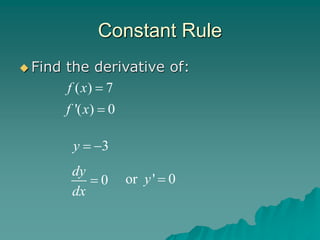
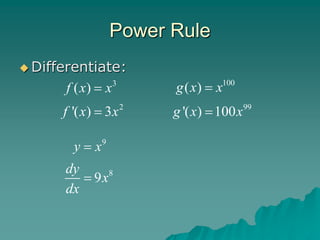
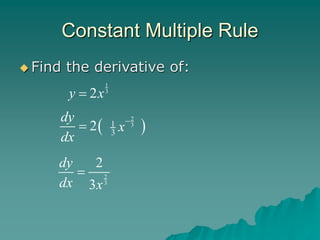
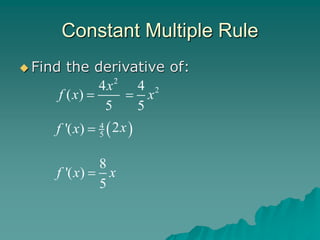
The document introduces rules for differentiation, including the power rule, constant rule, constant multiple rule, and sum and difference rules. It provides examples of applying each rule to take the derivative of various functions. The power rule states that the derivative of x^N is N*x^(N-1). The constant rule is that the derivative of a constant function is zero. The constant multiple rule is that the derivative of c*f(x) is c*f'(x). The sum and difference rules are that the derivative of f(x) + g(x) is f'(x) + g'(x) and the derivative of f(x) - g(x) is f'(x) - g'(








![The Power Rule
1
[ ] , is any real number
N N
d
x Nx N
dx
[ ] 1
d
x
dx
](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/day1-rulesfordifferentiation-240124154317-f98e9221/85/Rules_for_Differentiation-ppt-9-320.jpg)
![The Constant Rule
The derivative of a constant function
is zero.
[ ] 0, is a constant
d
c c
dx
](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/day1-rulesfordifferentiation-240124154317-f98e9221/85/Rules_for_Differentiation-ppt-10-320.jpg)
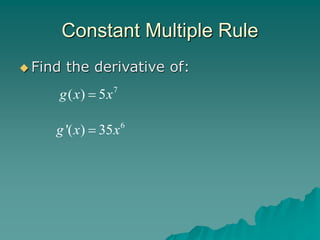
![The Constant Multiple Rule
[ ( ) ] '( ) , is a constant
d
c f x c f x c
dx
The derivative of a constant times a
function is equal to the constant
times the derivative of the function.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/day1-rulesfordifferentiation-240124154317-f98e9221/85/Rules_for_Differentiation-ppt-11-320.jpg)
![The Sum and Difference Rules
[ ( ) ( )] '( ) '( )
d
f x g x f x g x
dx
[ ( ) ( )] '( ) '( )
d
f x g x f x g x
dx
The derivative of a sum is the sum of the derivatives.
The derivative of a difference is the difference of the derivatives.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/day1-rulesfordifferentiation-240124154317-f98e9221/85/Rules_for_Differentiation-ppt-12-320.jpg)