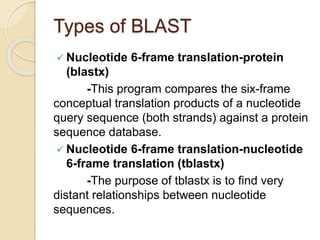
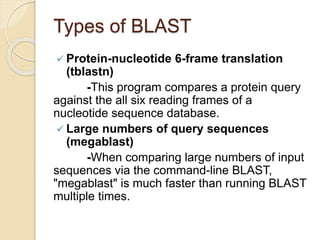
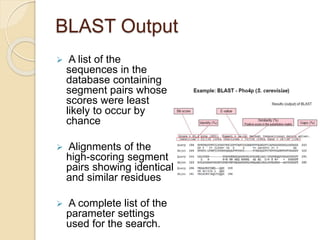
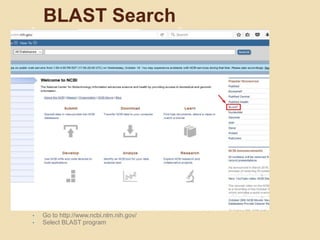
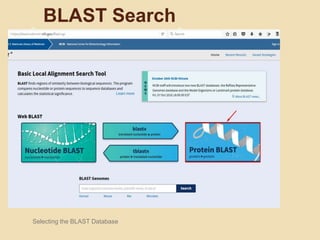
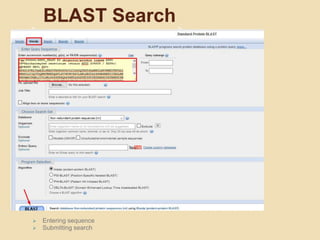
The document provides an introduction to BLAST (Basic Local Alignment Search Tool), which is an algorithm used to compare gene and protein sequences to those in public databases. It discusses the types of BLAST programs, the BLAST algorithm, input/output, how to perform a BLAST search, and the functions and objectives of BLAST. Specifically, BLAST is faster than previous sequence comparison methods, it outputs alignments and statistical values to evaluate matches, and its main objectives are to identify related sequences and locate domains through local alignments.