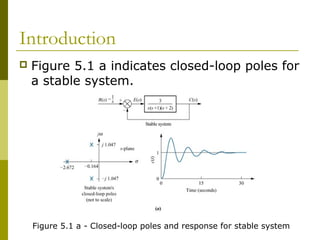
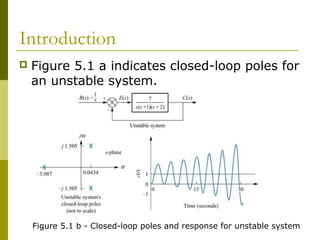
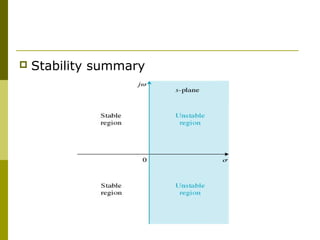
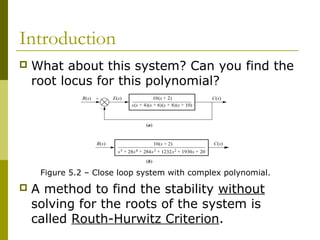
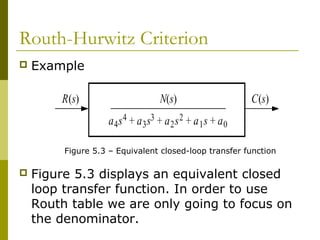
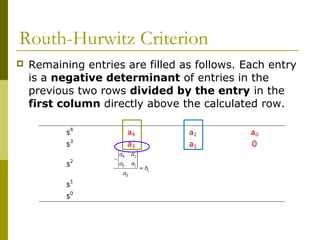
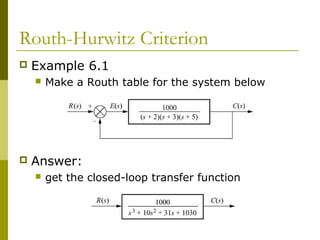
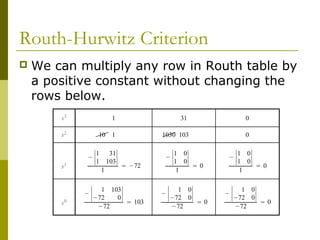
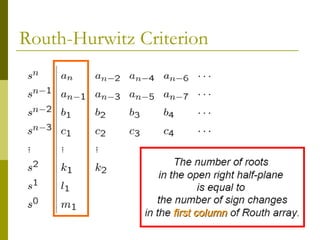
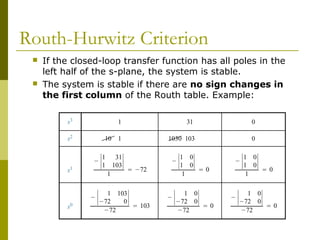
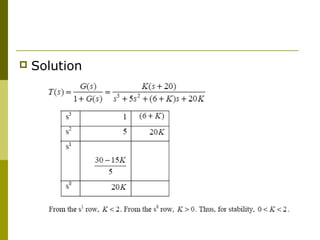
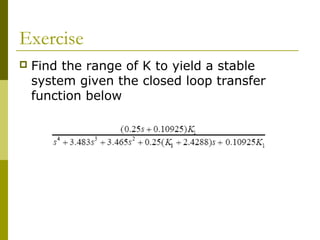
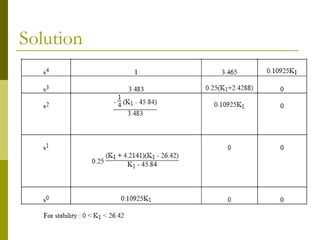
This document discusses stability analysis of control systems using transfer functions and the Routh-Hurwitz criterion. It begins by defining stability and describing different types of system responses. The key points are:
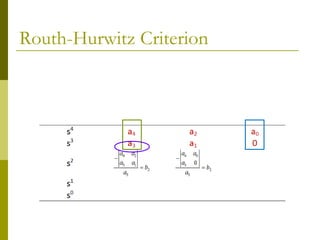
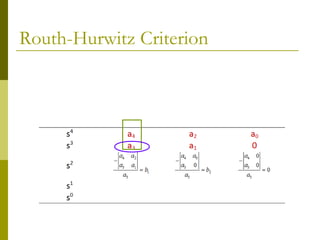
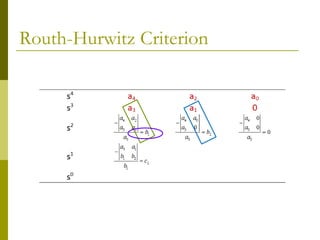
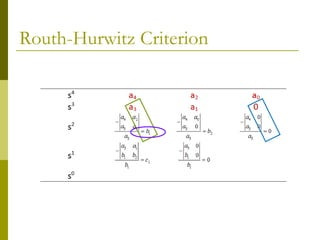
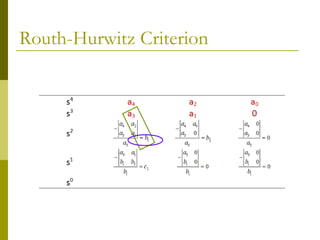
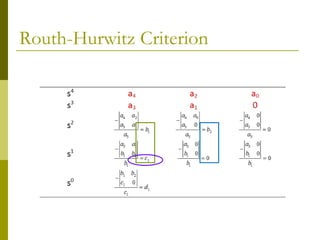
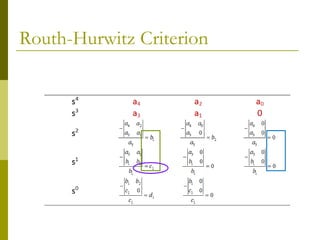
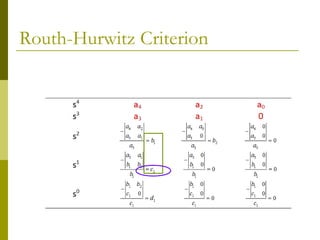
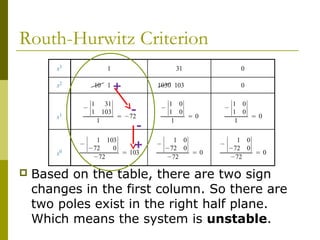
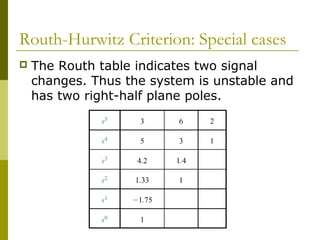
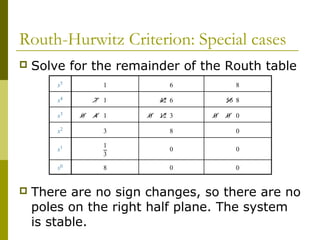
1) The Routh-Hurwitz criterion can determine stability by analyzing the signs in the first column of a constructed Routh table, with changes in sign indicating right half-plane poles and instability.
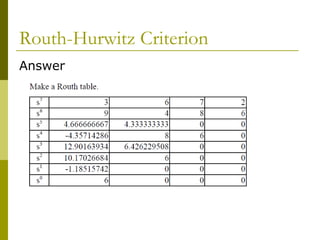
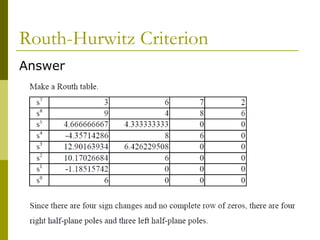
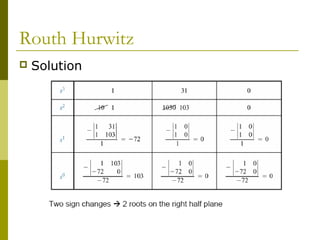
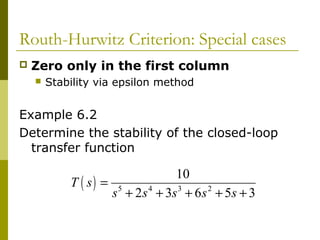
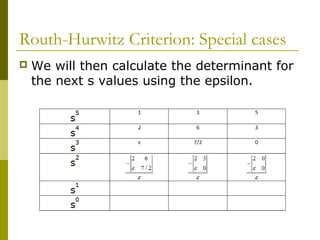
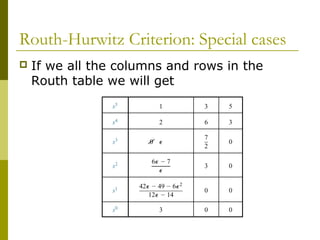
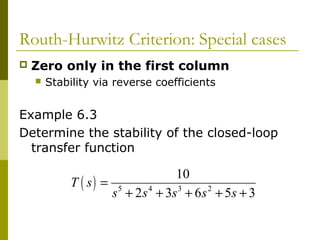
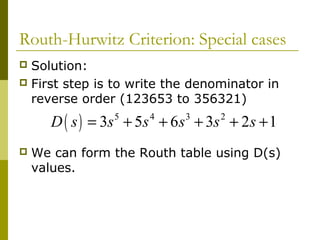
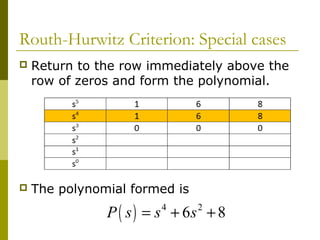
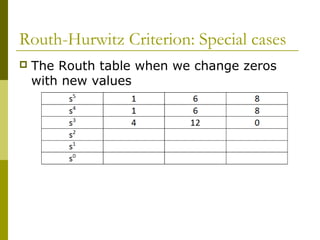
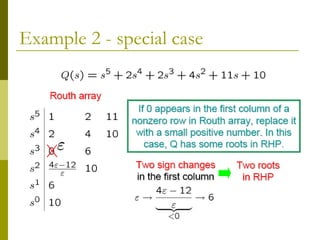
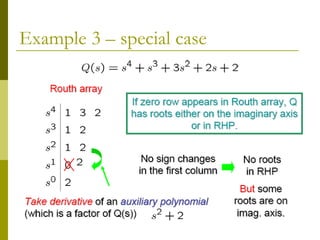
2) Special cases like a zero only in the first column or an entire row of zeros require alternative methods like the epsilon method or reversing coefficients.
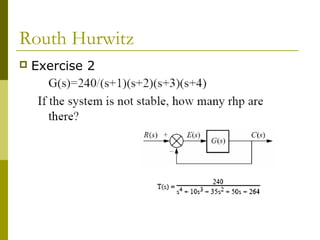
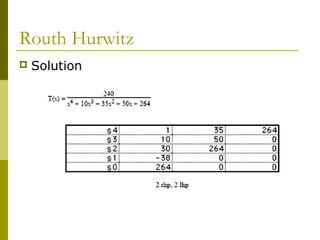
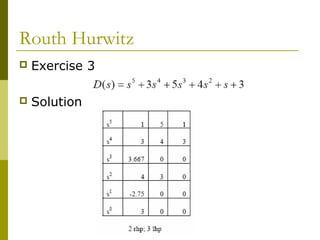
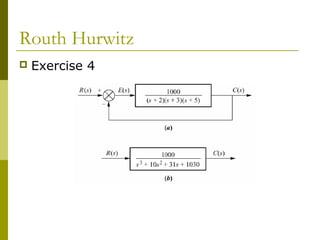
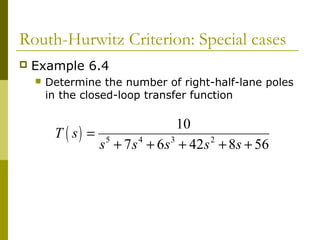
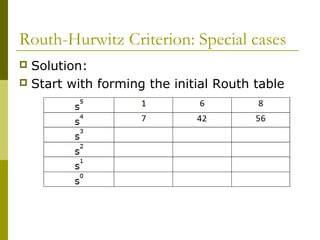
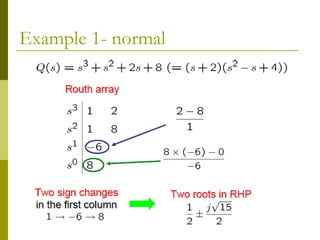
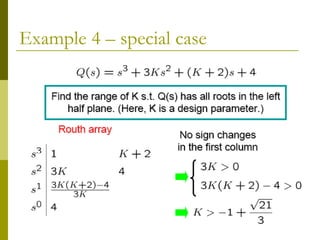
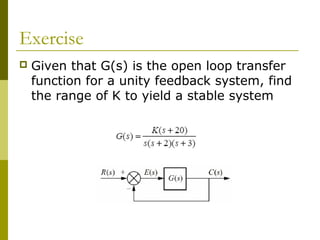
3) Examples demonstrate applying the Routh-Hurwitz criterion to determine stability for different polynomials, including handling special cases. Exercises also have readers practice stability analysis using