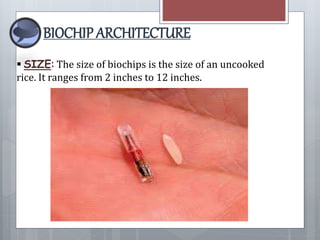
Biochips can perform thousands of biological reactions in seconds. They integrate sensors to detect substances like glucose, oxygen, and blood pressure. While biochips can help monitor health and identify individuals, they also raise privacy concerns. The future of biochips depends on balancing their advantages in healthcare with ethical issues around personal freedom and privacy.