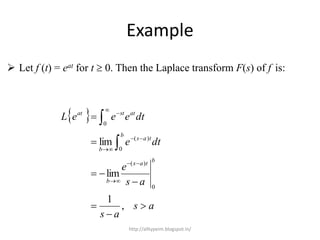
The document discusses the Laplace transform and its uses. The Laplace transform converts a differential equation into an algebraic equation, making it easier to solve. It allows one to directly find the particular solution of a differential equation without first finding the general solution. The Laplace transform also allows solving nonhomogeneous equations directly without first solving the corresponding homogeneous equation. It can also be used to find solutions to problems with discontinuous driving forces. The Laplace transform of a function f(t) is defined as the integral from 0 to infinity of f(t)e^-st dt. It transforms the function from depending on t to depending on s.




![Piecewise Continuous Function
A function f is piecewise continuous on an interval [a, b] if
this interval can be partitioned by a finite number of points
a = t0 < t1 < … < tn = b such that
(1) f is continuous on each (tk, tk+1)
In other words, f is piecewise continuous on [a, b] if it is
continuous there except for a finite number of jump
discontinuities.
nktf
nktf
k
k
tt
tt
,,1,)(lim)3(
1,,0,)(lim)2(
1
http://alltypeim.blogspot.in/](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/laplacetransforms-151203051430-lva1-app6892/85/Laplace-transforms-6-320.jpg)
![Example
Consider the following piecewise-defined function f.
From this definition of f, and from the graph of f below, we
see that f is not piecewise continuous on [0, 3].
32,4
21,2
10,1
)(
1
2
t
tt
tt
tf
http://alltypeim.blogspot.in/](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/laplacetransforms-151203051430-lva1-app6892/85/Laplace-transforms-7-320.jpg)



