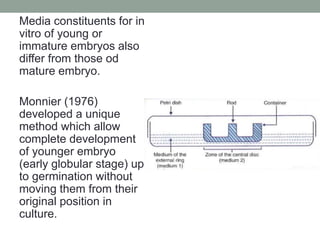
1. Zygotic embryo culture involves the aseptic isolation and growth of sexually produced embryos in vitro with the goal of obtaining viable plants.
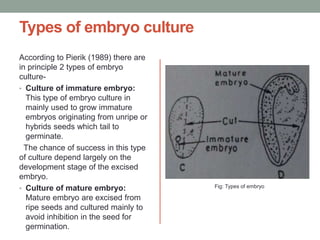
2. There are two main types of embryo culture: culture of immature embryos from unripe or hybrid seeds that fail to germinate, and culture of mature embryos excised from ripe seeds to avoid seed inhibition.
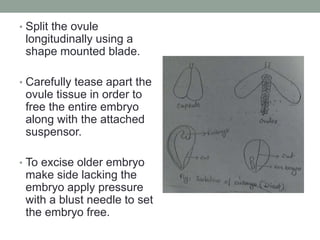
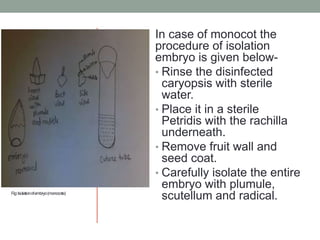
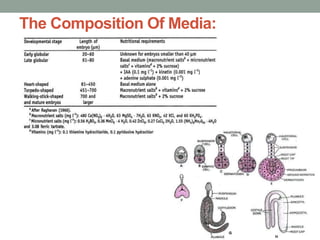
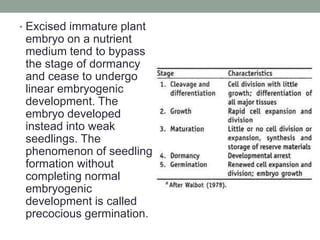
3. Successful zygotic embryo culture depends on several factors, including the composition of the culture medium, excision technique, plant material used, and growth conditions like temperature, light and pH levels. The goal is to support the embryo's development from heterotrophic to autotrophic phases.