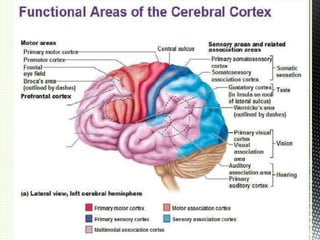
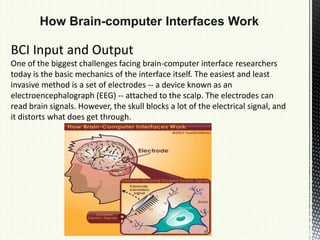
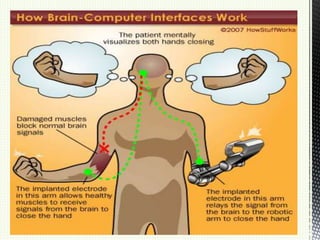
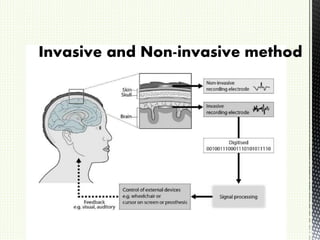
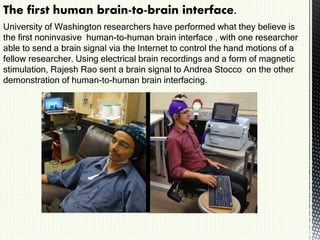
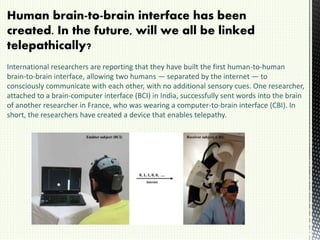
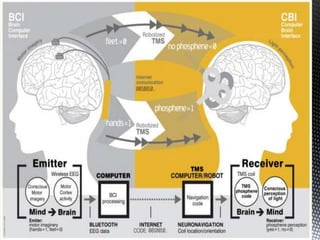
A brain-computer interface (BCI) is a direct communication pathway between the brain and external devices, aimed at assisting cognitive or sensory-motor functions. BCIs can be invasive or non-invasive, and while advancements have been made in mapping brain activity through various methods, challenges such as signal distortion and ethical concerns remain. Future applications of BCI technology could enable paralyzed individuals to control prosthetic limbs or facilitate direct brain communication between people.