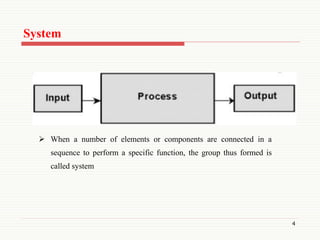
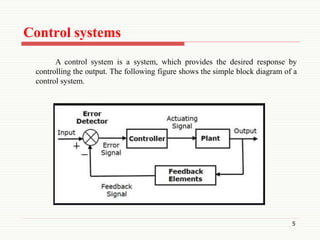
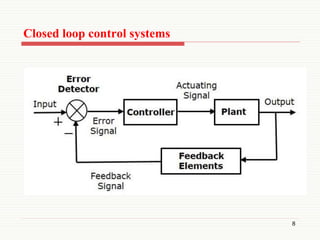
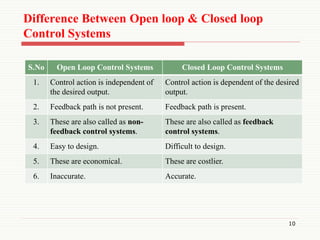
The document presents an overview of control systems, detailing their purpose, types, and key differences between open loop and closed loop systems. Control systems are essential for ensuring the accurate and optimal performance of automatic systems across various applications. Important distinctions include feedback presence and dependency on desired output, highlighting the complexities of closed loop systems compared to open loop systems.