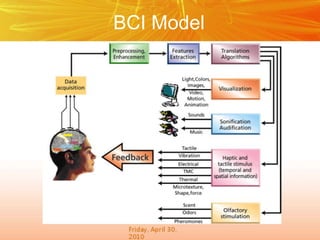
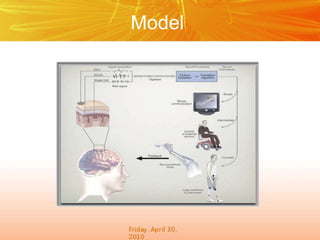
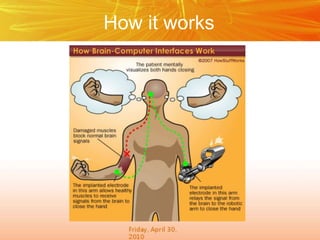
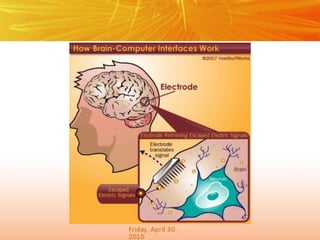
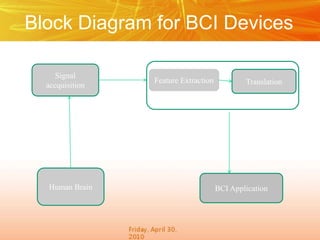
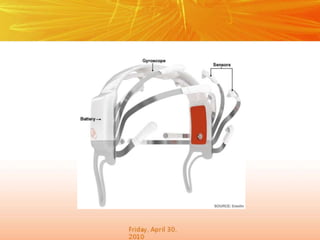
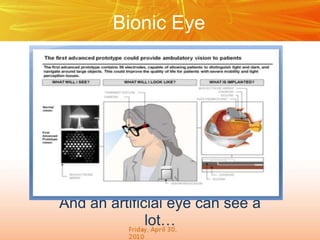
The document discusses brain-computer interfaces (BCIs), which create a direct communication link between the human brain and computers, focusing on their development and applications. It outlines the evolution of BCIs from early experiments with animals to current applications such as assisting disabled individuals, controlling devices, and potential therapeutic benefits. The conclusion emphasizes the promising future of BCIs in rehabilitation and enhancing human capabilities.