The superposition theorem states that for a linear circuit with multiple independent sources, the total response at any point in the circuit is equal to the sum of the individual responses produced by each independent source acting alone. To determine the individual contribution of each source, all other sources are replaced by their internal impedances. The theorem can be applied to circuits containing resistors, inductors, capacitors, transformers, and independent and dependent sources, as long as the elements have linear responses. The document provides an example using the superposition theorem to calculate the voltage drop and current across a resistor in a circuit with two independent voltage sources.

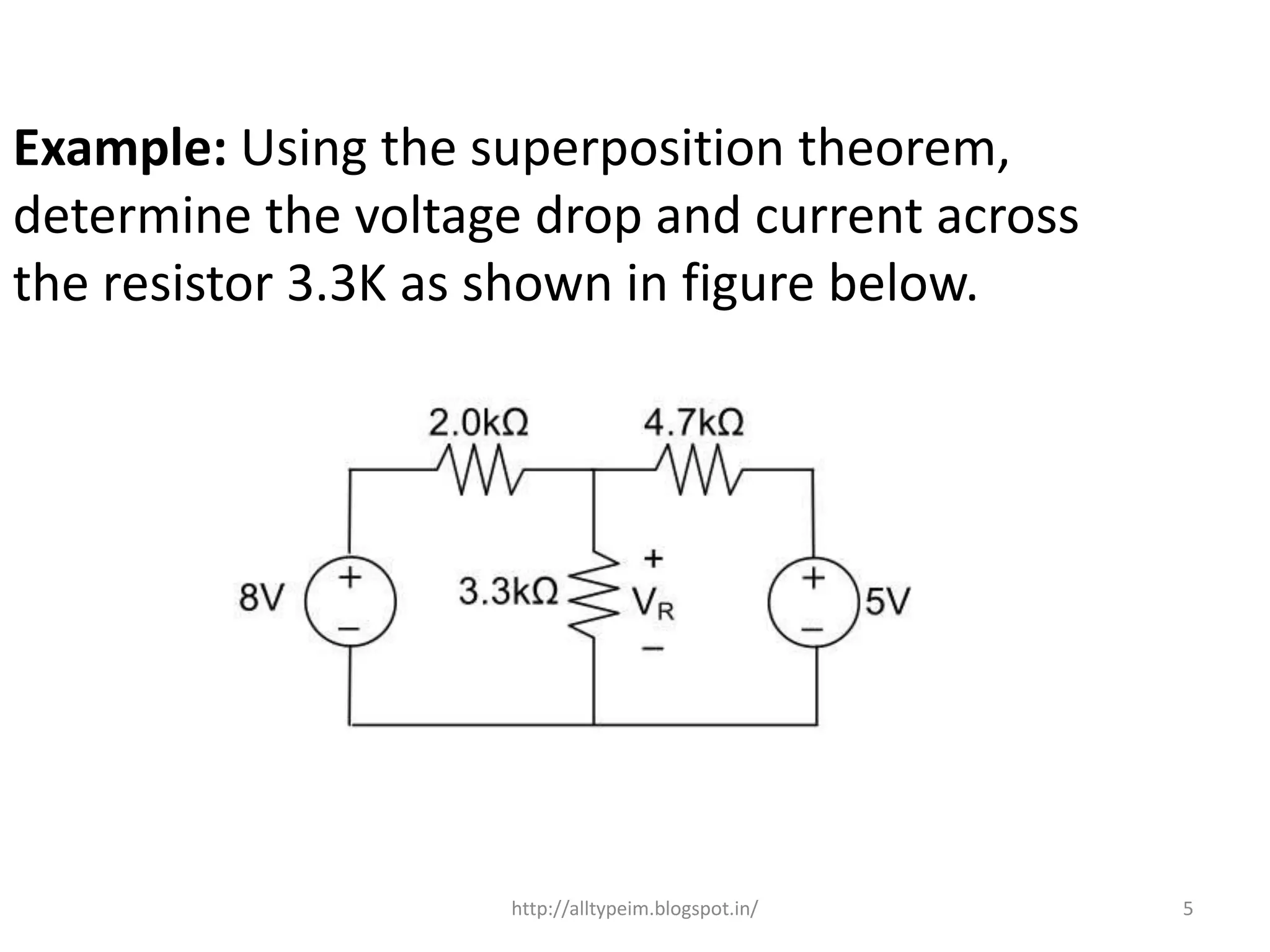
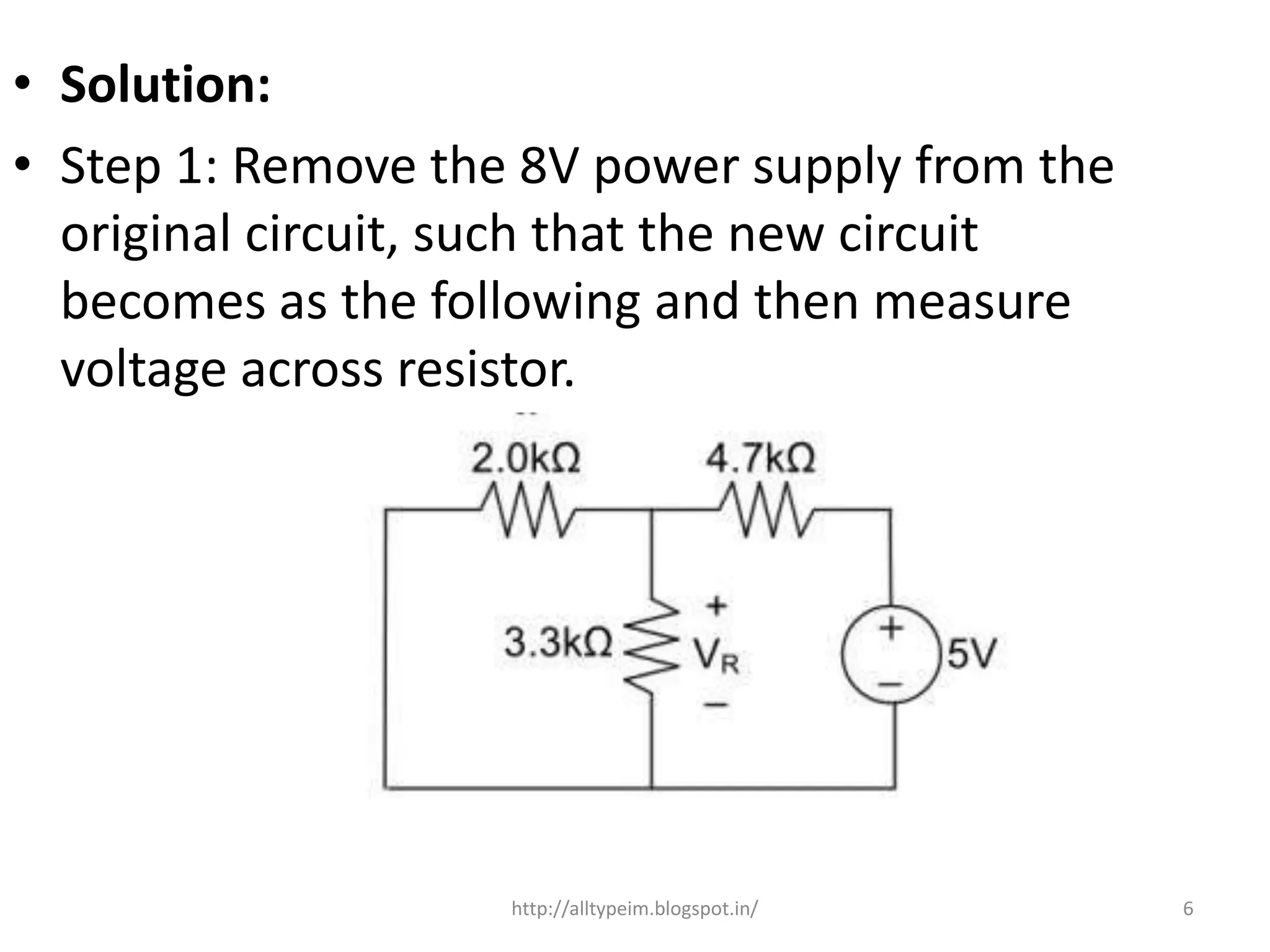
![• Here 3.3K and 2K are in parallel, therefore
resultant resistance will be 1.245K.
• Using voltage divider rule voltage across
1.245K will be
• V1= [1.245/(1.245+4.7)]*5 = 1.047V
7http://alltypeim.blogspot.in/](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/superpositiontheorem-151203051406-lva1-app6892/75/Superposition-theorem-7-2048.jpg)
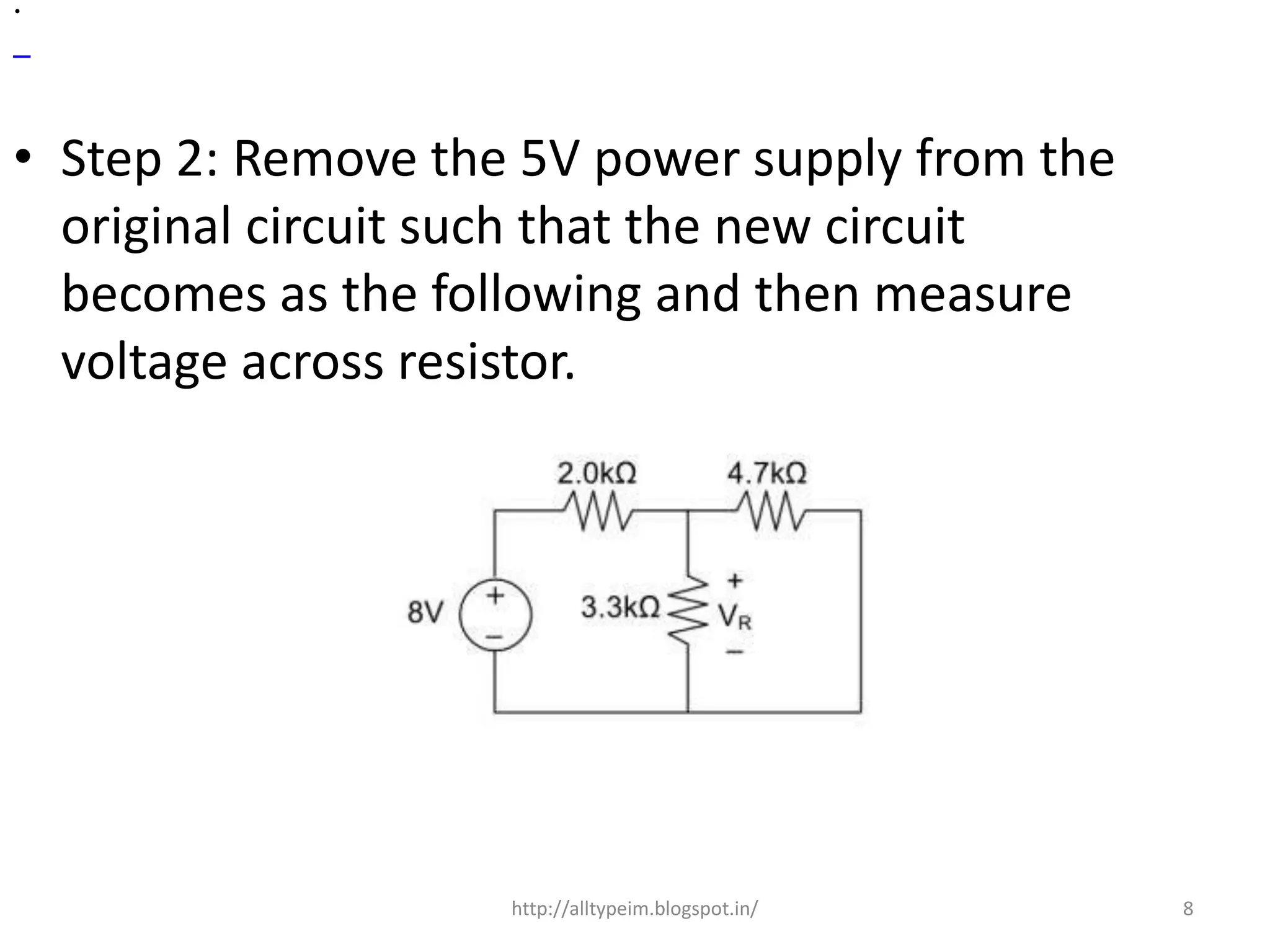
![• Here 3.3K and 4.7K are in parallel, therefore
resultant resistance will be 1.938K.
• Using voltage divider rule voltage across
1.938K will be
• V2= [1.938/(1.938+2)]*8 = 3.9377V
• Therefore voltage drop across 3.3K resistor is
V1+V2 = 1.047+3.9377=4.9847
9http://alltypeim.blogspot.in/](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/superpositiontheorem-151203051406-lva1-app6892/75/Superposition-theorem-9-2048.jpg)
