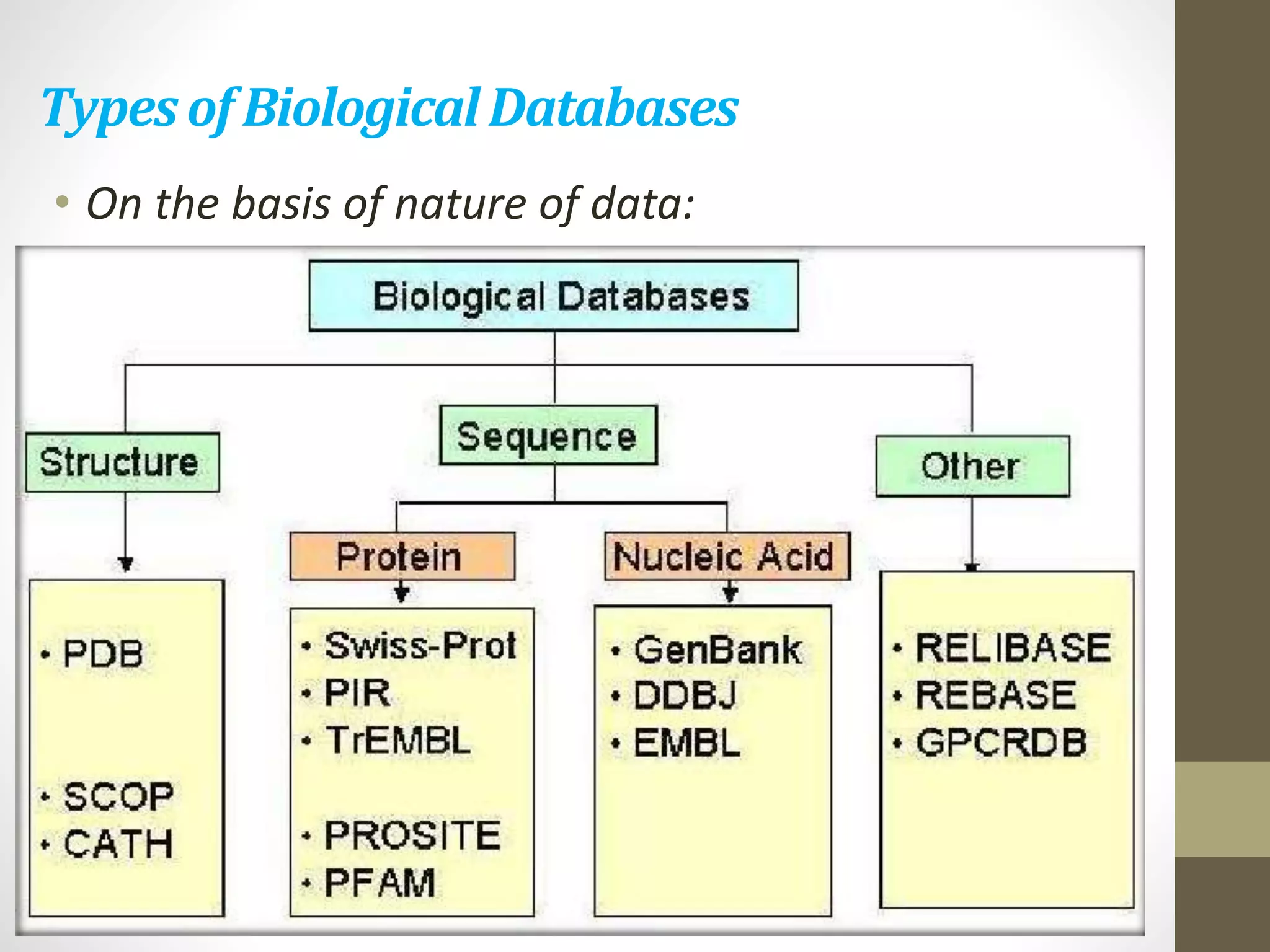
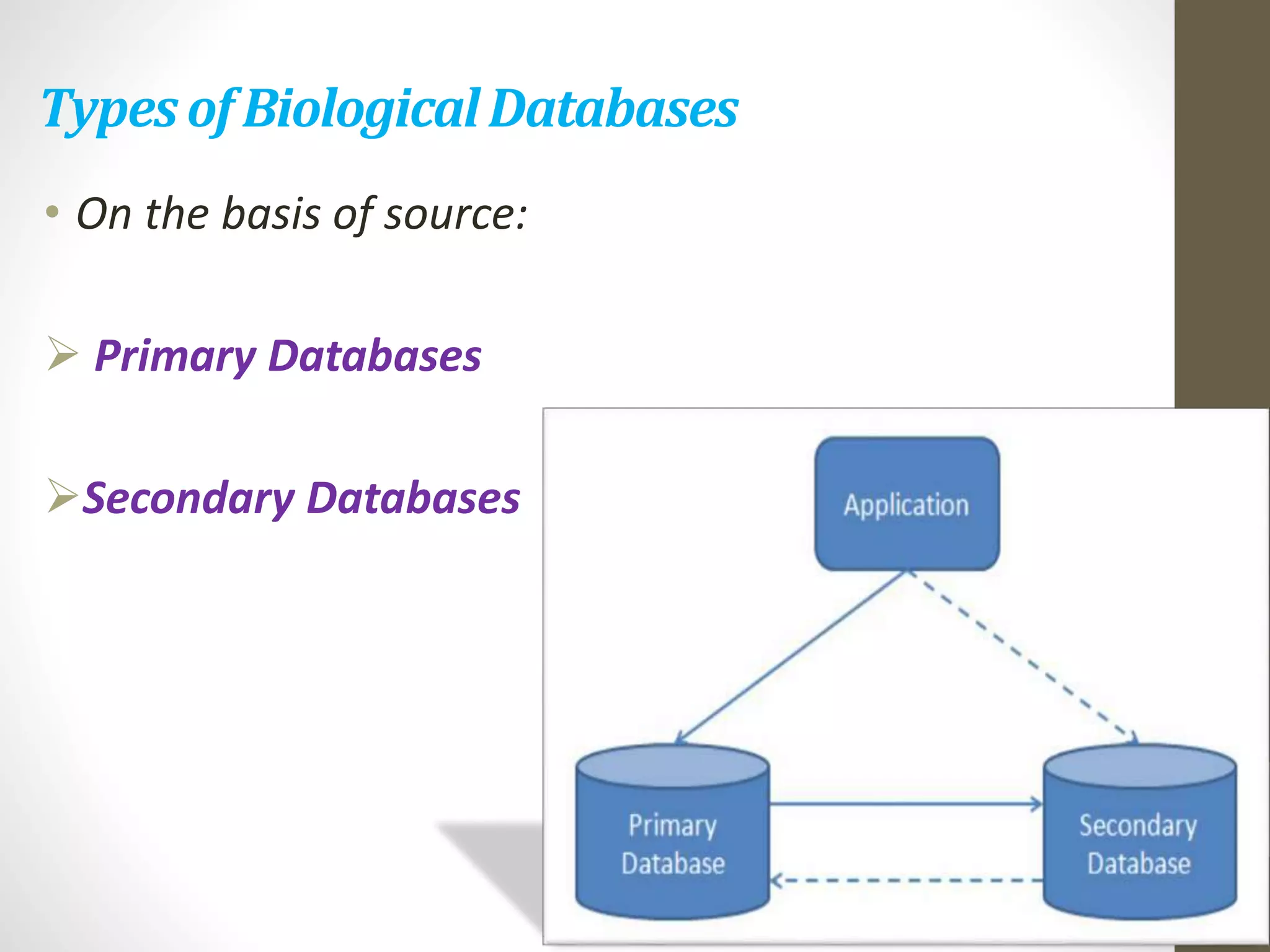
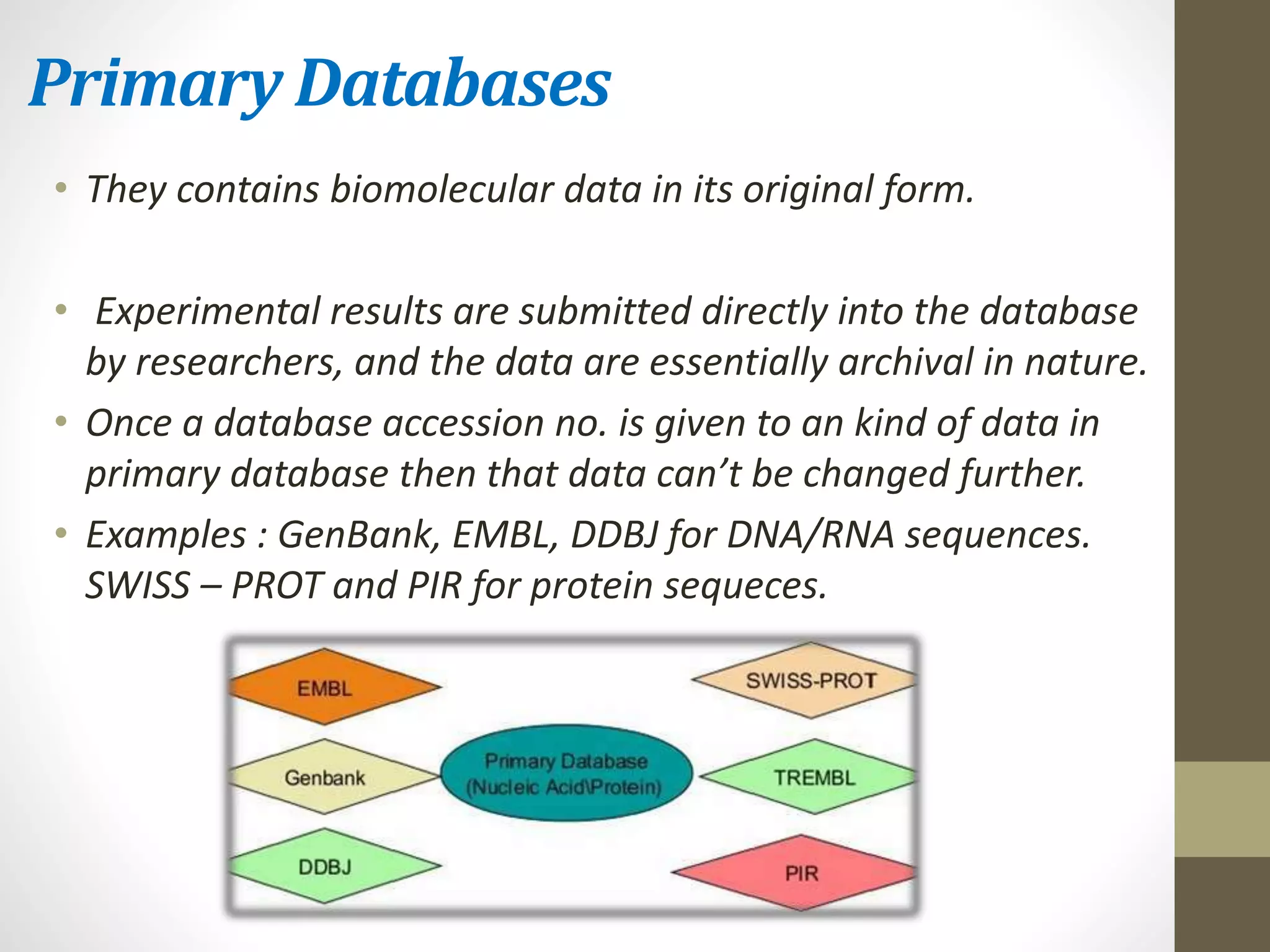
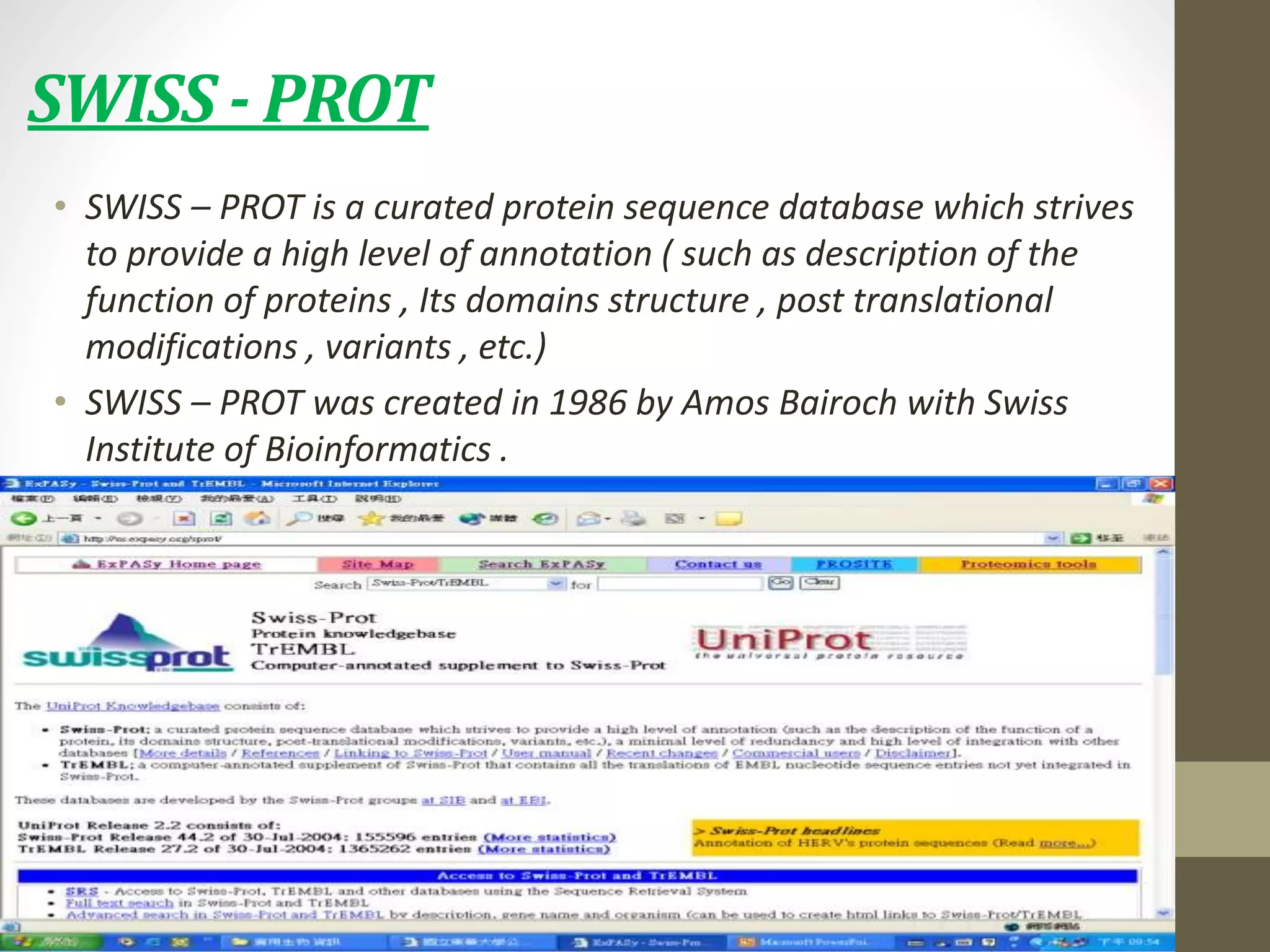
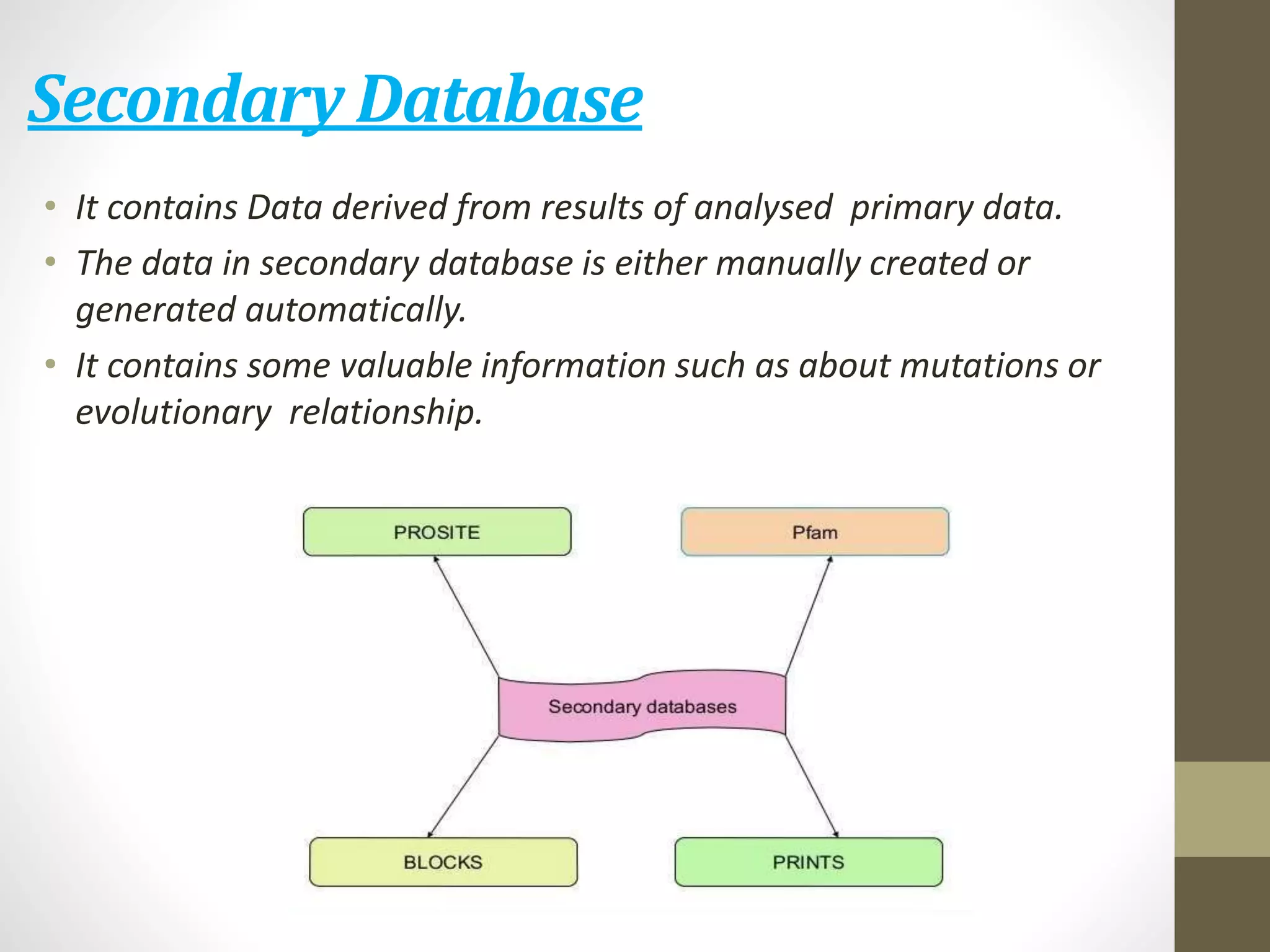
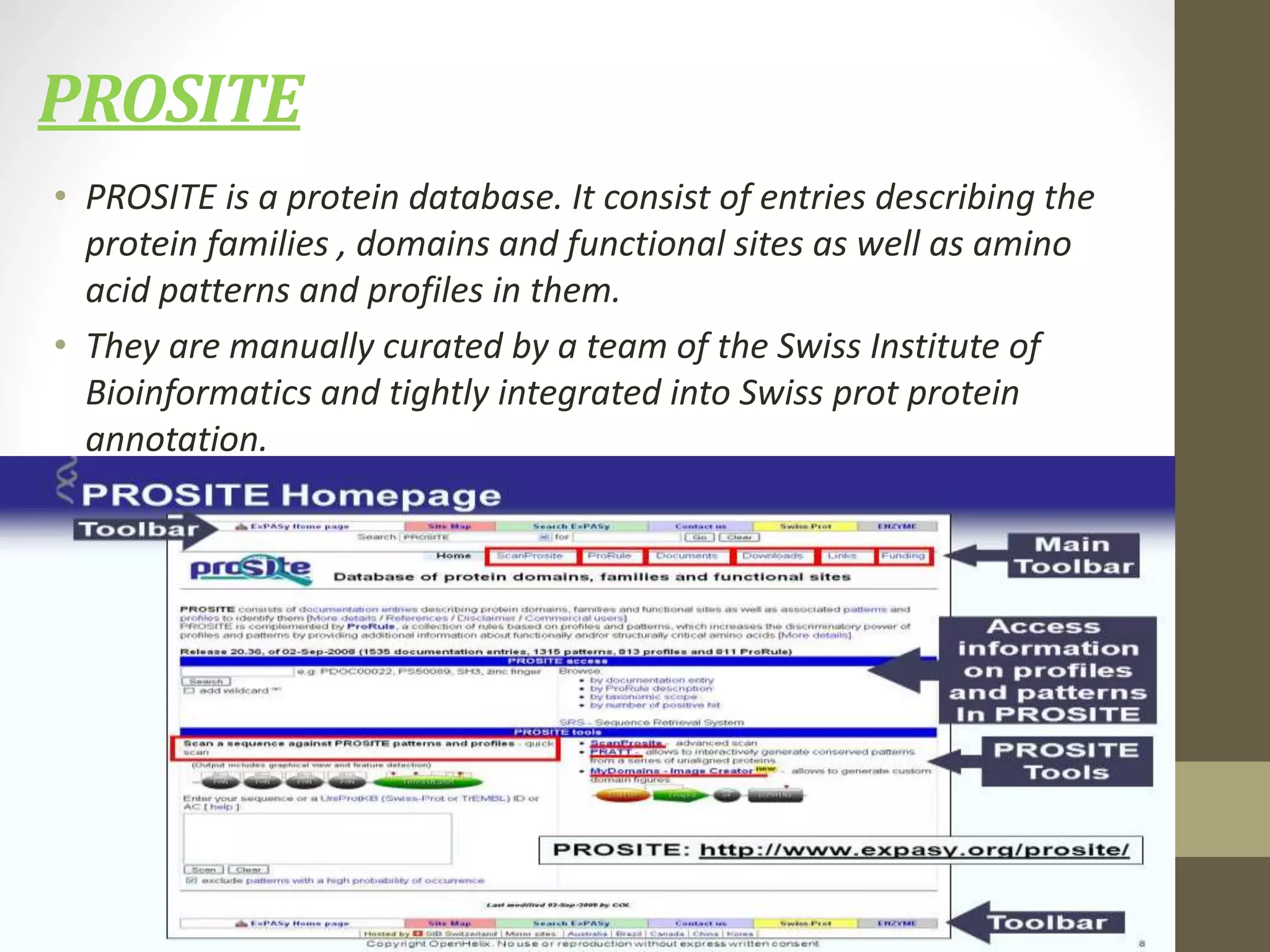
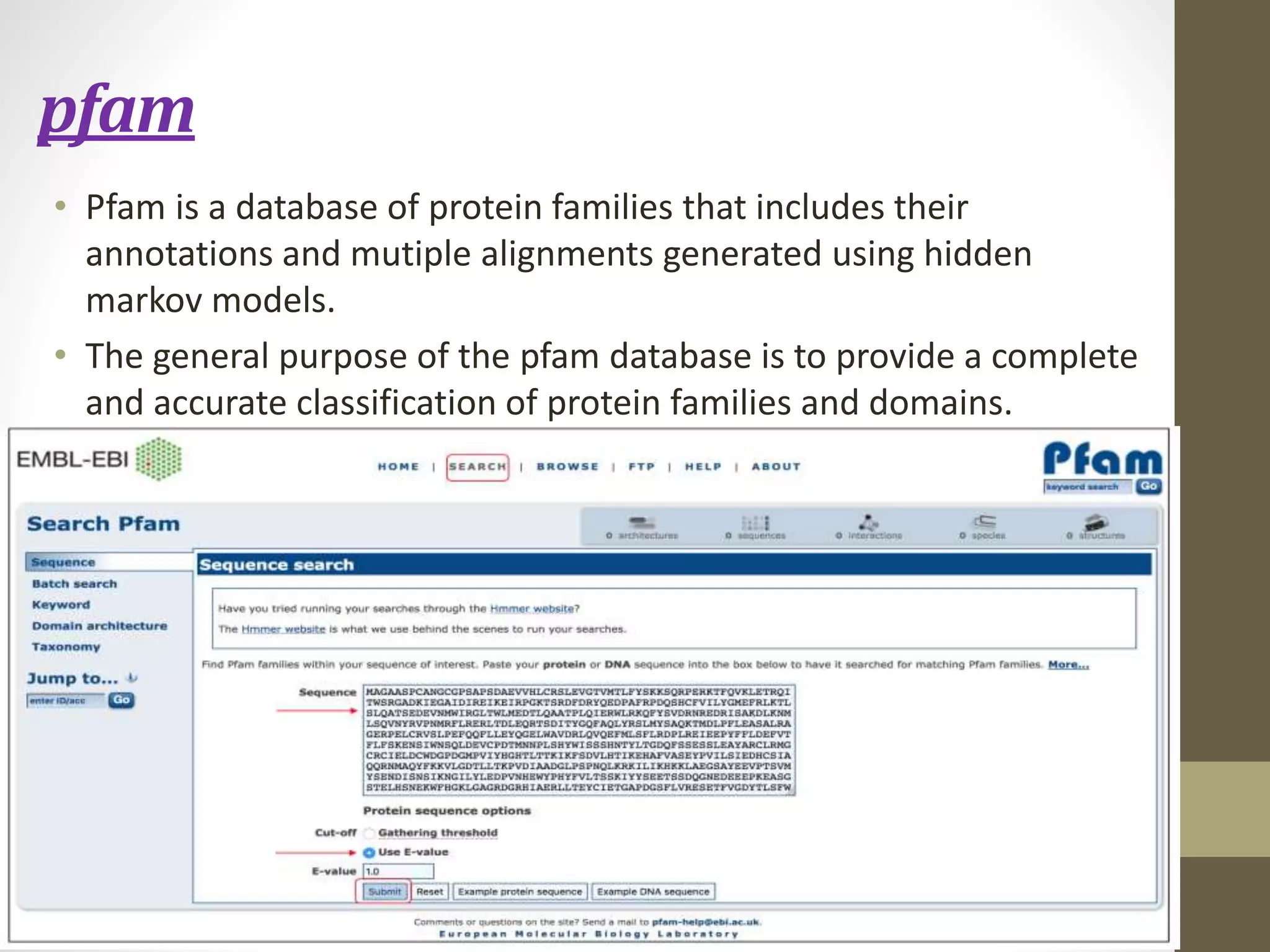
Biological databases store and organize biological data and information. There are two main types - primary databases that contain original experimental data that cannot be changed, and secondary databases that contain derived data analyzed from primary sources. Examples of primary databases include GenBank for DNA sequences and SWISS-PROT for protein sequences. Secondary databases include PROSITE for protein families and domains, and Pfam for protein family alignments. Biological databases allow sharing of genomic and protein information worldwide and provide a foundation for research.