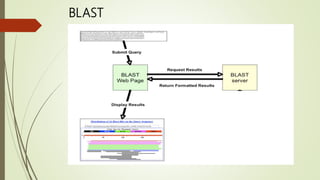
BLAST is a sequence similarity search program that compares biological sequences like protein or DNA sequences to sequence databases. It was developed by researchers at the National Institutes of Health and published in 1990. BLAST uses substitution matrices to find short matches between sequences and detect both local and global alignments. There are different BLAST programs that compare nucleotide or protein queries against nucleotide or protein databases. BLAST is useful for identifying species, establishing phylogeny, DNA mapping, and locating domains in protein sequences.