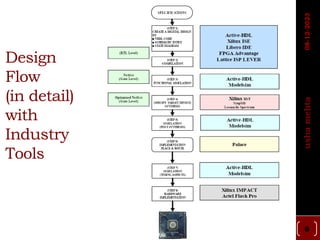
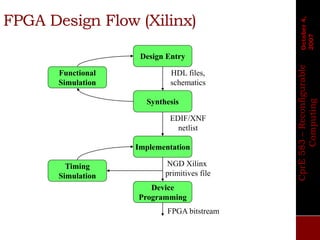
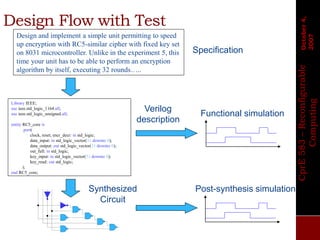
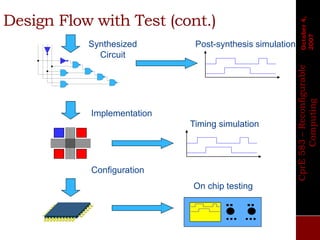
The document describes the basic design flow for FPGA development, including selecting a target device, defining system requirements, and major steps in the design process. Key aspects covered are selecting an FPGA with sufficient resources and I/O standards to meet requirements, defining functionality and interfaces in HDL code, simulating and synthesizing the design, and programming the FPGA with a generated bitstream file. Standard FPGA tools are used to implement the design through synthesis, mapping, placement and routing steps.