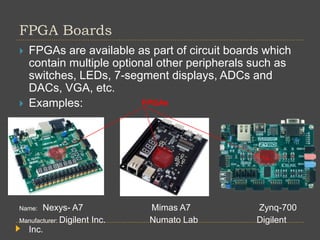
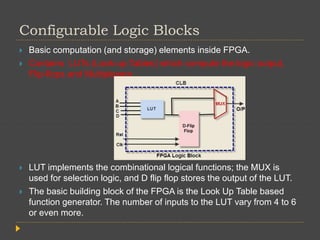
FPGAs can be programmed after manufacturing to implement custom logic functions. They contain programmable logic blocks and interconnects that can be configured to create custom circuits. FPGAs have advantages over ASICs like lower development costs and shorter time to market, though ASICs can be produced more cheaply at scale. FPGA architecture consists of configurable logic blocks, programmable interconnects, and I/O blocks. Logic blocks contain LUTs that implement functions. Interconnects connect blocks, and I/O blocks interface with external components. FPGAs are used for applications like hardware emulation, ASIC prototyping, and parallel computing.