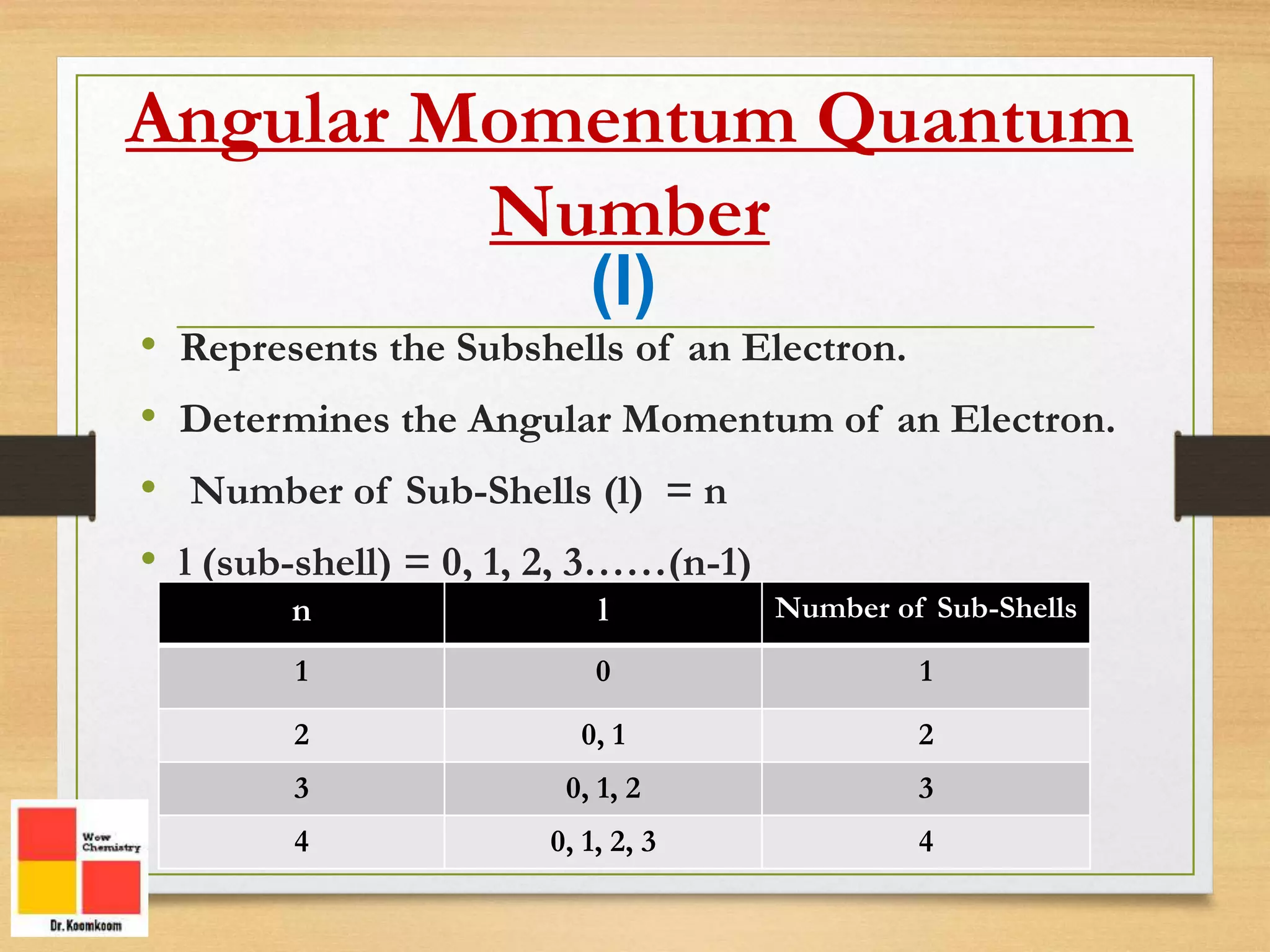
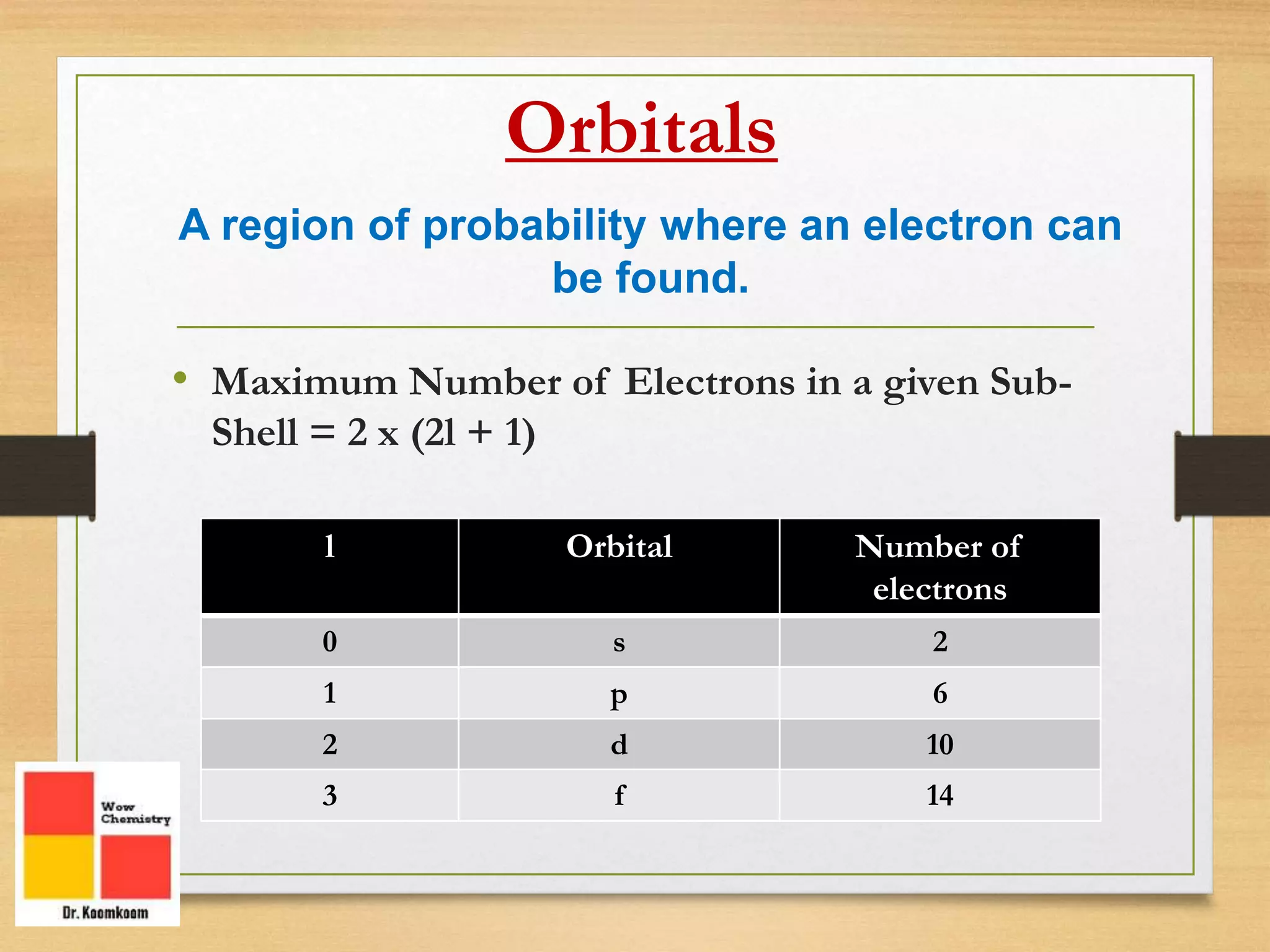
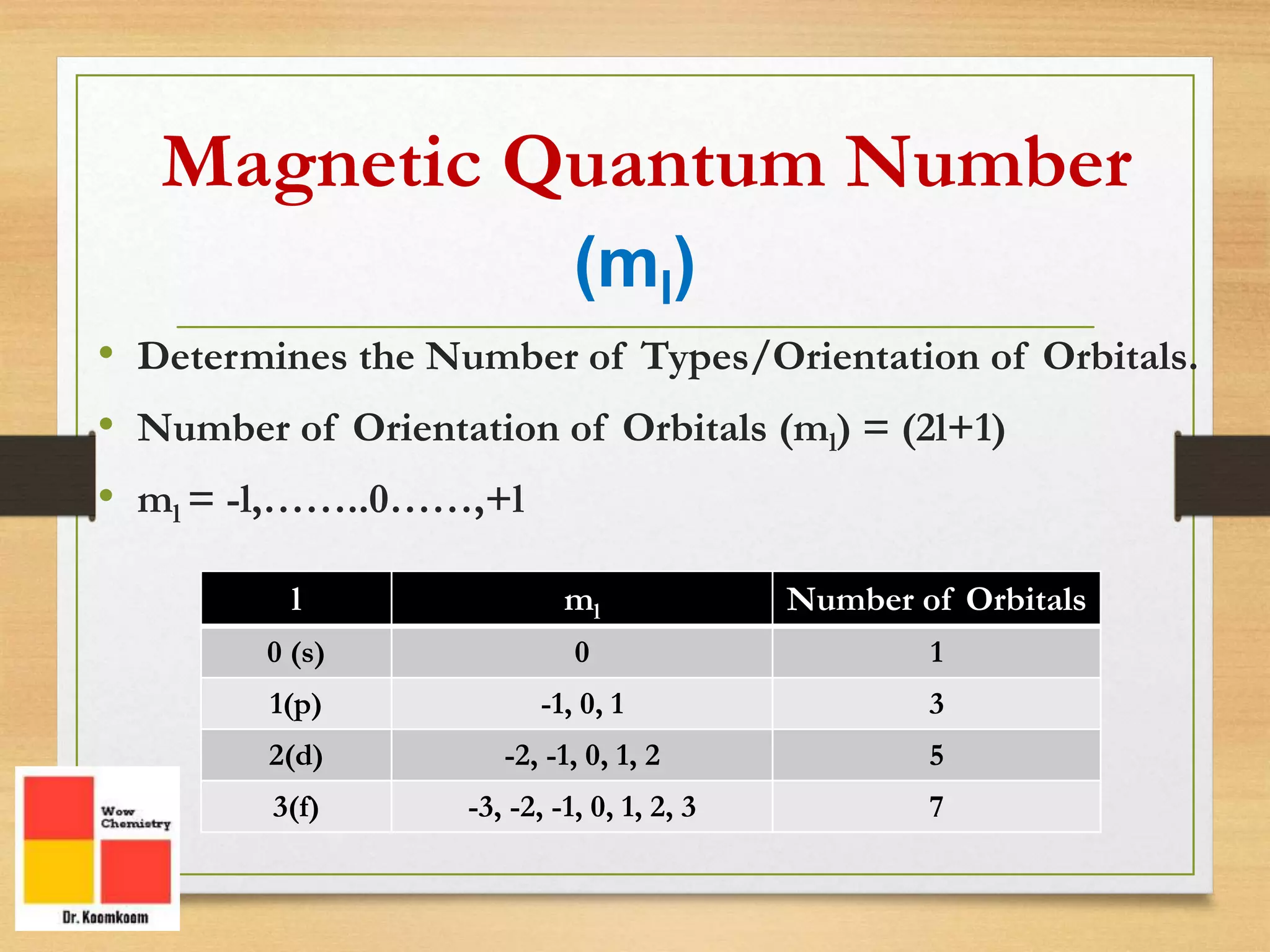
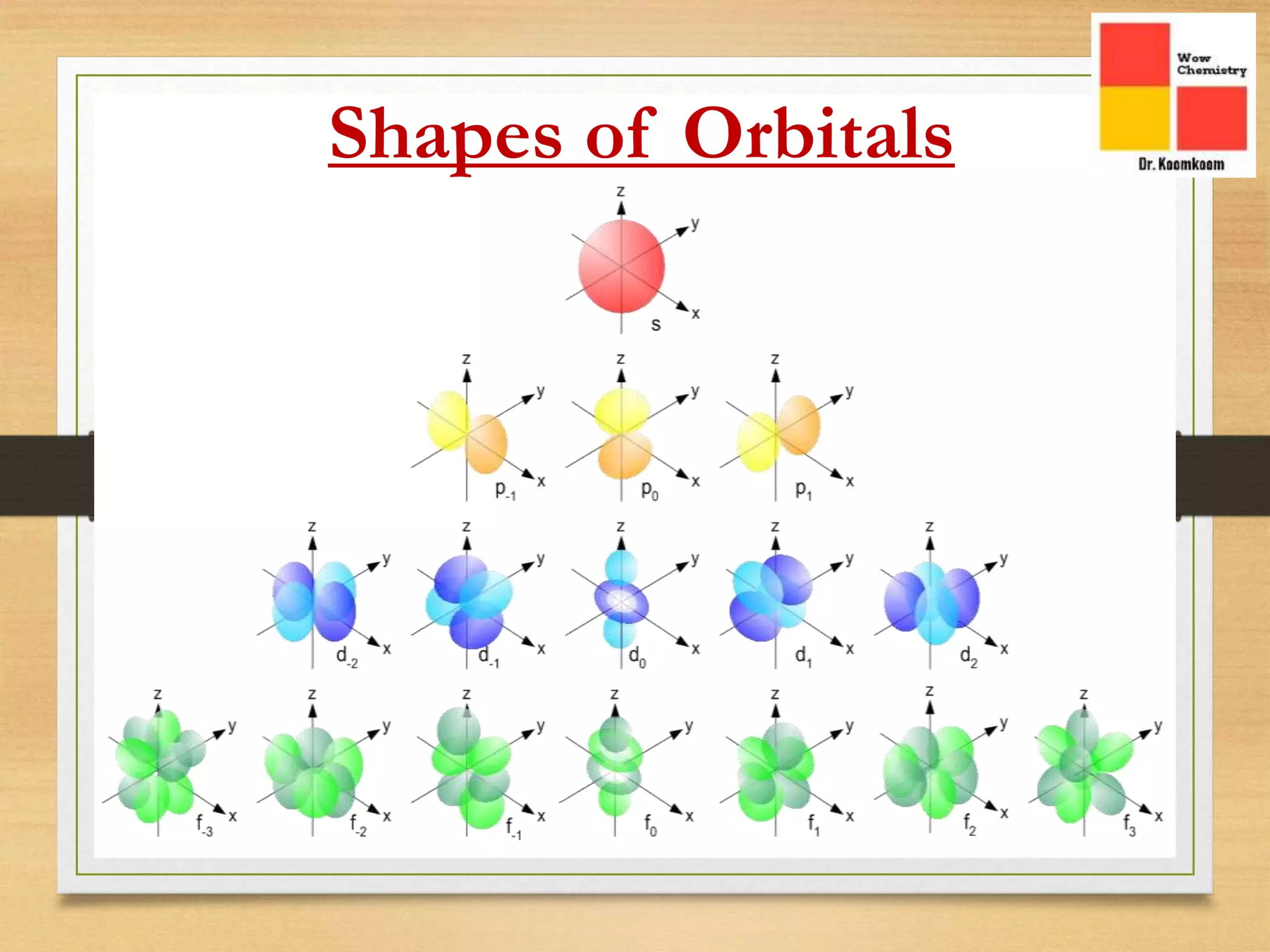
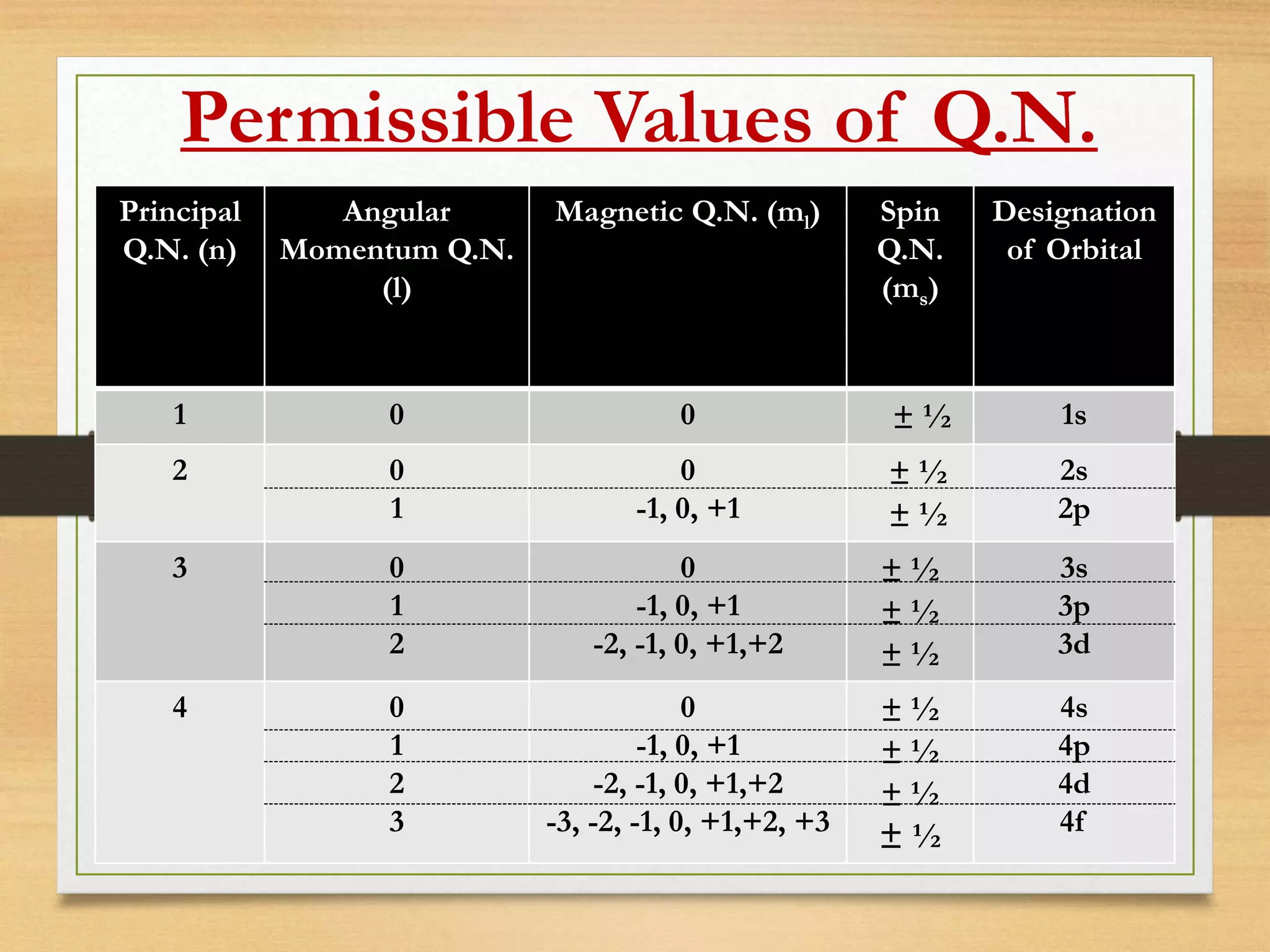
The document outlines the different quantum numbers that describe the characteristics of electrons in an atom, including principal (n), angular momentum (l), magnetic (ml), and spin (ms) quantum numbers. Each quantum number provides specific information about the electron's energy level, subshell, orbital orientation, and spin direction. The document includes details on the maximum number of electrons in shells and subshells, as well as the shapes of orbitals associated with each quantum number.