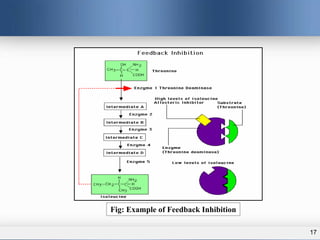
1) Allosteric enzymes have additional sites called allosteric sites that are distinct from the active site. Binding of an effector molecule to these sites can induce a conformational change in the active site, increasing or decreasing the enzyme's activity.
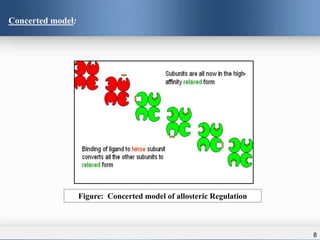
2) There are two main models that describe allosteric regulation - the concerted model where binding causes simultaneous changes in all subunits, and the sequential model where changes occur sequentially.
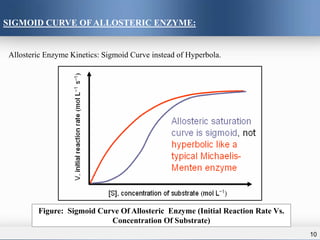
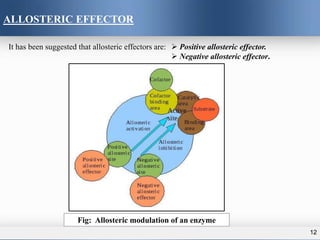
3) Allosteric enzymes exhibit sigmoidal kinetics curves rather than traditional hyperbolic curves due to their cooperative binding behavior. Positive allosteric effectors increase enzyme activity while negative effectors decrease it.




![5
•Allosteric enzyme have one or more allosteric sites
•Allosteric sites are binding sites distinct from an enzyme active site or substrate binding site
•Molecule that bind to allosteric sites are called effector or modulator
•Effector may be positive or negative, this effector regulate the enzyme activity. The enzyme
activity is increased when a positive allosteric effector binds at the allosteric site known as
activator site. On the other hand, negative allosteric effector bind at the allosteric site called
inhibitor site and inhibit the enzyme activity.
•Binding to allosteric sites alter the activity of the enzyme, this is called cooperative binding.
Allosteric enzymes display sigmoidal plot of V₀ vs [S].
PROPERTIES OF ALLOSTERIC ENZYME](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/allostericenzymes-151202093719-lva1-app6892/85/Allosteric-enzymes-5-320.jpg)