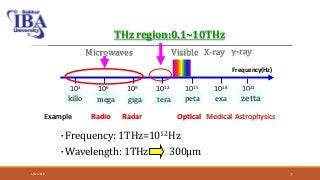
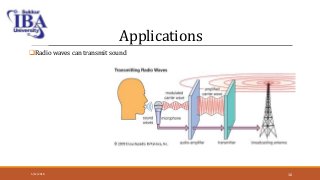
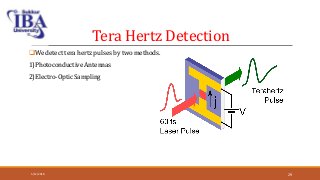
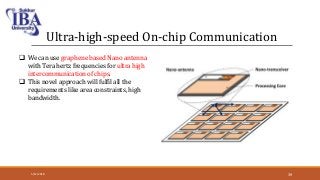
The document presents an overview of terahertz (THz) electromagnetic waves, detailing their properties, history, and various applications in fields such as medicine and wireless communication. Terahertz radiation, which lies between microwaves and infrared frequencies, is non-ionizing and can penetrate various materials, making it valuable for imaging and security purposes. Despite current challenges in generation and detection, ongoing research aims to enhance THz applications, particularly in medical diagnostics.
![Tera Hertz
Electromagnetic Waves
Presented By: Zeeshan Ahmed Lodro
B.E-VIII [ECE]
CmS ID#033-14-0062
Wireless And Mobile Communication
Department Of Electrical Engineering
Sukkur IBA University
5/12/2018 1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/terahertzpresentation-180413082417/85/Tera-Hertz-Electromagnetic-Waves-1-320.jpg?cb=1723022612)