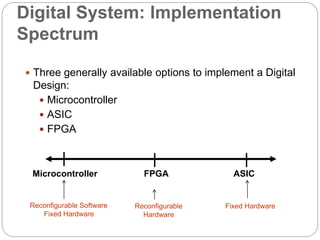
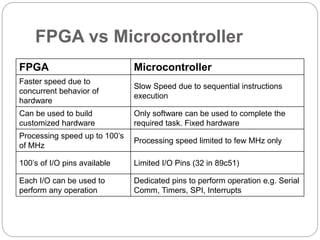
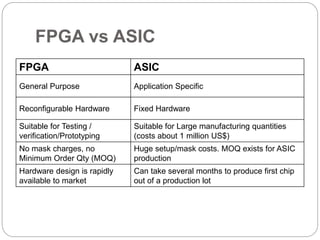
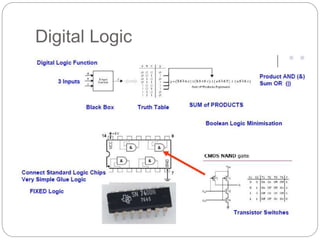
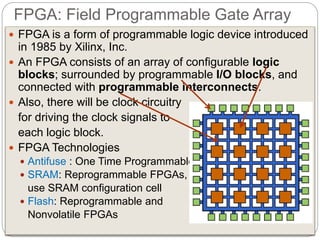
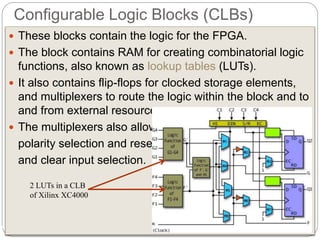
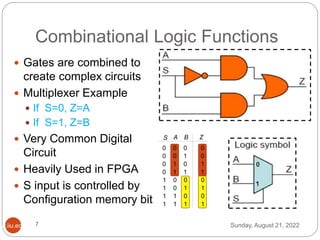
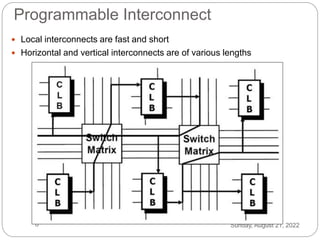
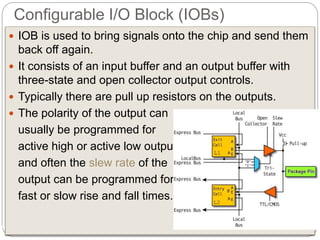
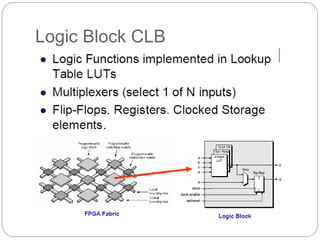
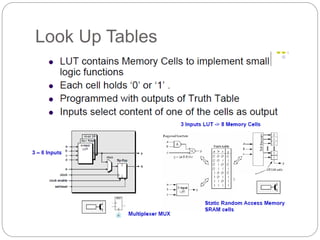
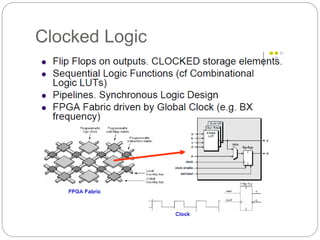
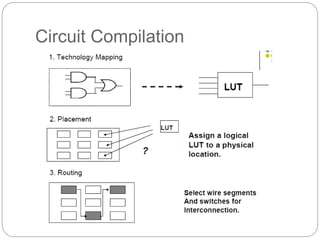
This document discusses three options for implementing digital designs: microcontrollers, ASICs, and FPGAs. It provides details on the differences between FPGAs and microcontrollers, and between FPGAs and ASICs. FPGAs offer reconfigurable hardware, faster speeds than microcontrollers due to parallel processing, and more flexible I/O. However, ASICs are best for high volume manufacturing due to lower costs. The document also provides information on the internal architecture of FPGAs, including configurable logic blocks, look up tables, programmable interconnects, and I/O blocks.