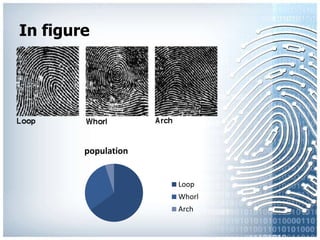
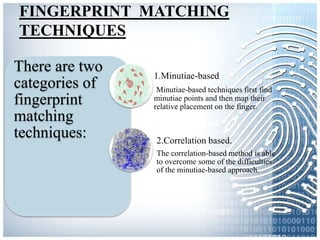
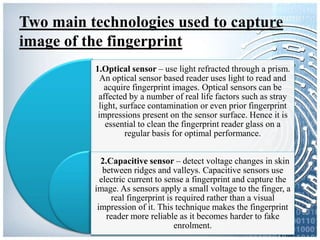
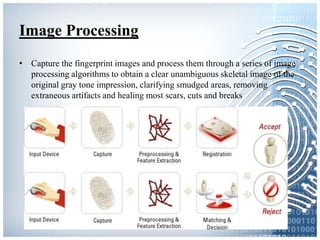
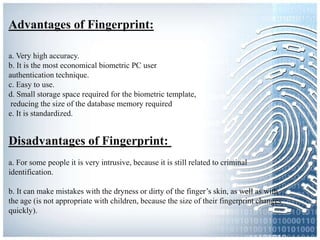
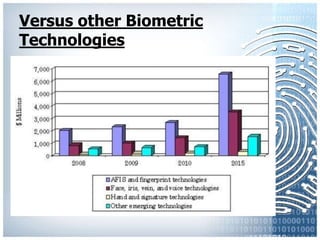
The document provides an overview of biometric systems, focusing on fingerprint recognition, its historical background, system components, matching techniques, and future applications. It outlines the advantages and disadvantages of using fingerprints for identification, including their accuracy and ease of use, while also addressing potential intrusiveness and reliability issues. Additionally, it highlights various applications of fingerprint technology, such as access control and India’s national ID program, Aadhaar.