Embed presentation
![Order of filling orbitals © my-chem-tutor.blogspot.com [1] Fill orbitals with lower energy 1st [Aufbau Principle] [2] Each orbital can accommodate 2 electrons [Pauli Exclusion Principle] [3] Where there is a choice between orbitals of equal energy, fill the orbitals singly 1st [Hund’s Rule] (minimise electron repulsion) 4s orbital is lower in E than 3d ( when unfilled )!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/atomic-structure-ii-1209875614351978-9/85/Atomic-Structure-II-5-320.jpg)
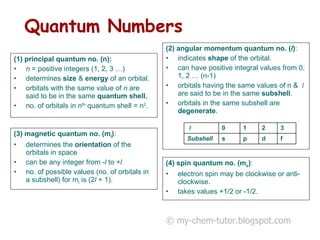
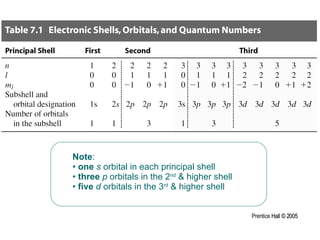
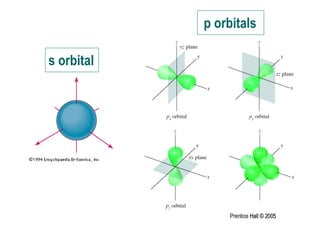
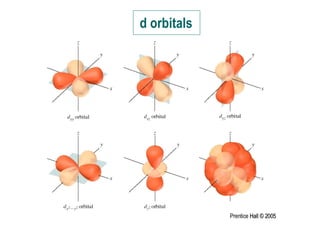
The document discusses quantum numbers and their roles in describing electron orbitals. It explains that the principal quantum number (n) determines the size and energy of an orbital, the angular momentum quantum number (l) indicates the shape of an orbital, and the magnetic quantum number (ml) determines the orientation of orbitals in space. It also mentions that the spin quantum number (ms) describes electron spin as either clockwise or counterclockwise.




![Order of filling orbitals © my-chem-tutor.blogspot.com [1] Fill orbitals with lower energy 1st [Aufbau Principle] [2] Each orbital can accommodate 2 electrons [Pauli Exclusion Principle] [3] Where there is a choice between orbitals of equal energy, fill the orbitals singly 1st [Hund’s Rule] (minimise electron repulsion) 4s orbital is lower in E than 3d ( when unfilled )!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/atomic-structure-ii-1209875614351978-9/85/Atomic-Structure-II-5-320.jpg)
