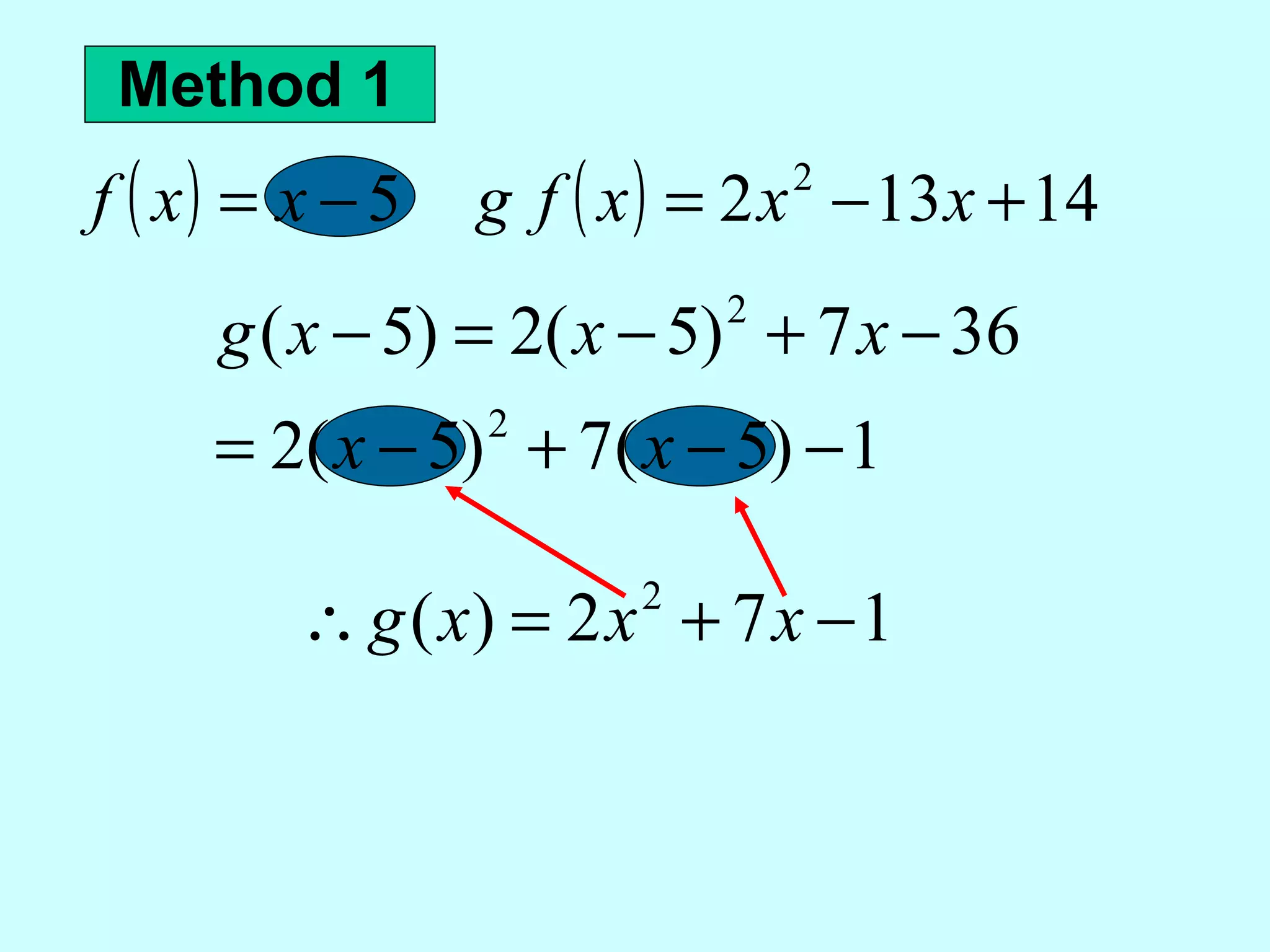
The document discusses operations and composition of functions. It explains that to find the sum of two functions f and g, you add them together and combine like terms. To find the difference, you subtract the second function from the first and distribute negatives. To find the product, you multiply corresponding terms of f and g. For the quotient f/g, you divide the first function by the second. The domain of sums, differences and products is where x is in the domains of both f and g, while the domain of the quotient excludes values where the denominator would be 0. Composition means substituting one function into another, written as f(g) or g(f).