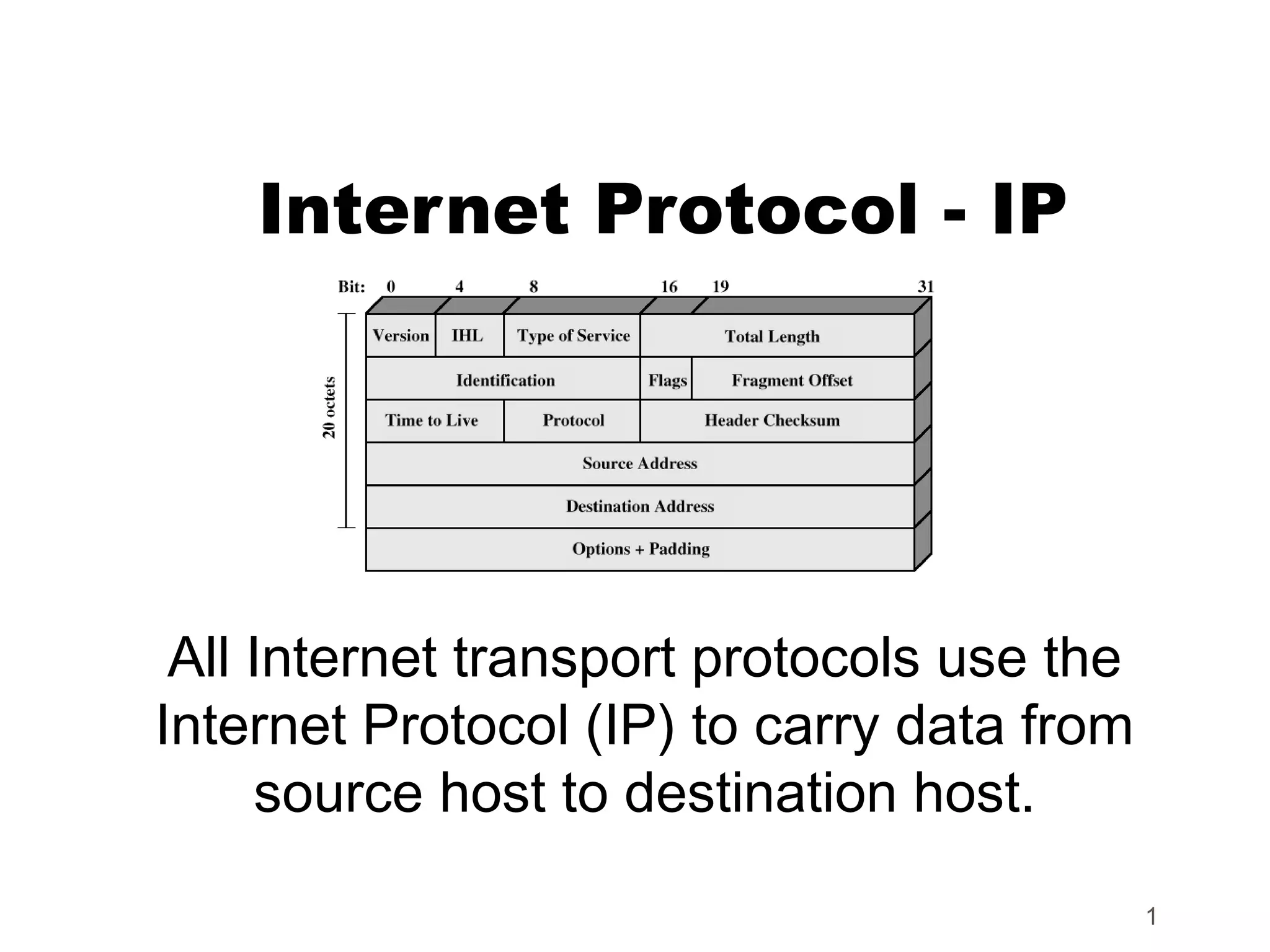
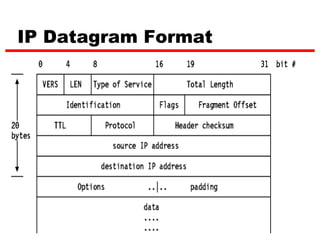
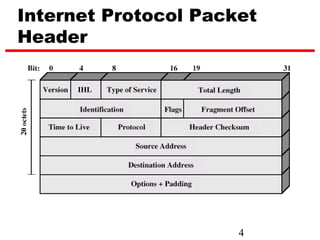
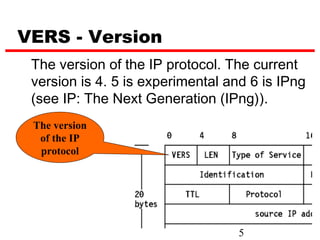
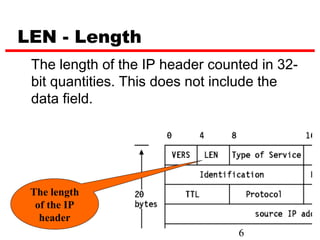
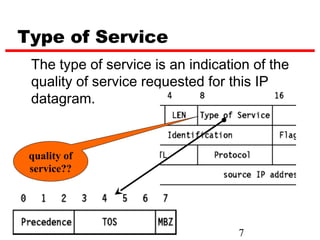
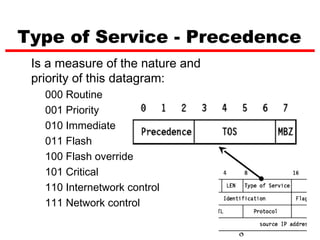
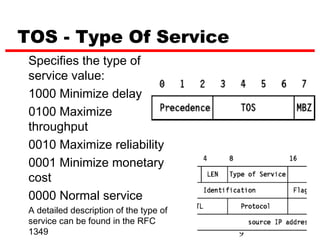
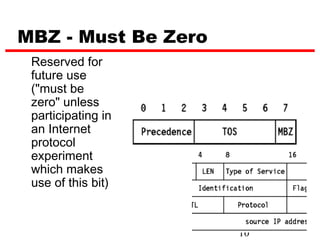
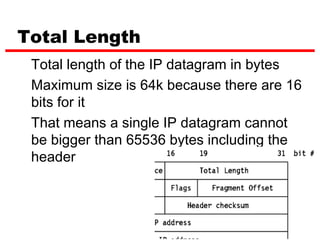
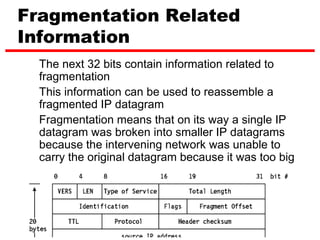
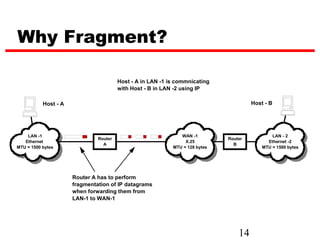
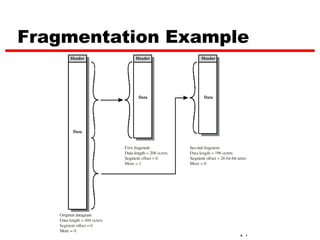
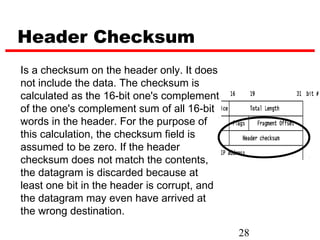
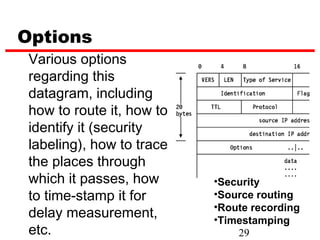
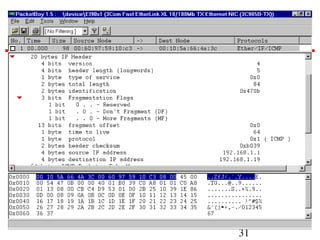
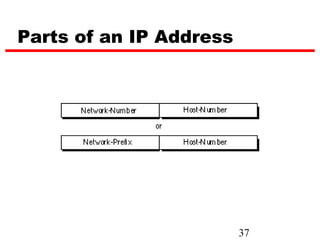
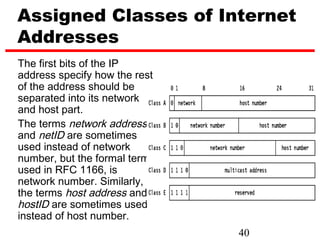
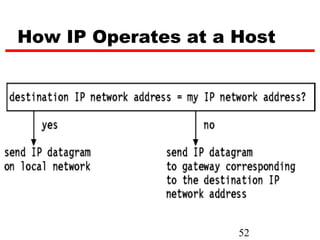
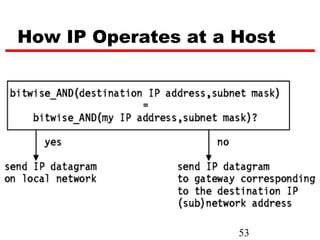
Internet Protocol (IP) is used to carry data from source to destination hosts across the Internet by providing addressing, fragmentation and reassembly, packet timeouts, and prioritization of traffic. IP uses 32-bit addresses to identify sending and receiving hosts and allows packets to be split into smaller fragments if needed to travel across networks. Routers use the IP Time to Live field to discard packets that have been traveling too long to prevent flooding of networks.