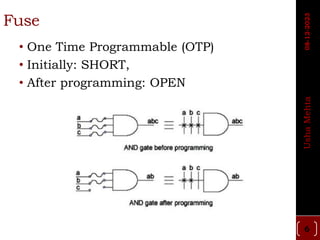
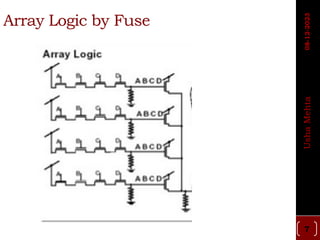
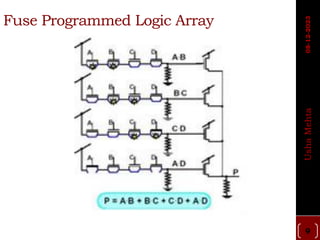
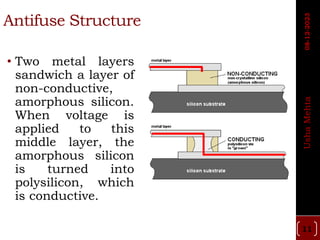
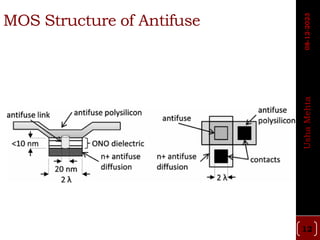
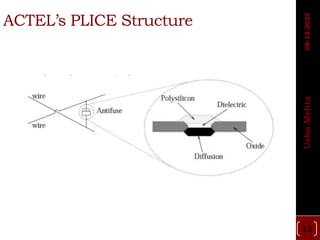
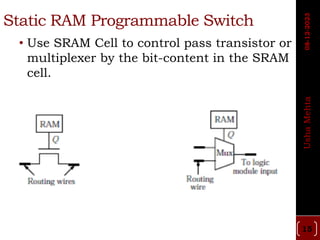
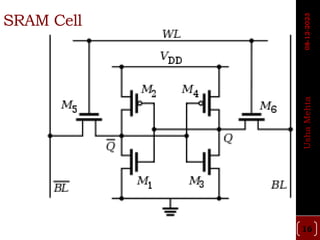
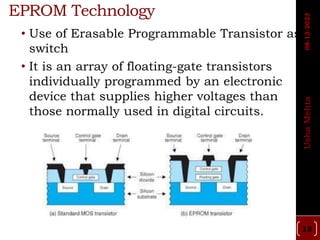
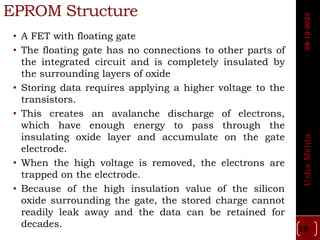
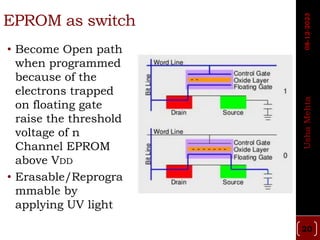
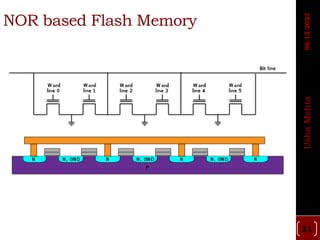
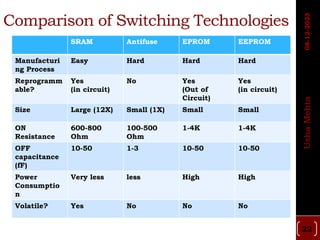
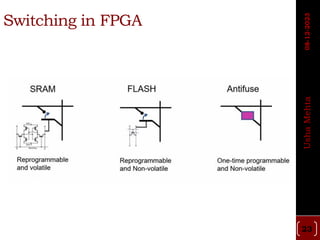
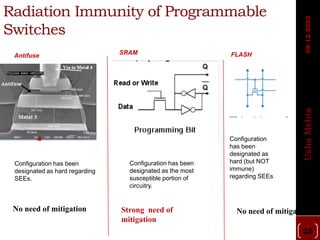
The document discusses different types of programmable switches used in programmable logic devices (PLDs) including fuse-based switches, antifuse switches, static RAM switches, EPROM switches, and flash memory switches. It provides details on the operation, advantages, and disadvantages of each switch type. It also compares the different switches based on manufacturing process, reprogrammability, size, resistance, capacitance, power consumption, volatility, and radiation immunity. The ideal properties for switches in PLDs are also outlined.