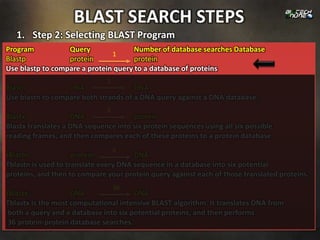
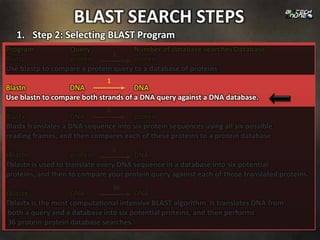
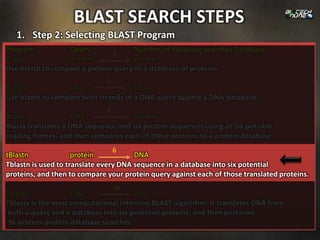
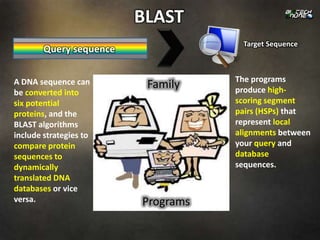
BLAST (Basic Local Alignment Search Tool) is a program for comparing gene or protein sequences to sequence databases and calculating the statistical significance of matches. It can be used to identify orthologs and paralogs of a query sequence, determine what proteins or genes exist in a particular organism, or discover new genes. A BLAST search involves specifying a query sequence, selecting a BLAST program like blastp or blastn, choosing a database to search, and setting optional search parameters. The program returns high-scoring segment pairs that represent local alignments between the query and database sequences.







![BLAST SEARCH STEPS
1. Step 1: Specifying Sequence of Interest:
First Cutting and pasting DNA or protein sequence (e.g., in
the FASTA format).
Second using an accession number (e.g., a RefSeq or
GenBank Identification [GI] number)
BLAST searches, your query can be in uppercase or
lowercase, with or without intervening spaces or numbers.
If the query is DNA, BLAST algorithms will search both strands. It
is often convenient to input the accession number to a BLAST
search.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/blast-120911083837-phpapp02/85/BLAST-Basic-Alignment-Local-Search-Tool-9-320.jpg)