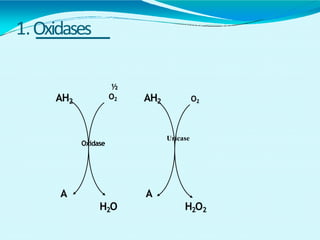
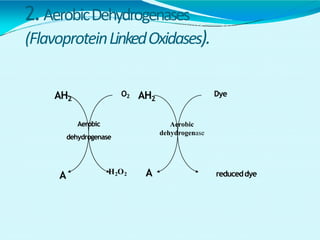
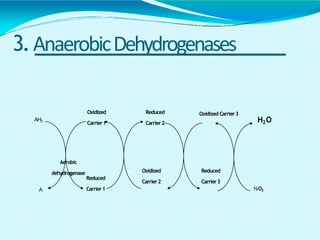
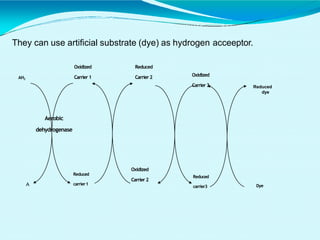
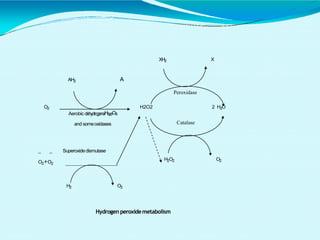
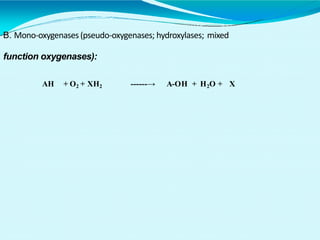
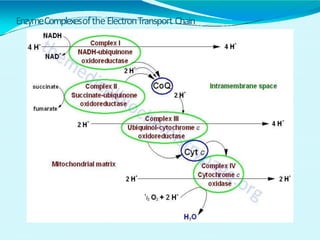
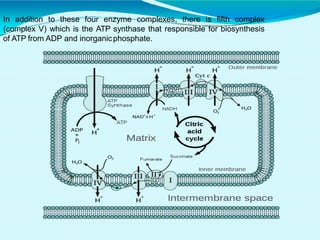
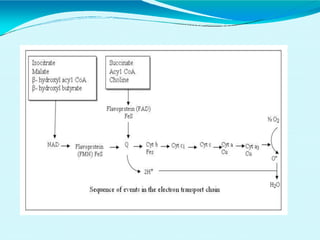
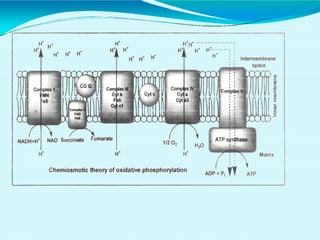
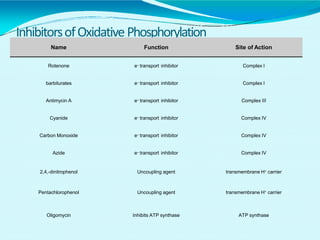
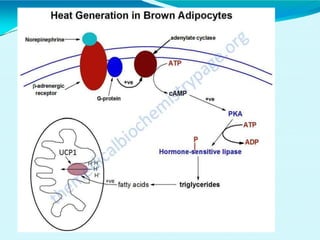
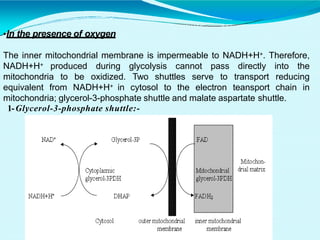
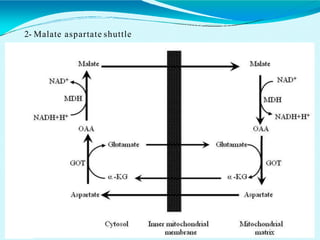
This document discusses biological oxidation and the electron transport chain. It notes that biological oxidation produces energy and occurs through the removal of electrons, hydrogen, or oxygen. The electron transport chain transfers electrons from substrates to oxygen via a series of carriers and enzyme complexes with increasing redox potentials. This establishes an electrochemical gradient that is used by ATP synthase to phosphorylate ADP and produce ATP through oxidative phosphorylation. Inhibitors of oxidative phosphorylation can block specific sites on the electron transport chain or the phosphorylation process more generally.