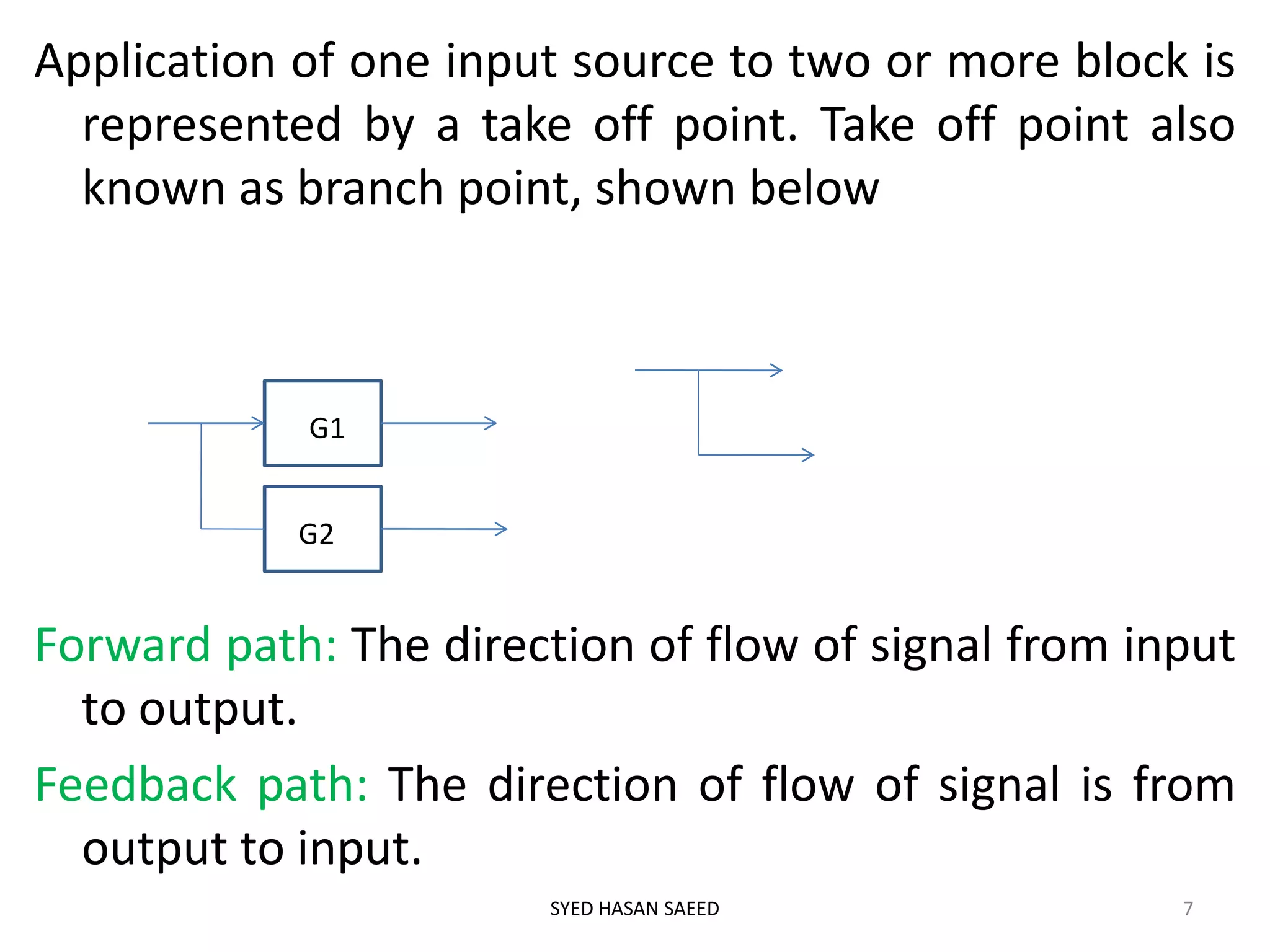
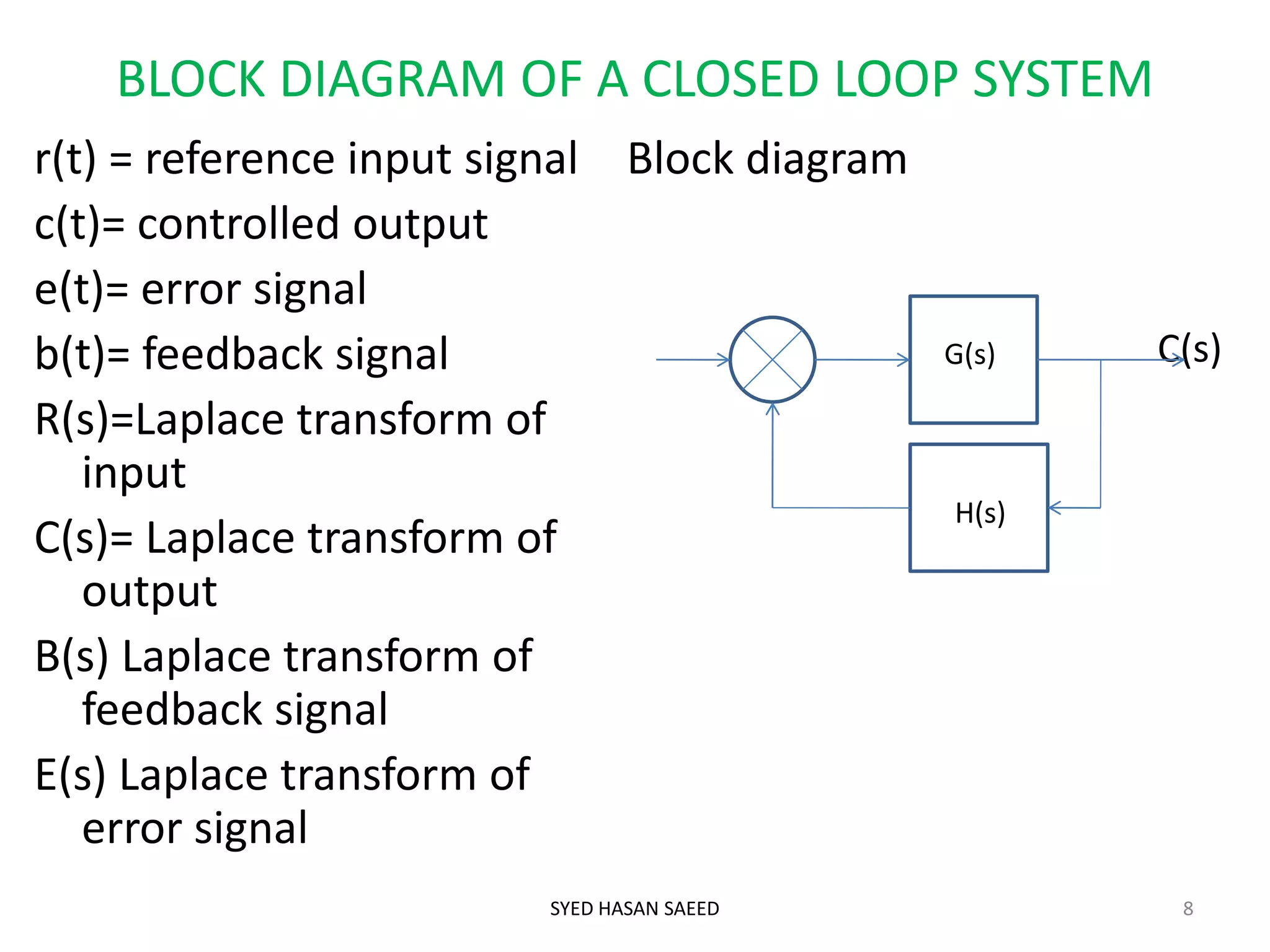
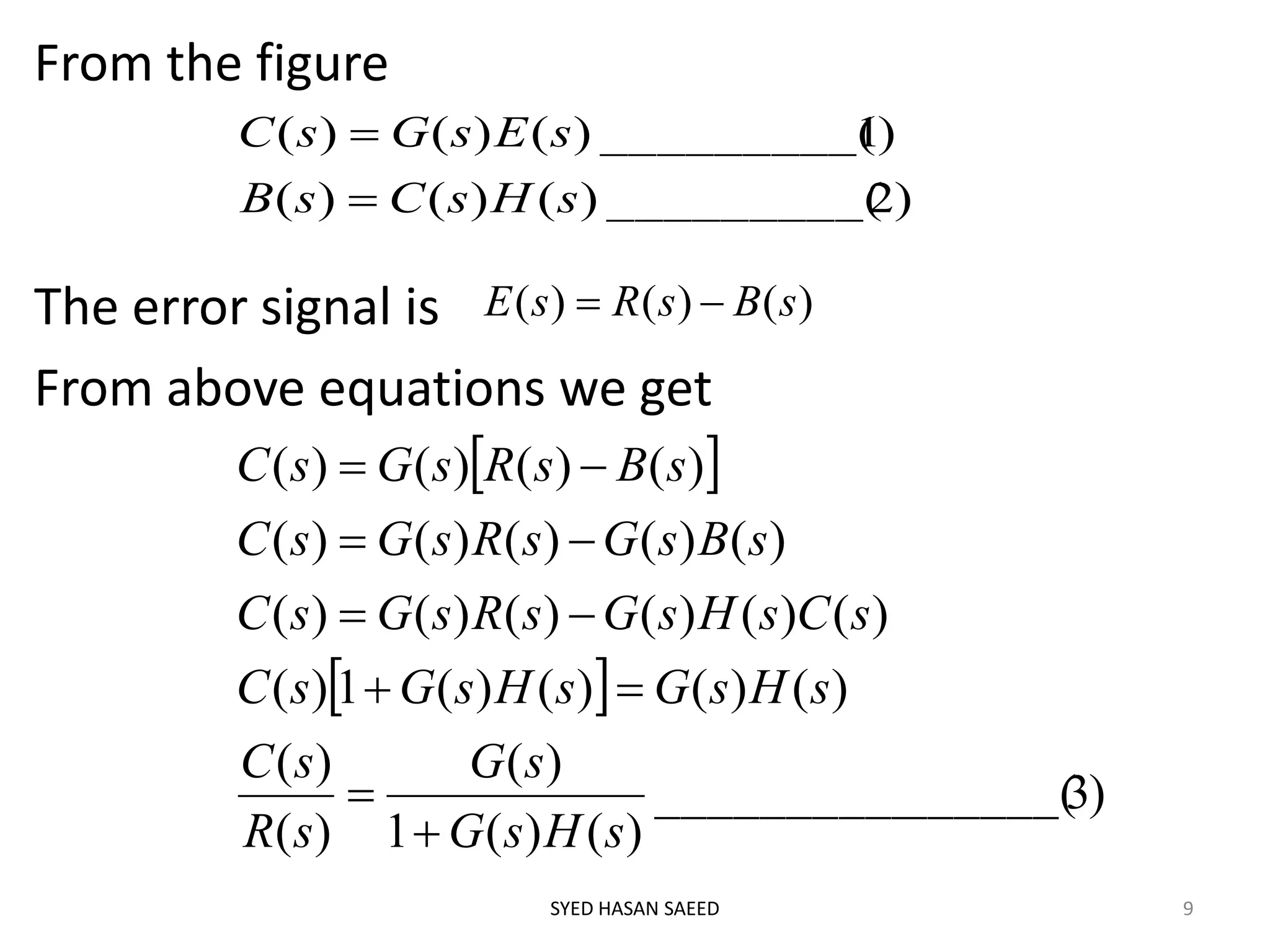
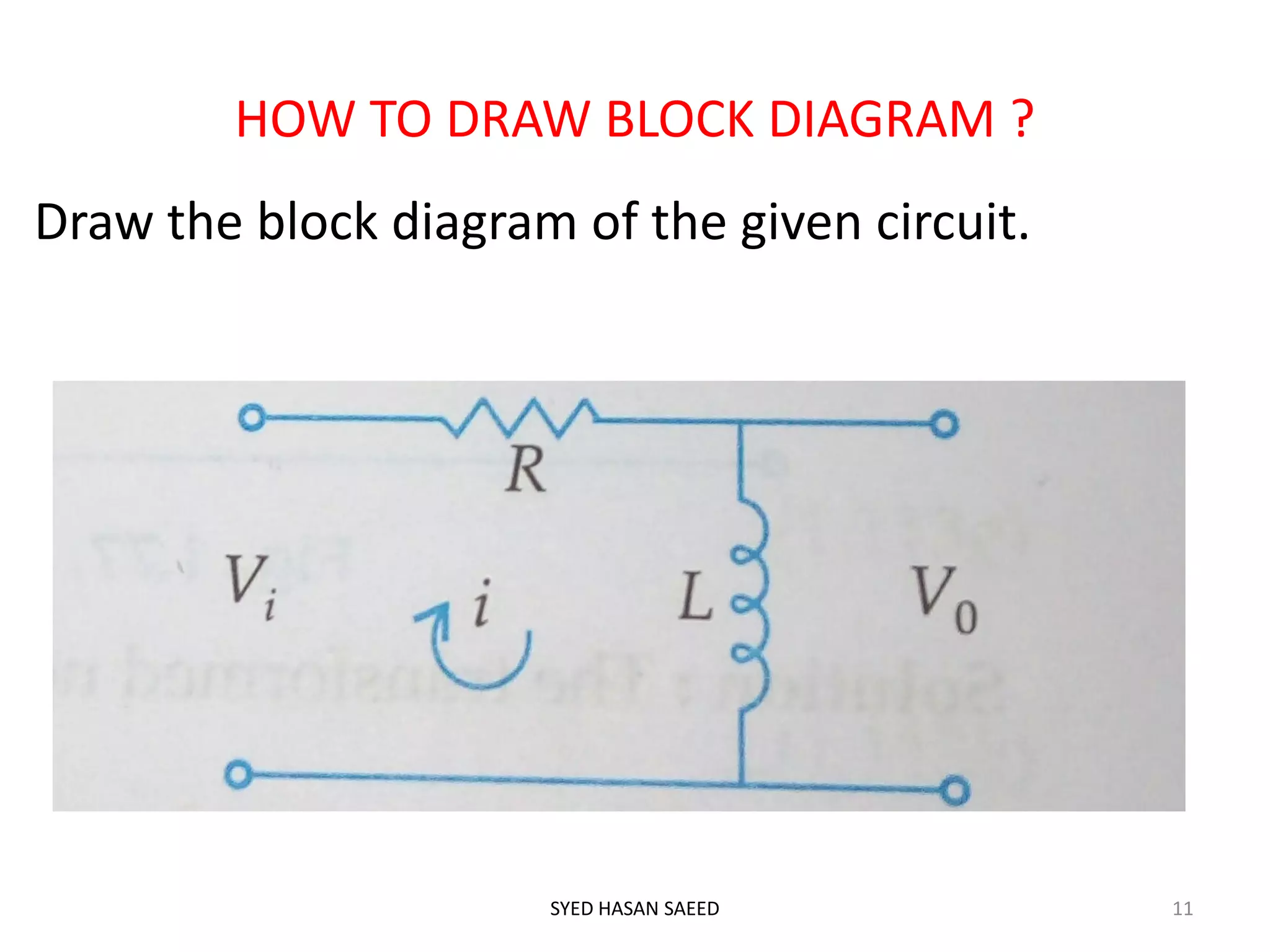
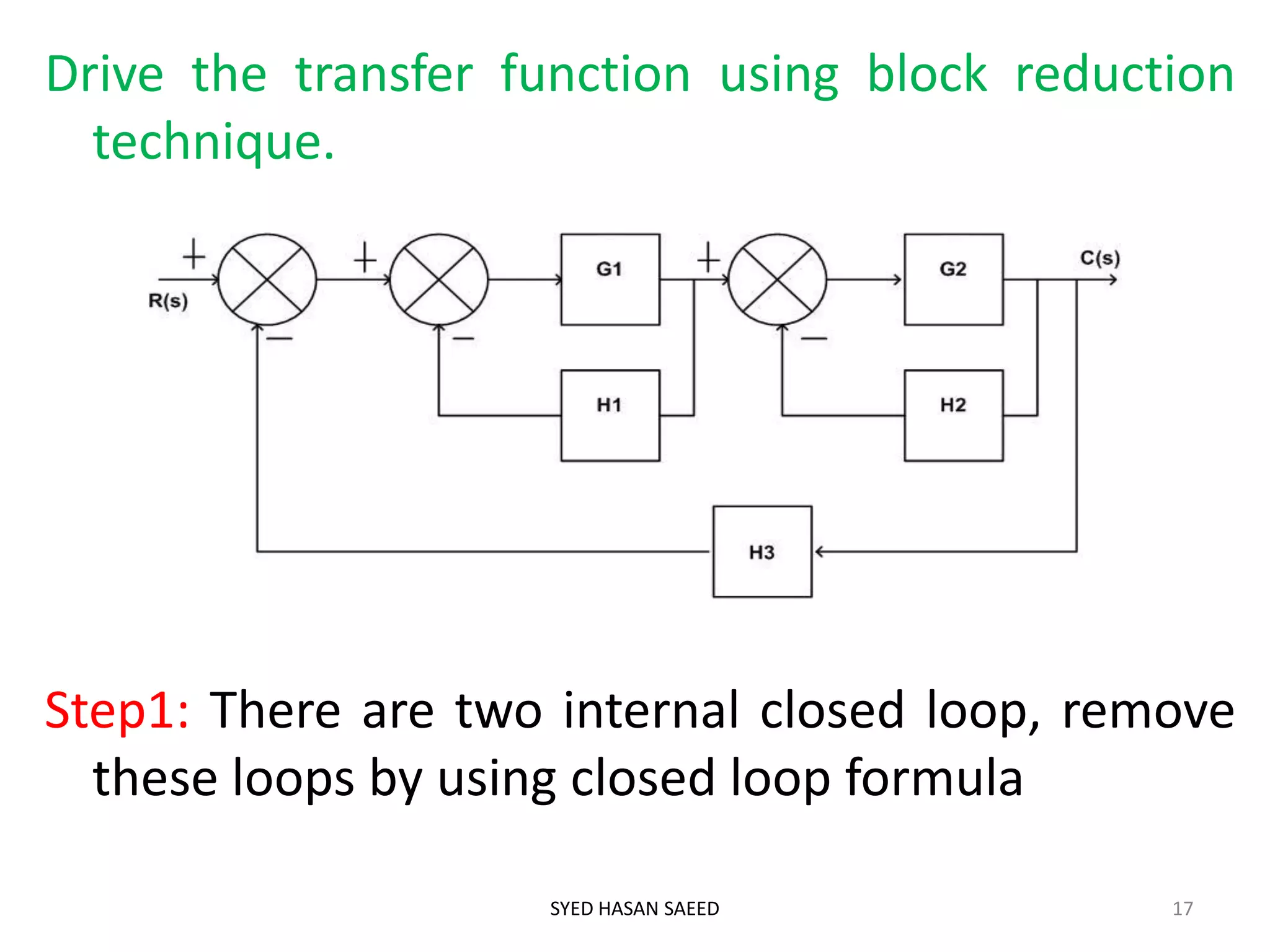
The document discusses block diagram representation of systems. It describes that a block diagram shows the relationship between inputs and outputs of a system using blocks. Each block represents a component and is characterized by a transfer function. The document outlines advantages like easy analysis and design, and disadvantages such as not showing energy sources. It also describes drawing block diagrams, closed loop systems, and the block reduction technique to simplify diagrams.