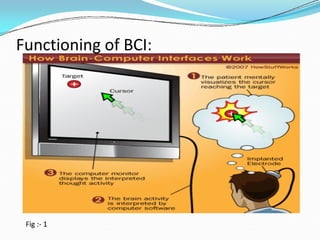
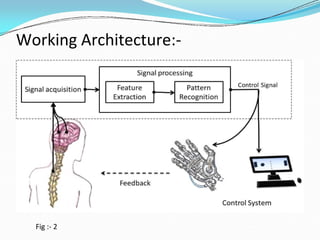
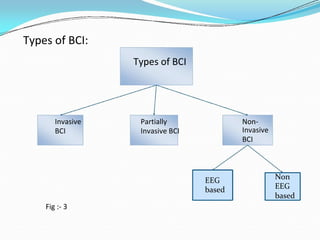
The document provides an overview of brain-computer interfaces (BCIs), including their history, functioning, types, applications, advantages, and disadvantages. BCIs enable communication between the brain and external devices, assisting individuals with disabilities to control technology through thought. While promising, challenges such as ethical issues and early-stage research hinder their widespread adoption.