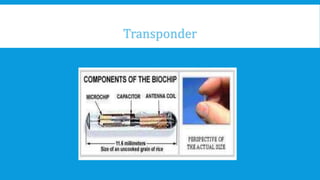
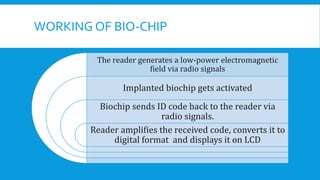
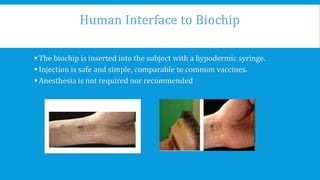
This document discusses bio-chip sensors. A bio-chip is a small-scale device analogous to an integrated circuit that analyzes organic molecules from living organisms. It consists of a transponder with a microchip storing a unique ID number, an antenna coil, tuning capacitor, and glass capsule. A scanner generates an electromagnetic field to activate the implanted bio-chip, which then sends its ID code back to the scanner via radio signals. Potential applications include tracking people and animals globally and storing medical, financial and personal data on a single chip. While bio-chips could identify individuals and perform many reactions quickly, they also raise privacy concerns and could be implanted without consent.
![[BIO—CHIP ] SENSOR
By:
Zeeshan Ahmed](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/biochipsensor-160414183218/75/Bio-chip-sensor-1-2048.jpg)















![Zeeshan Ahmed Lodro
Instrumentation and Measurement
B.E-IV
CmS ID: [033-14-0062]
Department of Electrical Engineering
Sukkur IBA](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/biochipsensor-160414183218/85/Bio-chip-sensor-23-320.jpg)