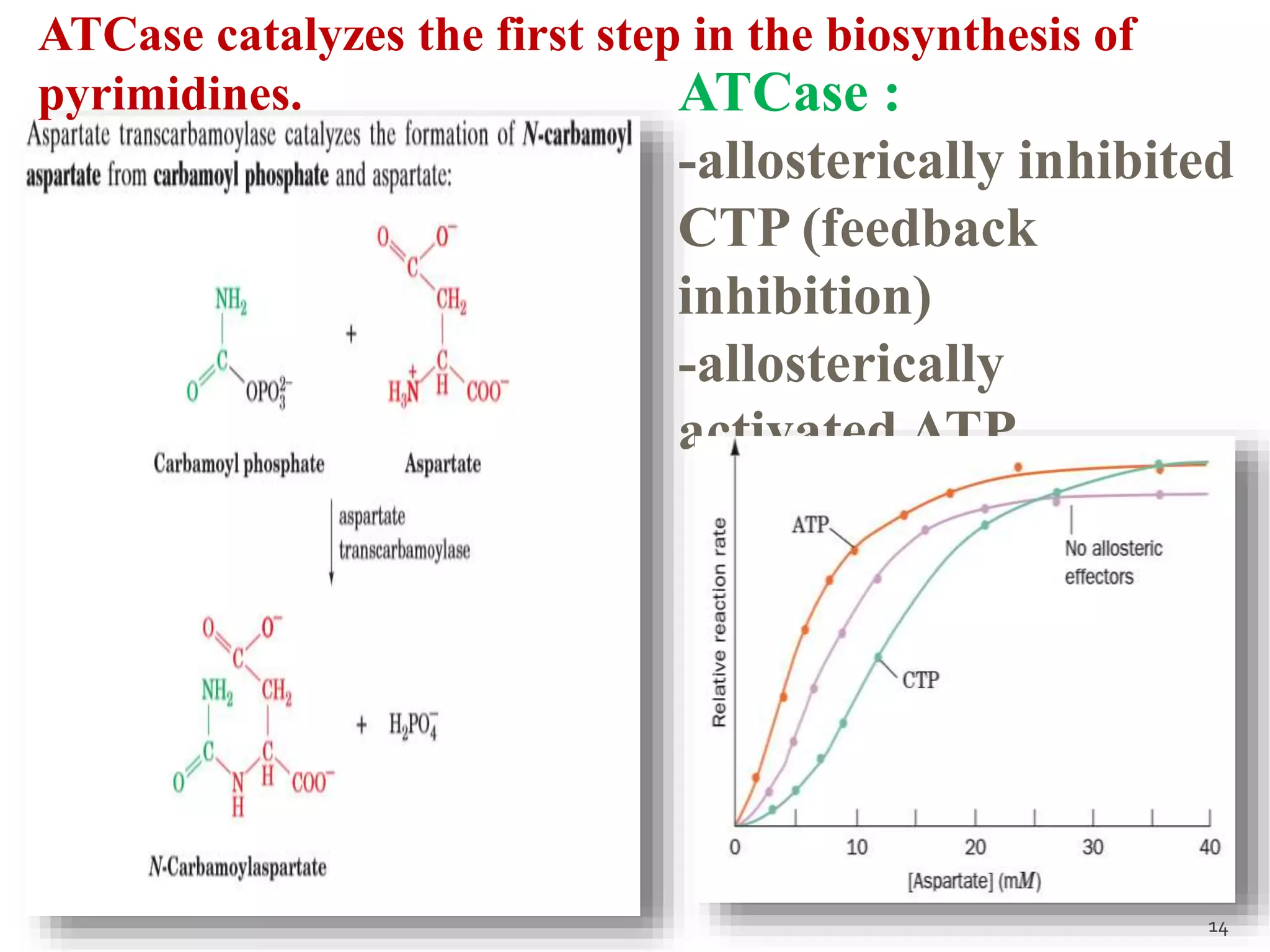
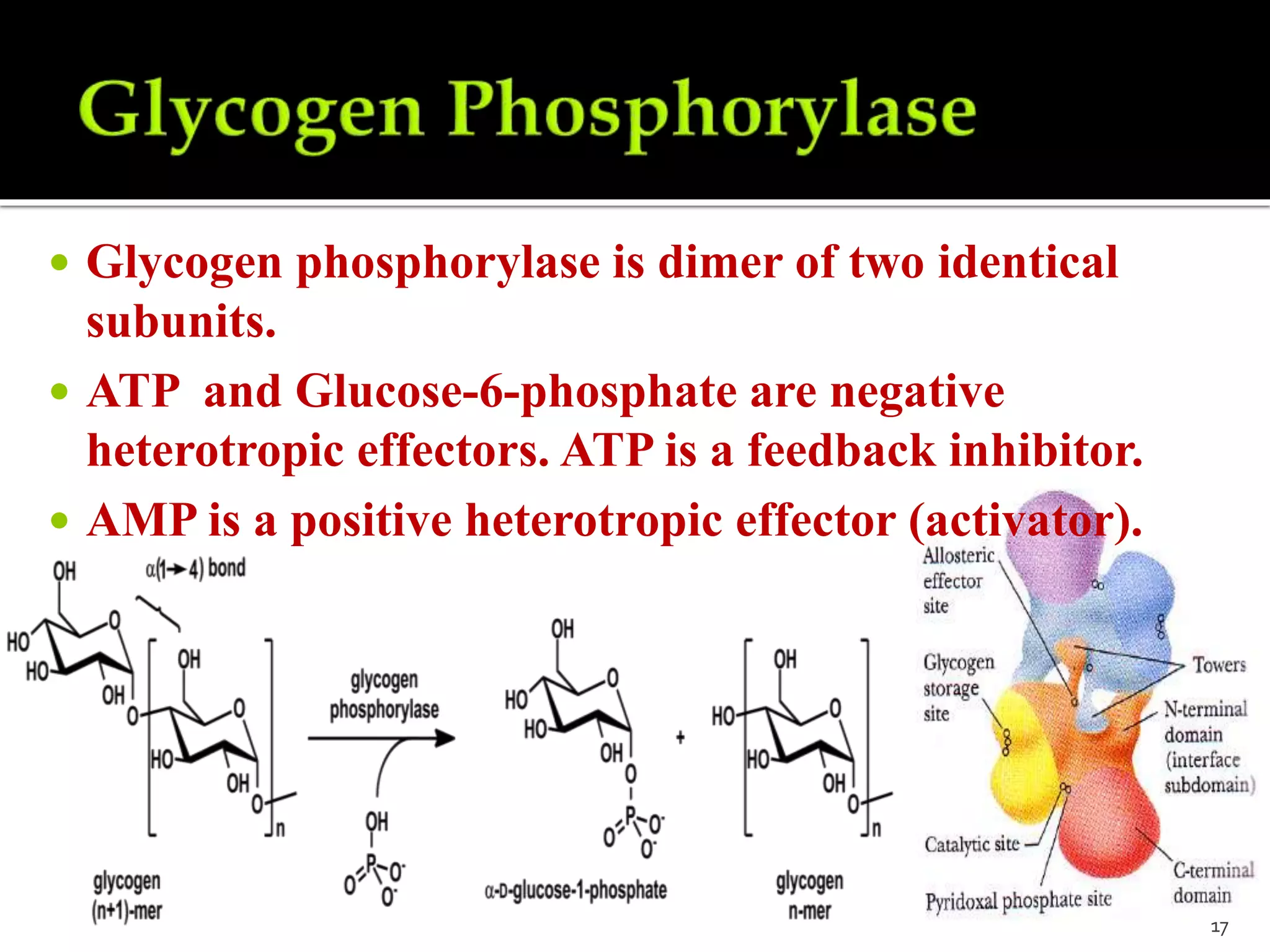
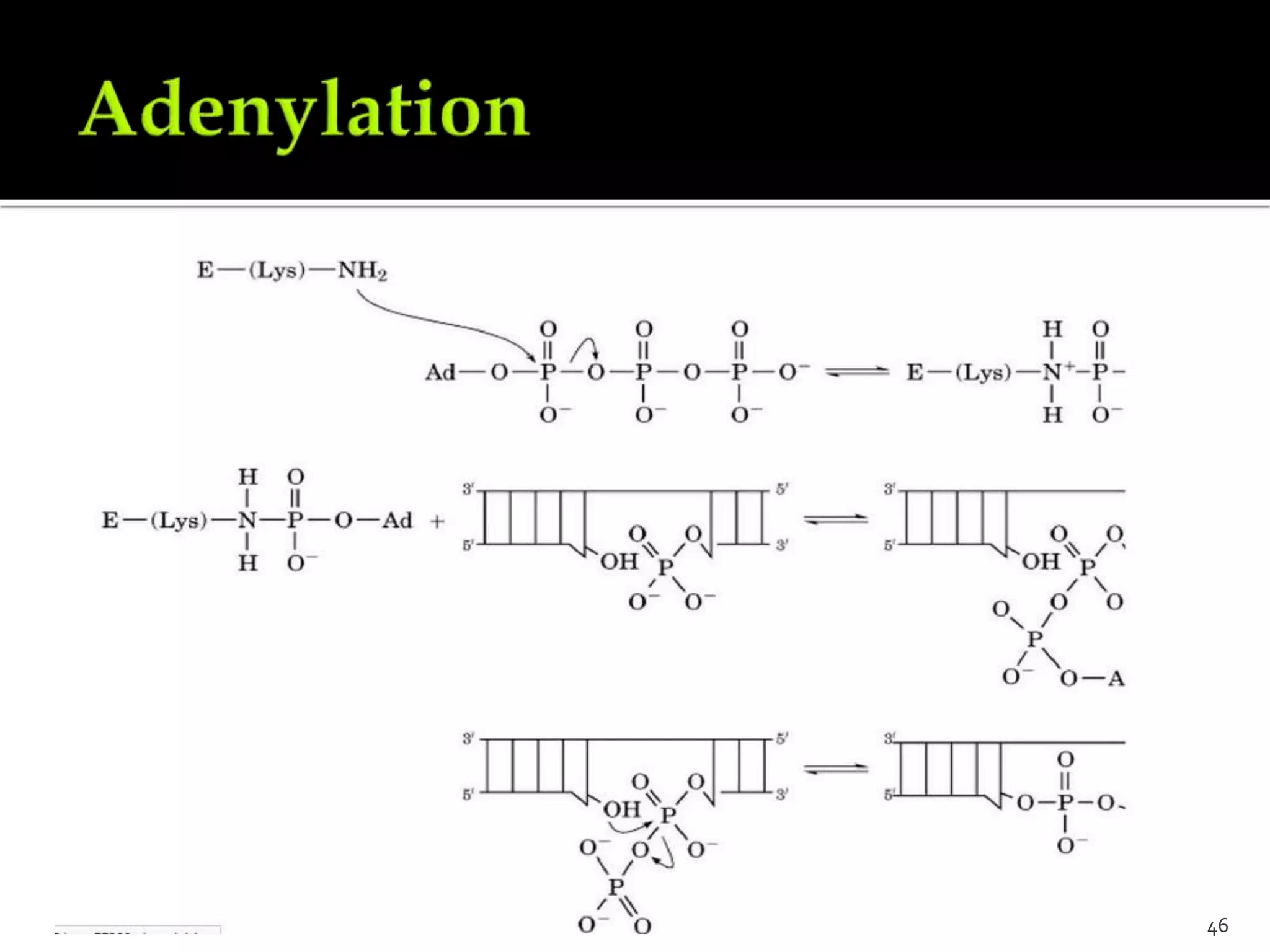
This document discusses various mechanisms of enzyme regulation in living systems. It begins by explaining that hundreds of enzyme-catalyzed reactions must be precisely controlled for proper cellular functioning. It then describes several key mechanisms by which this regulation can be achieved, including allosteric regulation, isoenzyme expression, zymogen activation, and covalent modification via phosphorylation or glycosylation. Specific examples are provided for each type of regulation, such as feedback inhibition of threonine dehydratase and phosphorylation control of glycogen phosphorylase activity. The document concludes by emphasizing that multiple regulatory strategies acting together ensure survival of the cell and maintenance of homeostasis.







![Allosteric proteins show the property of cooperativity i.e.,
activity at one functional site affects the activity at others. A
slight change in substrate concentration can produce
substantial changes in activity.
Their kinetics do not obey the
Michaelis–Menten equation.
Their V versus [S] plots yield
sigmoid curves rather than
hyperbolas.
9](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/enzymeregln-180925002851/75/Enzyme-regulation-9-2048.jpg)