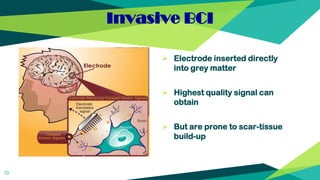
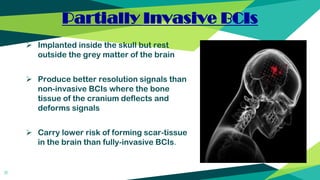
The document discusses brain-computer interfaces (BCIs), which allow direct communication between the human brain and external devices to restore sensory functions and control prosthetic devices. Major historical milestones and the different types of BCIs, including invasive and non-invasive methods, are highlighted, along with their advantages and limitations. The document concludes that while promising, BCI technology faces challenges such as high costs, ethical concerns, and the need for further advancement.